The post Embolism: Definition, Types, Causes, Treatment and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>“Embolism is the process of partial or complete obstruction of some part of the cardiovascular system by any mass carried in the circulation; the transported intravascular mass detached from opits site of origin is called embolus.”
1.] Most usual forms of emboli i.e. 90% are thromboemboli i.e. originating from thrombi or their parts detached from the vessel wall.
TYPES OF EMBOLISM :-
A.] Depending upon the matter in the embolism :
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gaseous
B.] Depending upon whether infected or not :
- Bland, when sterile
- Septic, when infected
C.] Depending upon the source of embolism :
- Cardiac emboli
- Arterial emboli
- Venous emboli
- Lymphatic emboli
D.] Depending upon the flow of the blood :
- Paradoxical embolus
- Retrograde embolus
PULMONARY EMBOLI :-
- Most if the pulmonary emboli arise in the deep leg vein above the level of knee.
- Paradoxical embolus is a rare embolus that can pass through an inter – arterial or inter – ventricular defect, thereby entering systemic circulation.
- Most of the pulmonary emboli (60% – 80%) are clinically silent because they are small.
- They rarely may cause pulmonary infarction.
- Sudden death may also occur in >60% of pulmonary circulation if obstructed.
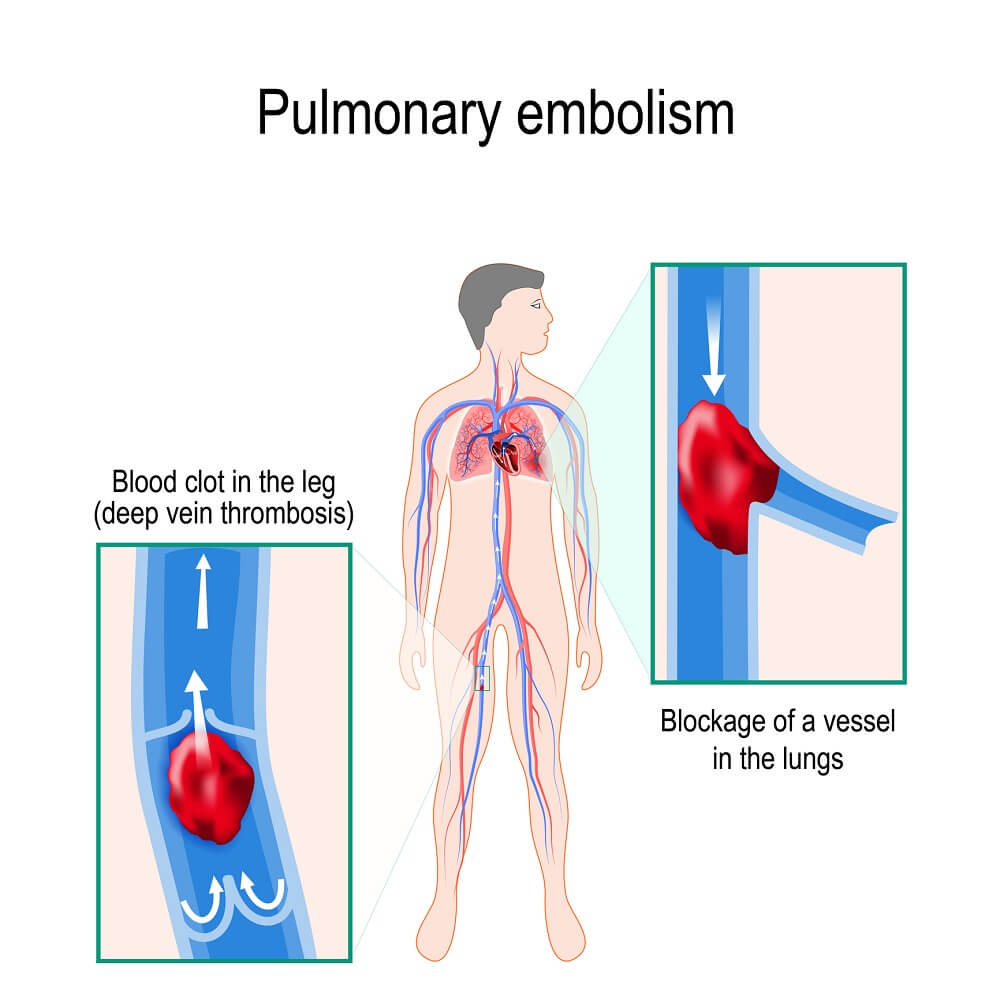
Above figure is taken for educational purpose only (Credit from-Flushing Hospital)
FAT EMBOLISM :-
- Fat embolism syndrome is characterized by pulmonary insufficiency, neurologic symptoms, anemia and thrombocytopenia.
- It is seen after the fractures of long bones or after soft tissue trauma.
- It is fatal in 10% of cases.
- The pathogenesis involves both mechanical obstructions and free fatty acid causing local toxic injury to endothelial.
CAUSES OF EMBOLISM :-
Most embolisms happen to people who have risk factors for blood clot formation, such as smoking and heart disease. Other risk factors for other types of emboli include high blood pressure, atherosclerosis (buildup of fatty plaque in the blood vessels), high cholesterol, and obesity.
The primary cause of most pulmonary embolisms is deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This is a condition in which the veins of the legs develop clots. Natural agents in the blood often dissolve small clots without causing any effects of blockage. Some clots are too big to dissolve and are big enough to block major blood vessels in the lungs or in the brain.
Factors that slow blood flow in the legs may promote clotting. People can develop a DVT or pulmonary emboli after sitting still on long flights or after immobilization of the leg in a cast, or after prolonged bed rest without moving the legs. Other factors associated with DVT or pulmonary embolism include cancer, previous surgery, a broken leg or hip, and genetic conditions affecting the blood cells that increase the chance of blood clot formation.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION :-
The treatment for thromboembolism (blood clot embolism) involves anticoagulant or thrombolytic medications.
Anticoagulants, such as heparin, low molecular weight heparin, warfarin, or factor Xa inhibitors, are the main medications given for pulmonary embolism.
Anticoagulants prevent further clotting of the blood.
Thrombolytics such as alteplase and streptokinase help the body to dissolve the original clot. The most effective way to prevent pulmonary embolism is to prevent DVTs from forming or starting to move in the blood vessels. If you have DVT, you may be prescribed an anticoagulant. Anticoagulants can also be given to people with DVT to prevent the condition. They can also protect against stroke.
Non-medication methods to help prevent DVT include using compression devices and compression stockings (to ensure blood doesn’t pool in the legs), and frequently stretching, massaging, and moving your lower leg muscles if you are inactive for a long time.
You can also reduce your risk factors for getting blood clots, for instance by quitting smoking and controlling your blood pressure.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [MCQs] :-
1.] Fat embolism is commonly seen in ?
a. Head injuries
b. Long bone fractures
c. Drowning
d. Hanging
2.] Having a pulmonary embolism include risk of possible ?
a. Sudden death
b. Diabetes
c. High blood pressure
d. Amputation of limbs
3.] Who is at greater risk for pulmonary embolism ?
a. Men
b. Women
c. Young women
d. The risk is same for both Men and Women
4.] A pulmonary embolism is a blood clot that becomes lodged in the lungs ?
a. True
b. False
5.] If a clot “embolise” this means it has ?
a. Attached itself to another clot
b. Decreased in size
c. Broken loose
d. Hardened
6.] What is most frequent cause of pulmonary embolism ?
a. Congestive heart failure
b. Hemorrhagic fever
c. Deep vein thrombosis
d. Pneumonia
7.] What is pulmonary embolism ?
a. A pulmonary clot obstructing a pulmonary artery
b. Right sided heart failure
c. A blood clot obstructing the aorta
d. None of the above
8.] Which of the following symptoms are not characteristic for pulmonary embolism ?
a. Hemoptysis
b. Cyanosis
c. Painful respiration
d. Hemorrhagic diathesis
9.] What are the symptoms of DVT ?
a. Swelling of the affected leg
b. Cyanosis or redness of the skin above the DVT
c. Warmness of the skin above the DVT
d. Pain in the affected leg
e. All of the above
10.] Medication for DVT and PE are called anticoagulates ?
a. True
b. False
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (b) Long bone fractures
2.] (a) Sudden death
3.] (d) The risk is same for both Men and Women
4.] (a)
5.] (c) Broken loose
6.] (c) Deep vein thrombosis
7.] (a) A pulmonary clot obstructing a pulmonary artery
8.] (d) Hemorrhagic diathesis
9.] (e)
10.] (a)
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 105 – 109.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no. 111 – 114.
The post Embolism: Definition, Types, Causes, Treatment and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post Vascular Permeability : Causes, Pathogenesis, Patterns of increased Vascular Permeability, Disorders And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>CAUSES OF VASCULAR PERMEABILITY :-
- It is caused by the separation of the endothelial cells resulting in the movement of fluids, cells and proteins out of the blood vessels collectively called as exudate.
- The exudate is a protein rich fluid which is responsible foe the swelling (tumor) associated with an injury.
- It is maxima,y seen in venules.
PATHOGENESIS :-
1.] In and around the inflamed tissue, their is accumulation of edema fluid in the interstitial compartment which comes from the blood plasma
2.] In the initial stage the escape of the fluid is due to the vasodilation and consequent elevation in hydrostatic pressure.
3.] The appearance of inflammatory edema due to increased vascular permeability of microvascular bed is explained on the basis of Starling’s hypothesis.
4.] According to Starling’s hypothesis the fluid balance is maintained by two opposing sets of forces :-
- Forces that causes outward movement of fluid from microcirculation : These are intravascular hydrostatic pressure and colloid osmotic pressure of interstitial fluid.
- Forces that cause inward movement of interstitial fluid in circulation : There are intravascular colloid osmotic pressure and hydrostatic pressure of interstitial fluid.
PATTERNS OF INCREASED VASCULAR PERMEABILITY :-
1.] Increased vascular permeability in acute inflammation by which normally non – permeable endothelial layer of microvascular become leaky can have following patterns and mechanism :
- Contraction of endothelial cells.
- Contraction or mild endothelial damage.
- Direct injury to endothelial cells.
- Leukocytes mediated endothelial injury.
- Leakiness in neurovascularisation.
Above figure is taken for Educational purpose only from Saad Hussai Et al 2015 (DOI: 10.13140/2.1.1526.0968)
DISORDERS OF VASCULAR PERMEABILITY :-
The endothelial barrier maintains vascular and tissue homeostasis and modulates many physiological processes, such as angiogenesis.
Vascular barrier integrity can be disrupted by a variety of soluble permeability factors, and changes in barrier function can exacerbate tissue damage during disease progression. Understanding endothelial barrier function is critical for vascular homeostasis.
Many of the signaling pathways promoting vascular permeability can also be triggered during disease, resulting in prolonged or uncontrolled vascular leak. It is believed that recovery of the normal vasculature requires diminishing this hyperpermeable state. Although the molecular mechanisms governing vascular leak have been studied over the last few decades, recent advances have identified new therapeutic targets that have begun to show preclinical and clinical promise. These approaches have been successfully applied to an increasing number of disease conditions.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [MCQs] :-
1.] Vasoconstriction in acute inflammation is shown by ?
a. Venules
b. Arterioles
c. Capillaries
d. Vein
2.] Increased permeability in acute inflammation is due to ?
a. Histamine
b. IL – 2
c. TGFB
d. FGF
3.] All the following vascular changes are observed in acute inflammation except ?
a. Vasodilation
b. Status of blood
c. Increased vascular permeability
d. Decreased hydrostatic pressure
4.] Which of the following is the most characteristic feature of acute inflammation ?
a. Vasodilation and increased vascular permeability
b. Margination of leukocytes
c. Vasoconstriction
d. Vascular stasis
5.] The hallmark of acute inflammation is ?
a. Increased blood flow
b. Increased vascular permeability
c. Vascular stasis
d. All of the above
6.] The role of histamine in acute inflammatory response include ?
a. Platelet release and aggregation
b. Increased vascular permeability of the venules
c. Membrane lysis
d. None of the above
7.] The complex process of leukocyte movement through the blood vessel are all except ?
a. More protein
b. Adhesion
c. Migration
d. Phagocytosis
8.] All the following are signs of inflammation except ?
a. Pain
b. Swelling
c. Redness
d. Absence of functional loss
9.] In acute inflammation the tissue response consist of all except .
a. Vasodilation
b. Exudation
c. Neutrophilic response
d. Granuloma formation
10.] Brandykinin causes ?
a. Pain at the site of inflammation
b. Vasoconstriction
c. Bronchodiltion
d. None of the above
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (b) Arterioles
2.] (a) Histamine
3.] (d) Decreased hydrostatic pressure
4.] (a) Vasodilation and increased vascular permeability
59] (b) Increased vascular permeability
6.] (b) Increased vascular permeability of the venules
7.] (d) Phagocytosis
8.] (d) Absence of functional loss
9.] (d) Granulaoma formation
10.] (a) Pain at the site of inflammation
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 117 – 119.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no. 54 – 56.
The post Vascular Permeability : Causes, Pathogenesis, Patterns of increased Vascular Permeability, Disorders And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post Stem Cells: Definition, Types of stem cells, Self renewal, Potency, Stem cell studies, Stem cell therapy and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>1.] Stem cells are the primitive cells which has two main functions :
- They have the capacity of self renewal
- They can be coaxed into differentiation.
SELF RENEWAL :-
1.] Self renewal can be achieved in two ways :
- Asymmetric cell division : Produces one daughter cell that is identical to the parental cell and one daughter cell that is different from the rental cell and is a progenitor or differentiated cell.
- Symmetric cell division : Produces two identical daughter cells.
POTENCY :-
1.] It is used to indicate a cell’s ability to differentiate into specialized cell type.
2.] Potency is classified as :
- Totipotent cells : These cells can form an entire organism autonomously.
- Multipotent cells : These cells can form multiple cell lineage but cannot form all of the body’s cell lineage.
- Oligopotent cells : These cells can form more than one cell lineage but are more restricted than multipotent cells.
- Unipotent or Monopotent cells : These cells can form a single differentiated cell lineage.
3.] Embryonic cells are pleuripotent, that is, they are capable of forming all the tissues of the body.
4.] Adult stem cells are usually only able to differentiate into a particular tissue.
TYPES OF STEM CELLS :-
1.] Stem cells are located in special sites called niches.
2.] Some stem cells are as follows :
- Oval cells are found in canals of Herrings of the liver.
- Satellite cells found in basal lamina of myotubules.
- Limbus cells found in canals of schlemm.
- Ito cells found in subendothelial space of Disse.
- Paneth cells found in the bottom of crypts.
STEM CELL STUDIES :-
Researchers and doctors hope stem cell studies can help to:
- Increase understanding of how diseases occur. By watching stem cells mature into cells in bones, heart muscle, nerves, and other organs and tissue, researchers and doctors may better understand how diseases and conditions develop.
- Generate healthy cells to replace diseased cells (regenerative medicine). Stem cells can be guided into becoming specific cells that can be used to regenerate and repair diseased or damaged tissues in people.People who might benefit from stem cell therapies include those with spinal cord injuries, type 1 diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, heart disease, stroke, burns, cancer and osteoarthritis.Stem cells may have the potential to be grown to become new tissue for use in transplant and regenerative medicine. Researchers continue to advance the knowledge on stem cells and their applications in transplant and regenerative medicine.
- Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness. Before using investigational drugs in people, researchers can use some types of stem cells to test the drugs for safety and quality. This type of testing will most likely first have a direct impact on drug development first for cardiac toxicity testing.New areas of study include the effectiveness of using human stem cells that have been programmed into tissue-specific cells to test new drugs. For the testing of new drugs to be accurate, the cells must be programmed to acquire properties of the type of cells targeted by the drug. Techniques to program cells into specific cells continue to be studied.For instance, nerve cells could be generated to test a new drug for a nerve disease. Tests could show whether the new drug had any effect on the cells and whether the cells were harmed.
STEM CELL THERAPY :-
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives. It is the next chapter in organ transplantation and uses cells instead of donor organs, which are limited in supply.
Researchers grow stem cells in a lab. These stem cells are manipulated to specialize into specific types of cells, such as heart muscle cells, blood cells or nerve cells.
The specialized cells can then be implanted into a person. For example, if the person has heart disease, the cells could be injected into the heart muscle. The healthy transplanted heart muscle cells could then contribute to repairing defective heart muscle.
Researchers have already shown that adult bone marrow cells guided to become heart-like cells can repair heart tissue in people, and more research is ongoing.

Above Figure is taken from article written by Chinedu Cletus Ude et al 2018 (DOI: 10.1186/s40779-018-0154-9). Figure is used only for educational purpose
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS [MCQs] :-
1.] “Oval cells” are seen in the stem cells of which of the following tissues ?
a. Skin
b. Cornea
c. Liver
d. Bone
2.] Which of the following is the source of hepatic stem cells ?
a. Limbus cells
b. Ito cells
c. Oval cells
d. Paneth cell
3.] What is the process of cell specialization called ?
a. Proliferation
b. Differentiation
c. Cryopreservation
d. All of the above
4.] Adult stem cells are described as ?
a. Somatic
b. Syngenic
c. Specialized
5.] Name two sources of “ethical” stem cell ?
a. Cord blood
b. Bone marrow
c. Peripheral blood
d. All of the above
6.] Which of the statement is incorrect regarding stem cells ?
a. Developmental elasticity
b. Trans differentiation
c. Can be harvested from embryo
d. All of the above
7.] Cells or tissues donated by a related or unrelated individuals are called ?
a. Autologus
b. Synfenic
c. Allogenic
8.] Stem cell treatment are risk free if they come from your own body ?
a. True
b. False
9.] Where can scientist obtain stem cell ?
a. Only from an embryo
b. Only from tissue in the body
c. Only from the brain
d. From an embryo or tissue in the body
10.] What is the least invasive source of stem cells from the human body ?
a. Cord blood
b. Adipose tissue
c. Bone marrow
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (c) Liver
2.] (c) Oval cell
3.] (b) Differentiation
4.] (a) Somatic
5.] (d)
6.] (a) Development elasticity
7.] (c) Allogenic
8.] (b)
9.] (d) From an embryo or tissue in the body
10.] (a) cord blood
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 163 – 164.
2.] Robbin’s Basic Pathology; 5th edition; Page no. 583 – 584.
The post Stem Cells: Definition, Types of stem cells, Self renewal, Potency, Stem cell studies, Stem cell therapy and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post Acidosis And Alkalosis : Definition, Types of Imbalances And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>TYPES OF IMBALANCES :-
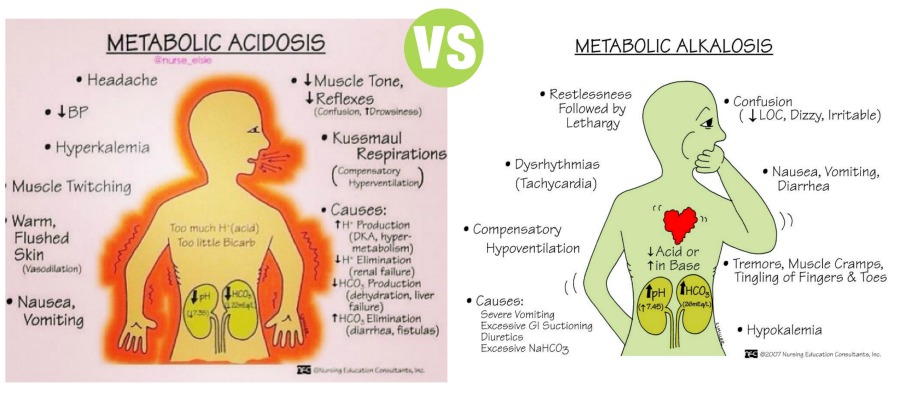
A.] METABOLIC ACIDOSIS :-
1.] A fall in blood pH level due to the metabolic component is brought by the fall of bicarbonate level and excess of H+ ion in the blood. It occurs in the following situation :-
- Increased production of lactic acid which causes lactic acidosis.
- Starvation.
- Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus which causes diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Therapeutic administration of ammonium chloride or acetazolamide (diamox).
- Chronic renal failure.
2.] Due to high blood level of H+ ion in metabolic acidosis this stimulates the respiratory center so that there would be a deep and rapid breathing.
3.] Also, there is a fall in plasma bicarbonates level.
B.] METABOLIC ALKALOSIS :-
1.] A rise in blood pH due to rise in the bicarbonate level of plasma and loss of H+ ion is called metabolic alkalosis. This metabolic alkalosis can be seen in following situations :-
- Due to administration of alkaline salts like sodium bicarbonate.
- Severe and prolonged vomiting.
- Hypokalemia such as in Cushing’s syndrome, increased secretion of aldosterone.
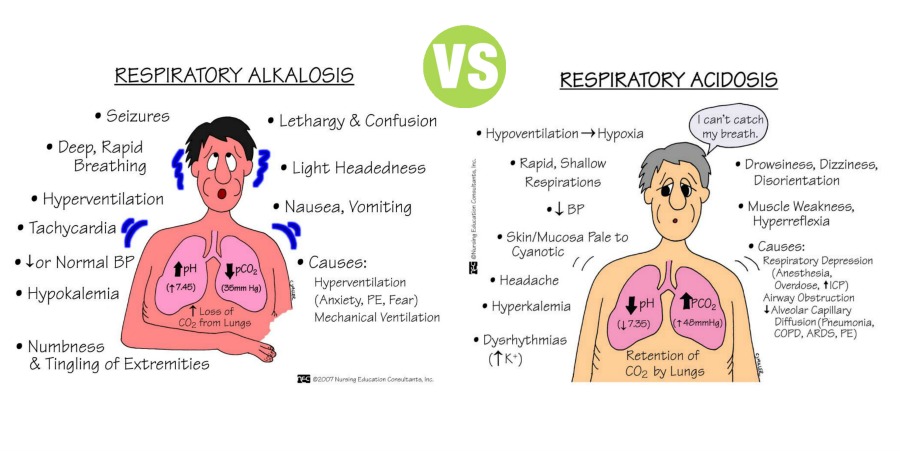
C.] RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS :-
1.] It is the condition that occurs when the lungs can’t remove enough to the CO2 produced by the body.
2.] Excess of CO2 causes the pH of blood and other bodily fluids to decrease making them too acidic.
3.] This respiratory acidosis can occur in following situations :-
- Impaired neuromuscular function.
- Due to air obstruction which are caused in chronic bronchitis, asthma, emphysema.
- Due to restricted thoracic movement.
4.] Acute respiratory acidosis : Occurs quickly can become life threatening.
5.] Chronic respiratory acidosis : Develop overtime, it doesn’t cause symptoms, instead the body adapts to increased acidity.
D.] RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS :-
1.] It is the condition which occurs when the level of CO2 and O2 in the blood are not balanced.
2.] Respiratory alkalosis occur when you breathe too fast and too deep and CO2 level drops too low.
3.] This causes the pH of the blood too rise and become too alkaline.
4.] Hyperventilation (over breathing) is the underlying cause of respiratory alkalosis.
5.] Panic attacks and anxiety are the mist common cause of hyperventilation.
6.] Other symptoms include :-
- Dizziness
- Blotting
- Discomfort in the chest area
- Confusions
- Dry mouth
- Felling short of breath
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION [MCQs] :-
1.] Excessive citrate is transfused blood can cause which of the following abnormalities ?
a. Metabolic alkalosis
b. Metabolic acidosis
c. Respiratory alkalosis
d. Respiratory acidosis
2.] Choose the incorrect statement about anion gap out of the following ?
a. In lactic acidosis anion gap is increased
b. Anion gap is decreased in hypercalcemia
c. Anion gap is decreased in lithium toxicity
d. Anion gap is decreased in ketoacidosis
3.] All are true for renal handling of acids in metabolic acidosis except ?
a. Hydrogen ion secretion is increased
b. Bicarbonate reabsorption is decreased
c. Urinary acidity is increased
d. Urinary ammonia is increased
4.] Carbonic anhydrase is present at all places except ?
a. Gastric parietal cells
b. Red blood cells
c. Renal tubular cells
d. Plasma
5.] All are true about metabolic alkalosis except ?
a. Associated with hyperkalemia
b. Associated with decreased ionic calcium concentration
c. Can be caused due to hyperaldosteronium
d. Can be caused due to renin secreting tumor
6.] Which of the following condition will cause respiratory alkalosis ?
a. Fever
b. Anxiety
c. Laryngeal obstruction
d. Salicylate toxicity
7.] Causes of lactic acidosis include all except ?
a. Acute myocardial infraction
b. Hypoxia
c. Circulatory failure
d. Infection
8.] Causes of metabolic alkalosis include all the following except ?
a. Mineralocorticoid deficiency
b. Hypokalemia
c. Thiazide diuretic therapy
d. Recurrent vomiting
9.] In metabolic alkalosis, the blood pH level is ?
a. Increases
b. Decreases
c. Stay the same
d. May increase or decrease
10.] Which of the following is not a cause of metabolic acidosis ?
a. Aspirin toxicity
b. Ileostomy
c. Hyperaldosteronism
d. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (a) Metabolic alkalosis
2.] (d) Anion gap is decreased in ketoacidosis
3.] (b) Bicarbonate reabsorption is decreased
4.] (d) Plasma
5.] (a) Associated with hyperkalemia
6.] (c) Laryngeal obstruction
7.] (d) Infection
8.] (a) Mineralocorticoid deficiency
9.] (a) Increases
10.] (c) Hyperaldosteronism
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 89.
The post Acidosis And Alkalosis : Definition, Types of Imbalances And MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post Electrolyte Imbalance : Symptoms, Causes, Abnormalities, Treatment and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>1.] There are many chemicals in our blood stream that regulate important function of our bodies. These chemicals are called electrolytes.
2.] Our body’s nerve reaction and muscle formation are dependent upon the popular exchange of these electrolyte ion outside and inside cell.
3.] Intracellular compartment has higher concentration of potassium, calcium, magnesium and phosphate ion than the blood.
4.] In extracellular fluid (including serum) has higher concentration of sodium, chloride and bicarbonate ion.
5.] For electrolyte homeostasis, the electrolyte concentration in both the compartment should be within the normal limits.
6.] Normal serum level of electrolytes are maintained in the body by the careful balance of 4 processes : Their intake, absorption, distribution and excretion.
7.] Disturbance in any of the above mentioned process is in diverse pathophysiologic state may cause electrolyte imbalance.
SYMPTOMS OF ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE :-
Common symptoms of an electrolyte disorder include :-
- Irregular heartbeat
- Fast heart rate
- Fatigue
- Lethargy
- Convulsions or seizures
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Abdominal cramping
- Muscle cramping
- Headache
CAUSES OF ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE :-
1.] It may cause because of excessive loss of body fluids through prolonged vomiting, diarrhea or sweating.
2.] This may also develop due to fluid loss related to burns.
3.] Certain medication can also cause electrolyte imbalance.
CERTAIN ABNORMALITIES :-
A.] SODIUM : Hyponatraemia and Hypernatraemia
B.] POTASSIUM : Hypokalaemia and Hyperkalaemia
C.] CALCIUM : Hypocalcaemia and Hypercalcaemia
D.] MAGNESIUM : Hypomagnesaemia and Hypermagnesaemia
TREATMENT :-
In general, certain treatments are used to restore the proper balance of minerals in the body. These include:
Intravenous (IV) fluids
Intravenous (IV) fluids, typically sodium chloride, can help rehydrate the body. This treatment is commonly used in cases of dehydration resulting from vomiting or diarrhea. Electrolyte supplements can be added to IV fluids to correct deficiencies.
Certain IV medications
IV medications can help your body restore electrolyte balance quickly. They can also protect you from negative effects while you’re being treated by another method.
The medication you receive will depend on the electrolyte disorder you have. Medications that may be administered include calcium gluconate, magnesium chloride, and potassium chloride.
Oral medications and supplements
Oral medications and supplements are often used to correct chronic mineral abnormalities in your body. This is more common in if you’ve been diagnosed with ongoing kidney disease.
Depending on your electrolyte disorder, you may receive medications or supplements such as:
- calcium (gluconate, carbonate, citrate, or lactate
- magnesium oxide
- potassium chloride
- phosphate binders, which include sevelamer hydrochloride (Renagel), lanthanum (Fosrenol), and calcium-based treatments such as calcium carbonate
They can help replace depleted electrolytes on a short- or long-term basis, depending on the underlying cause of your disorder. Once the imbalance has been corrected, your doctor will treat the underlying cause.
Although some of the supplements can be purchased over the counter, most people with electrolyte disorders get a prescription for supplements from their doctor.
Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis is a type of dialysis that uses a machine to remove waste from your blood.
One way to get the blood to flow to this artificial kidney is for your doctor to surgically create a vascular access, or an entrance point, into your blood vessels.
This entrance point will allow a larger amount of blood to flow through your body during hemodialysis treatment. This means more blood can be filtered and purified.
Hemodialysis can be used when an electrolyte disorder is caused by sudden kidney damage and other treatments aren’t working. Your doctor may also decide on hemodialysis treatment if the electrolyte problem has become life-threatening.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION [ MCQs] :-
1.] Electrolyte balance in the body usually refers to the balance of ?
a. Bases
b. Salts
c. Organic molecules
d. Acids
2.] Pica occurs when there is a deficiency of ?
a. Mineral such as iron
b. Electrolytes
c. Salts
d. Water
3.] Edema is the accumulation of fluid in the ?
a. Interstitial space
b. Special fluid compartments
d. Plasma
4.] The most prevalent electrolyte in the extracellular fluid is ?
a. Potassium
b. Calcium
c. Phosphate
d. Sodium
5.] The condition in which sodium level are too low is referred to as ?
a. Hyponatremia
b. Hypokalemia
c. Aldosteronism
d. Hypernatremia
6.] Which patient is at most risk for fluid volume deficiency ?
a. A patient who has been vomiting and having diarrhea for 2 days
b. A patient with continuous nasogastric suction
c. A patient with an abdominal wound vac at intermittent suction
d. All of the above are correct
7.] Which patient is at most risk for the hypomagnesemia ?
a. A 55 year old chronic alcoholic
b. A 57 year old with hyperthyroidism
c. A patient reporting overuse of antacid and laxative
d. A 28 year old suffering from hypoglycemia
8.] All the following are important electrolyte in the body except ?
a. Potassium ion
b. Carbon ion
c. Chloride ion
d. Sodium ion
9.] Approximately one – third of the body water exist in the ?
a. Kidney and urinary bladder
b. Blood
c. Extracellular fluid compartment
d. Transcellular fluid compartment
10.] The intracellular fluid compartment refers to all the water found in ?
a. The bones of the body
b. Area outside the body cell
c. Areas within the gastrointestinal tract
d. All cells of the body
SOLUTIONS :-
1.] (b) Salts
2.] (a) Mineral such as iron
3.] (a) Interstitial space
4.] (d) Sodium
5.] (a) Hyponatremia
6.] (d)
7.] (a) A 55 year old chronic alcoholic
8.] (b) Carbon ion
9.] (c) Extracellular fluid compartment
10.] (d) All cells of the body
REFERENCES :-
1.] Textbook Of Pathology By Harsh Mohan; 7th edition; Page no. 88 – 89.
The post Electrolyte Imbalance : Symptoms, Causes, Abnormalities, Treatment and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, CSIR NET JRF appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>