The post Spinal Nerves Anatomy and MCQs For NEET, SSC, GPAT, Staff Nurse and CSIR NET JRF Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>- 8 cervical
- 12 thoracic
- 5 lumber
- 5 sacral
- 1 coccygeal
Although there are only 7 cervical vertebrae, but there are 8 nerves; as the 1st nerve leaves the vertebral canal between the occipital bone and atlas(C1). The lumber, sacral and coccygeal nerves leave the spinal cord at the level of the 1st lumber vertebrae.
NERVE ROOTS
Spinal nerves arises from both sides of the spinal column, and leaves through the intervertebral foramina. A typical spinal nerve has two connections to the cord- a posterior root and the anterior root. Both these posterior and anterior roots unite to form a spinal nerve at the intervertebral foramen. Since the posterior root contains sensory axons and the anterior root contains motor neuron; all spinal nerves are classified as mixed nerve. The posterior root contains the posterior root ganglia in which the cell bodies of sensory neurons lies.
BRANCHES
Just after leaving the intervertebral foramen, the spinal nerves divides into several branches. These branches are also called as rami. There are several types of rami
- The posterior rami, supplies to the muscles and skin of posterior surface of trunk.
- The anterior rami supplies to the muscles and skin of lateral and anterior surface of trunk, and upper and lower limbs.
- The meningeal branch(rami) supplies to the vertebrae, vertebral ligaments, blood vessels of spinal cord and meninges.
- The rami communicantes is one of the component of ANS.
PLEXUSES
Axons from the anterior rami of spinal nerves, except from the thoracic nerves; do not directly go to the body surfaces they supply. Instead they form networks on both the left and right side of the body by joining with various axons of adjacent rami. Such a networks is known as plexuses. The various kinds of plexuses are as follows:
- Cervical plexus:- This is formed by the anterior rami of 1st four cervical nerves. It lies within the neck opposite to 1st four cervical vertebrae. This plexus is protected by the sternocleidomastoid muscles.
Its superficial branches supplies at the back structure and the side of head; deep branches supply muscles of neck; and phrenic nerve supplies the diaphragm, hence initiates inhalation.
- Brachial plexus:- It is formed by the anterior rami of C5-C8 and T1 and T2 nerves. It is situated deeply within the neck and shoulder above. The branches of this plexus supply the skin and muscles of upper limbs and chest muscles.
Nerves that emerges from this plexus which are- axillary nerve, radial nerve, musculocutaneous nerve, median nerve, ulnar nerve and medial cutaneous nerve.
- Lumber plexus:- It is formed by the anterior rami of 1st three and some part of 4th lumber nerves. It lies in front of the transverse processes of lumber vertebrae and behind the psoas muscle. The main branches of this plexus are- iliohypogastric nerve, ilioinguinal nerve, genitofemoral nerve, lateral cutaneous nerve, femoral nerve, obturator nerve and lumbosacral nerve.
- Sacral plexus:- This plexus is formed by the anterior rami of lumbosacral trunk and the S1-S3 nerves. The lumbosacral trunk is formed by the 5th and part of L4. It lies in the posterior wall of pelvic cavity.
Sacral plexus is divided into a number of branches; these branches supplies the skin and muscles of pelvic floor, muscles around hip joint and pelvic organs. It also provides the sciatic nerve; the largest nerve in the body.
- Coccygeal plexus:- This plexus is very small and is formed by the part of S4 and S5 and also the coccygeal nerve. The nerve of this plexus supplies to the skin and muscles around the coccyx and also the anal area.

Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. Spinal nerves comes under which part of nervous system?
A. central nervous system B. peripheral nervous system
C. somatic nervous system D. autonomic nervous system
2. How many pairs of spinal nerves are present in the body?
A. 31 B. 12
C. 15 D. 30
3. Which of the following is a branch of lumber plexus?
A. femoral nerve B. ilioinguinal nerve
C. obturator nerve D. all of the above
4. Match the following-
a. cervical plexus 1. Phrenic nerve
b. brachial plexus 2. Median nerve
c. lumber plexus 3. Iliohypogastric nerve
d. sacral plexus 4. Sciatic nerve
5. Anterior root contains which kind of nerve fiber?
A. sensory fibers B. motor fibers
B. mixed fibers D. does not contain nerve fibers
6. Which branch supplies the lower and upper limbs?
A. anterior rami B. posterior rami
C. meningeal rami D. rami communicantes
7. Which of the following statement is true?
A. posterior rami supplies lower limb
B. spinal nerves is part of CNS
C. branches of spinal nerves occurs after reaches body structure
D. all spinal nerves are mixed nerves
8. Where do the cervical plexus lies?
A. above the neck B. below the neck
C. within the neck d. in front of neck
9. Which one is the branch of sacral plexus?
A. axillary nerve B. radial nerve
C. ulnar nerve D. none of the above
10. Through which structure, the spinal nerves leave the spinal cord?
A. intervertebral foramen B. intervertebral ligaments
c. grey matter of spinal cord D. white matter of spinal cord
ANSWERS:-
1. peripheral nervous system
2. 31
3. all of the above
4. a – 1 b – 2 c – 3 d – 4
5. motor fibers
6. anterior rami
7. all spinal nerves are mixed nerves
8. within the neck
9. none of the above
10. intervertebral foramen
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE:
1. Ross and Wilson-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.-: 165-169
2. Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 468-475.
The post Spinal Nerves Anatomy and MCQs For NEET, SSC, GPAT, Staff Nurse and CSIR NET JRF Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post AXIAL SKELETON: Hyoid bone, Vertebral column and Thorox and MCQs for NEET, GPAT appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>Hyoid Bone
It is a unique part of axial skeleton, as this bone does not articulate with any other bone. It is located in the anterior neck just between the mandible and larynx. The hyoid bone keeps the larynx open all the time; also the bone supports tongue and also serves as a site of attachment for tongue, neck and pharynx muscles. The bone consist of horizontal body and two projections: lesser horns and greater horns.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12540/hyoid-bone-anatomy_english.jpg)
Vertebral Column
There are 26 bones in the vertebral column. It is also called as backbone, spine or spinal column. The vertebral column is divided in different regions, which are discussed below-
1.CERVICAL VERTEBRAE
These are the smallest vertebrae among all other, except from those who forms coccyx. Their vertebral arch is longer. all the cervical vertebrae have 3 foramina: one vertebral foramina and two transverse foramina. The first two cervical vertebrae are atypical(different from others).
The first cervical vertebrae(C1) is atlas, on which the skull rests. It is essentially a ring of bone with no distinct body or spinous process. It has two small transverse process. It also have two facets with articulates with the occipital bone, through condyloid joint and they allow nodding movement.
Just below the atlas, is the second cervical vertebrae(C2) known as axis. It has small body and a superior projection known as odontoid process. This process lies on the posterior foramen of atlas and is held in position by transverse ligaments. This joint allows side to side movement.
THORACIC VERTEBRAE
The 12 thoracic vertebrae are larger than the cervical vertebrae. It is because that this part of vertebral column has to support more body weight. The facets of bodies and transverse process of thoracic vertebrae articulates with the ribs, except of T11 and T12. These joints are called as vertebrocostal joints. Movements of thoracic region are limited due to the attachment of ribs to the sternum.
LUMBER REGION
The 5 lumber vertebrae are the largest and strongest of the vertebral column as it has to bear the weight of upper body. They have spinous process to which the muscles of lower neck attaches.
SACRUM VERTEBRAE
The sacrum is a triangular bone which Is formed from the union of 5 bones. It has concave anterior surface. The upper part called as base articulates with the L5. On each side, sacrum articulates with the ilium of hip bone to form sacroiliac joint; and at its lower end, it articulates with the coccyx. The vertebral foramina are present; also many foramina are present on each side which allows passage for nerves.
COCCYX VERTEBRAE
The coccyx is a triangular bone, formed by the fusion of 4 coccygeal vertebrae. On lateral surface, are the series of transverse processes in which the pair is the largest. At the upper end, the base of coccyx articulates with the apex of sacrum. In females, the coccyx points inferiorly to allow passage for baby during birth; while in male, the coccyx points anteriorly.

Above Figure is taken for Educational Purpose Only.
Features of the vertebral column:-
- a. Intervertebral discs:- The body of adjacent vertebrae are separated by the intervertebral discs; it consist of outer rim made f fibrocartilage and central core made of soft gelatinous material.
- b. Intervertebral foramina:- When the two adjacent vertebrae are viewed from side , a foramen formed is seen by the gap between the two vertebrae.
- c. Ligaments of vertebral column:- These ligaments holds the vertebral column together and also holds the intervertebral discs in proper position.
- d. Curves of the vertebral column:- The vertebral column has four curves:- 2 primary curves and 2 secondary curves. When the fetus in the uterus lies in the curled position, it shows primary curve. The secondary cervical curve develops when the child can hold up his head; and the secondary lumber curve develops when the child is able to stand.
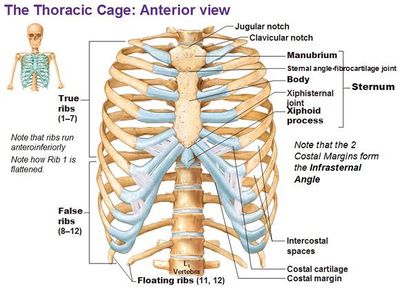
Thoracic Cage
The thoracic cage is the skeletal part of the thorax which consist of the ribs, sternum, their costal cartilages and the bodies of thoracic vertebrae. It protects the organs of thoracic and abdominal cavities; and also provides support to the bones of upper limb.
STERNUM
It is a flat bone which lies in the middle of the front of the chest. It is divided in 3 regions:-
- The manubrium is the uppermost part of the sternum and articulate with the clavicle to form sternoclavicular joint. It also articulates with the first two pairs of ribs
- The body is the middle portion of sternum. It provide attachment for the ribs
- The xiphoid process It is the inferior end of the sternum. It provides attachment to the diaphragm and anterior muscles of abdominal wall.
RIBS
The 12 pairs of ribs gives the structural support to the side of the thoracic cavity. The ribs increases in length till 7th pair; and then after decreases in length till 12th pair. Each ribs articulates posteriorly with its corresponding thoracic vertebrae.
The first seven pairs of ribs have direct anterior attachment with the sternum by the strip of hyaline cartilage known as costal cartilage. The ribs that have costal cartilages and attaches directly to the sternum are known as true ribs. The joints between the true ribs and the sternum are called as sterno-costal joints. The next 3 pairs (8, 9, 10th) are called as false ribs because their costal cartilages attaches indirectly to the sternum. The rest two pairs are called floating rib because their costal cartilage do not attach to the sternum at all.
Inflammation of any one or more costal cartilage is known as costochondritis. It causes local chest wall pain; and be resulted as a symptom for heart attack.
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. Which is the only bone of axial skeleton which does not articulate with any other bone?
A. occipital bone B. mandible
C. hyoid bone D. none of the above
2. How many bones form the vertebral column?
A. 31 B. 26
C. 22 D. 30
3. Which type of joint lies between the atlas and the occipital bone?
A. saddle joint B. pivot joint
C. hinge joint D. condyloid joint
4. Which bone of vertebral column facilitates side to side movements?
A. C7 B. C5
C. C4 D. C2
5. Match the following:-
A. sacrum vertebrae 1. Articulates with the ribs
B. coccyx vertebrae 2.articulates with the ilium
C. lumber vertebrae 3. Bears upper body weight
D. thoracic vertebrae 4. The lateral surface has transverse process
6. Which of the following is the part of sternum?
a. body B. xiphoid process
C. manubrium D. all of the above
7. Which connective tissue provides the attachment of the true ribs with sternum?
A. hyaline cartilage B. areolar tissue
C. fibrocartilage D. elastic cartilage
8. Which of the following statement is true?
A. transverse process of Lumber attaches neck muscle
B. the joint between C1 and occipital bone allows nodding
C. all the thoracic vertebrae articulates with ribs
D. the base of sacrum articulates with ilium to form sacroiliac joint
9. Which of the following is known as floating ribs?
A. 7th pair B. 10th pair
C. 9TH pair D. none of the above
10. What is costochondritis?
A. inflammation of ribs
B. inflammation of manubrium
C. inflammation of costal cartilage
D. inflammation of xiphoid process
ANSWERS:-
1. hyoid bone
2. 26
3. condyloid joint
4. C2
5. A – 2 B – 4 C – 3 D – 1
6. all of the above
7. hyaline cartilage
8. the joint between C1 and occipital bone allows nodding
9. none of the above
10. inflammation of costal cartilage
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFRENCE: 1. Ross and Wilson-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.-:401-406.
2. Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 216-226.
The post AXIAL SKELETON: Hyoid bone, Vertebral column and Thorox and MCQs for NEET, GPAT appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post AXIAL SKELETON: Cranial and facial bones and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse, Pharmacist and Lab Technician Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>There are 22 bones of skull. They lie on the superior end of vertebral column. These bones are divided in 2 groups: Cranial bones- which forms the cranial cavity are eight in number; Facial bones- these are 14 and forms the face.
CRANIAL BONES
1. FRONTAL BONE
Frontal bone forms the forehead, the anterior part of cranium, roofs of the orbits. It also forms prominent ridges above the eyes known as supraorbital margins. Just above these margins, inside the bone, are the two air-filled cavities. These cavities are also known as sinuses and opens into nasal cavity.
The coronal suture joins the frontal and parietal bone. Other sutures are formed with sphenoid, zygomatic, lacrimal, nasal and ethmoid bone.
2. PARIETAL BONE
These are present in pairs and forms the side and roof of the skull. They articulate with each other and forms sagittal suture, parietal bone and frontal bone forms coronal suture, occipital bone and parietal bone forms lambdoidal suture and with temporal bone the parietal bone forms squamous suture. The inner surface is concave and is used to accommodate the brain and blood vessels.
3. TEMPORAL BONE
There are two temporal bones and lies one on each side of the head and forms sutures with parietal, sphenoid, occipital and zygomatic bone. The squamous part of temporal bone is a thin fan-shaped area that articulates with the parietal bone. The mastoid part contains the mastoid process:- a thickened region present behind the ears. these processes contains large number of air sinuses that communicate with the middle ear.
The petrous portion forms part of the base of skull and also contains organs having receptors for hearing and balance(organ of corti , vestibule and semicircular canals). The temporal bone articulate with the mandible and forms temporomandibular joint; It is the only movable joint of skull. The styloid process of temporal bone supports hyoid bone and muscles of tongue and pharynx.
4. OCCIPITAL BONE
this bone forms the back of head and also the part of base of the skull. It articulates with parietal, sphenoid and temporal bone. The inner surface is concave in shape and contains occipital lobes of cerebrum and cerebellum. this bone have 2 condyles which forms condyloid joint with atlas(1st bone of vertebral column); this joint allows the nodding movement of head. Between the condyles is the foramen magnum through which the spinal cords passes into the cranial cavity.
5. SPHENOID BONE
This bone forms the Middle part of base of the skull. This bone links the cranial and facial bones. In the middle of the bone, on the superior surface is a depression known as hypophyseal fossa, where the pituitary gland lies. It also contains large number of small air sinuses which opens into the nasal cavity. The optic foramina of sphenoid bone forms a passage for the optic nerve to reach the brain.
6. ETHMOID BONE
This bone forms the anterior part of base of skull. It helps to form orbital cavity., the nasal septum and lateral walls of nasal cavity. On each side of the bone are the projections known as middle or superior conchae. It is a very delicate bone and contains small air sinuses with opening into nasal cavity. The cribriform plate forms the roof of nasal cavity nd contains large no. of small foramens through which the nerve fibers of olfactory nerve passes and leads to brain.
FACIAL BONES
Our face is formed by a group of 14 bones. some of these bones are present in pairs and others are single.
Zygomatic Bones
there are two zygomatic bones. Each bone earlier originate as 2 bones and later fuse after birth. The bones form prominences of the cheek and the part of floor and lateral walls of orbital cavities.
Maxilla
this is the upper jaw bone and forms the anterior part of the roof of the mouth, the upper jaw, part of orbital cavities and walls of nasal cavity. the alveolar process carries the upper teeth. On each side of the bone is the sinus known as maxillary sinus which opens into nasal cavity.
Nasal Bones
The two nasal bones meet at the midline and form the bridge of the nose. The rest of the supporting tissue of the nose consist of cartilage.
Lacrimal Bones
The two lacrimal bones are thin and are like fingernail in size as well as in shape. These are the smallest bones of face and forms a part of medial wall of each orbit. It contains lacrimal fossa that stores lacrimal sacs; the structures that gathers tears and passes into nasal cavity.
Palatine Bones
These are two L-shaped bones form the posterior portion of hard palate, floor of nasal cavity and some portion of floor of orbits. The horizontal plates form the posterior portion of hard palate.
Inferior Nasal conchae
There are two inferior nasal conchae, which are inferior to the middle nasal conchae of the ethmoid bone. These are separate bones. All the three nasal conchae(superior, inferior and middle) increase the surface area of the nasal cavity, to filter the air as it passes into the lungs. Only the superior nasal conchae are involved in sense of smell.
Vomer
Vomer is a triangular bone on the floor of nasal cavity that articulates superiorly with the ethmoid bone and inferiorly with maxillae and palatine bone. It also forms inferior portion of nasal septum.
Mandible
It is the lower jaw bone; It is the largest and strongest facial bone. It is the only skull bone which is movable. It consist of a curved horizontal portion, the body and two perpendicular portions known as rami. Each ramus has a posterior condylar process that articulates with the mandibular fossa and articular tubercle of temporal bone; and forms temporomandibular joint. The depression between coronoid process and condylar process is known as mandibular notch. The alveolar process contains the alveoli for lower teeth. The mental foramen is the one near which the dentist reach the mental nerve before injecting anesthetics.
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. How many bones come together to form skull?
A. 20 B. 22
C. 25 D. 14
2. Which is the smallest facial bone?
A. vomer B. zygomatic
C. mandible D. lacrimal bone
3. Which is the only movable joint of skull?
A. sagittal suture B. coronal suture
C. temporomandibular joint D. lambdoidal suture
4. The frontal bone articulates with which bone?
A. temporal B. parietal
C. sphenoid D. all of the above
5. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. palatine bones are L-shaped bones
B. maxilla is the lower jaw bone
C. zygomatic bone is a cheek bone
D. Vomer forms inferior portion of nasal septum
6. Which part of temporal bone contains organs for hearing and balance?
A. mastoid process B. petrous portion
C. squamous part D. styloid process
7. Which bone links the cranial and facial bone?
A. sphenoid bone B. ethmoid bone
C. nasal bones D. zygomatic bone
8. Which bone is roughly triangular in shape?
A. nasal bones B. inferior nasal conchae
C. lacrimal bone D. none of the above
9. Match the following-
1. ethmoid bone a. forms middle part of skull
2. sphenoid bone b. forms most of the base of skull
3. frontal bone c. forms anterior part of base of skull
D. occipital bone d. forms the forehead
10. Which bone forms the posterior portion of hard palate?
A. nasal bones B. palatine bone
C. vomer D. zygomatic bone
ANSWERS:-
1. 22
2. lacrimal bones
3. temporomandibular joint
4. all of the above
5. maxilla is the lower jaw bone
6. petrous portion
7. sphenoid bone
8. none of the above; it is vomer
9. 1 – c 2 – a 3 – d 4 – b
10. palatine bones
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE:
1. Ross and Wilson-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.-: 396-401.
2. Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 202-212.
The post AXIAL SKELETON: Cranial and facial bones and MCQs for NEET, GPAT, Staff Nurse, Pharmacist and Lab Technician Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post Acid-Base balance In Urinary System and MCQ for NEET, GPAT CSIR NET JRF and GATE Lifesciences Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>1. BUFFER SYSTEMS
Buffer acts to bind H+ ions, thus removes the highly reactive excess hydrogen ions from the solution. Buffers thus raise the pH, but do not remove H+ from the body. There are 3 buffer systems-
Protein buffer system
This type of buffer is found mostly in the intracellular fluid and blood plasma. The hemoglobin is a buffer within RBCs and albumins is a main protein buffer in blood plasma.
When the pH rises, following changes occur in the structure of protein. The released H+ ion reacts with the OH- ion(since pH rises) and forms water

When the pH falls and become acidic, following changes occur in its structure. The free amino group at the other end of a protein acts as a base reacting with H+ ion.
Since hemoglobin acts as a buffer for RBCs, so when blood flows through the systemic capillaries, The CO2 present in the tissue cells enters the RBCs and reacts with water to form carbonic acid(H2CO3). after the formation of H2CO3, it dissociates to form H+ and HCO3-. In the tissue cells when CO2 enters the RBCs at the same tine oxy-hemoglobin bond also breaks and hemoglobin picks up most of the H+ ion and forms Hb-H.
Carbonic Acid-Bicarbonate buffer system
It is based on two structures, carbonate ion(HCO3-) and carbonic acid(H2CO3).
If the Ph rises, the following reaction takes place. The carbonic acid thus formed dissociates into CO2 and water; The CO2 formed is exhaled through lungs
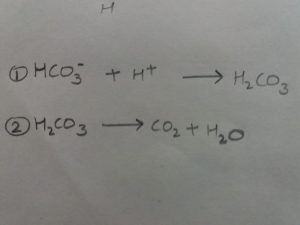
If the pH falls, the carbonic acid dissociates and following reaction occur.
Phosphate Buffer system
It is mainly important in cytosol of the cell and in urine. It is based on two structure: dihydrogen phosphate(H2PO4-) and mono-hydrogen phosphate.
If the Ph rises, the OH- ion reacts with dihydrogen phosphate; and when Ph falls, H+ ion combines with mon-hydrogen phosphate. the reactions are as follows.
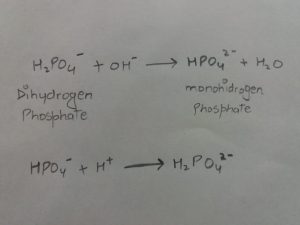
2.EXHALATION OF CO2
When the pH of blood rises, then the chemoreceptors present in the medulla oblongata, aortic sinus and carotid sinus are stimulated. as these chemoreceptors are stimulated, they send nerve impulses to the inspiratory area of medulla oblongata which results in contraction of diaphragm. These contractions further facilitates exhalations of CO2, and less carbonic acid is formed. Thus Ph of blood comes back to normal.
3.KIDNEY EXCRETION OF H+
The proximal convoluted tubules(PCT) present in the nephrons contains Na+/H+ antiporters. these antiporters reabsorbs Na ions and secretes H+. Thus Ph of urine becomes acidic due to increased concentration of H+ ions.
Also the intercalated cells of the collecting duct of nephrons reabsorbs the potassium ion and carbonate ions and secrete H+ ions and Ph becomes acidic. Some intercalated cells also secretes the carbonate ions because of which the Ph of urine becomes basic. In this way, the Ph of urine is maintained in the body.
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. What is the normal Ph range of blood?
A. 8.3-9.5 b. 7.3-7.
C. 5.5-5.8 D. 3.4-3.5
2. Which mechanism is not the part of acid base balance?
A. exhalation of CO2 B. inhalation of CO2
C. buffer system D. kidney mechanism
3. Which structures forms the basis of phosphate buffer system?
A. dihydrogen phosphate B. carbonic acid
C. mono-hydrogen phosphate D. both A and C
4. Which of the following buffers functions for buffer systems for maintaining Ph?
A. protein buffer B. carbonic-bicarbonate buffer
C. phosphate buffer D. all of the above
5. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. intercalated cells do not secrete carbonate ions
B. dissociation of carbonic acid forms CO2
C. OH ions reacts with dihydrogen phosphate
D. Ph becomes basic when carbonate ions are secreted
6. What acts as a buffer within RBCs?
A. hemoglobin B. water
C. oxygen D. CO2
7. Match the following-
a. protein buffer 1. chemoreceptors
b. phosphate buffer 2. Sodium-hydrogen antiporters
C. PCT 3. Cytosol and urine
D. exhalation of CO2 4. Intracellular fluid and blood
8. In which region of brain, the inspiratory area lies?
A. pons B. third ventricle
C. medulla oblongata D. fourth ventricle
9. Where are the Na/H+ antiporters present?
A. PCT B. DCT
C. collecting duct D. loop of henle
10. In which regions, the chemoreceptors for exhalation of CO2 mechanism NOT present?
A. medulla oblongata B. aortic sinus
C. carotid sinus D. none of the above
ANSWERS:-
1. 7.3-7.4
2. inhalation of CO2
3. both A and C
4. all of the above
5. intercalated cells do not secrete carbonate ion
6. hemoglobin
7. a – 4 b – 3 c – 2 d – 1
8. medulla oblongata
9. PCT
10. none of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE:-Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 1070-1075.
The post Acid-Base balance In Urinary System and MCQ for NEET, GPAT CSIR NET JRF and GATE Lifesciences Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post Epithelial Tissue and MCQ for NEET, GPAT, NET JRF, GATE, Staff Nurse and Pharmacist Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The epithelium consist of cells arranged in continuous sheets, in either single or multiple layers. It covers the body and also lines the cavities, organs and tubes. The functions of epithelial tissue includes-
• Protection of underlying structures from dehydration, chemicals etc
• Secretion
• Absorption
The cells are closely packed and the intercellular substance is called is matrix, the cells lies on the basement membrane. The blood supply and nerves to the epithelial tissue is done with the adjacent connective tissue.
The epithelium is broadly divided into 2
1. covering and lining epithelium- this forms the covering and lining of body organs tubes etc. these are again divided-
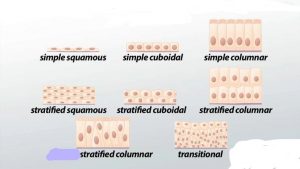
I. Simple epithelium
• Simple squamous epithelium:– composed of single layer of flat cells. It lines heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels etc. its functions are diffusion, filtration, osmosis and secretion.
• Simple cuboidal epithelium:- consist of single layer of cube shaped cells, covers the surface of ovary and lines kidney tubules, anterior surface of lens of eye etc, functions include secretion and absorption.
• Simple columnar epithelium:- it is of two types
a. Ciliated columnar– consist of single layer of ciliated column like cells with nuclei and contain goblet cells, lines bronchioles, uterine, central canal of spinal cord etc, it moves mucous by ciliary action
b. Non-ciliated columnar:- consist of non ciliated column like cells and lines the GIT, ducts of many glands etc and functions for secretion and absorption.
II. Stratified epithelium
• Stratified squamous:– several layers of different cells from cuboidal to columnar cells but the apical layer contains flat cells. Keratinized lines the layers of skin while the non-keratinized lines pharynx, larynx vagina etc. the main function is protection
• Stratified cuboidal:– more than two layers of cells in which the apical layer contain cube-shaped cells, lines the ducts of adult sweat glands and part of male urethra. It works for protection, absorption and limited secretion.
• Stratified columnar:– several layers of different cells but apical layer has column like cells, lines urethra, excretory ducts and parts of conjunctiva of eye. Its functions are protection and secretion
• Transitional epithelium:– cells in the apical surface are variable from squamous (when stretched) to cuboidal (when relaxed). It lines urinary bladder and part of urethra and uterus, functions is that it permits distension.
2. Glandular epithelium- these make the secreting portion of glands. These are of two types-
• Endocrine glands:- hormones diffuse into blood from interstitial fluid, examples include adrenal glands pituitary gland, pineal gland, pancreas etc, functions is that the hormones released regulates body activities.
• Exocrine glands:- hormones released in the lymphatic ducts and then into the blood. Exocrine glands are classified on two basis-
1. Structural classification:- in this, the glands are classified as unicellular or multicellular. As the name suggest, unicellular are single celled glands; eg is goblet cells which secrete mucus.
Multicellular glands are composed of many cells. Multicellular glands are again divided in two parts
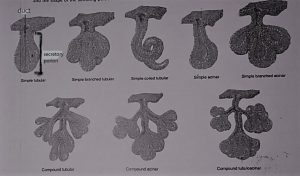
A. SIMPLE GLANDS
- simple tubular– in this the secretory portion is straight and is attached to the single unbranched duct; eg- glands of small intestine
- simple branched tubular– secretory portion is branched and is attached to single unbranched duct; eg- gastric glands
- simple coiled- secretory portion is coiled and is attached to unbranched duct; eg- sweat glands
- simple acinar – secretory portion is rounded is attached to single unbranched duct; eg- glands of penile urethra.
- simple branched acinar- the rounded secretory portion is branched and is attached to the unbranched duct; eg- sebaceous glands.
B. COMPOUND GLANDS
- compound tubular– secretory portion is straight and is attached to the branched duct; eg- bulbourethral glands.
- compound acinar– secretory portion is rounded and is attached to a branched duct; eg- mammary glands
- compound tubulo-acinar– secretory portion is both straight and rounded and is attached to a branched duct; eg- acinar glands of pancreas.
II. Functional classification:- it is done on the basis of how the secretory portion is released. these are of 3 types
- merocrine glands- secretions are synthesized on ribosomes attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum. Eg- salivary glands and pancreas
- apocrine glands- accumulate the secretory product at the apical surface of secreting cells. Eg- sweat glands
- holocrine glands– secretory portion is accumulated in the cytosol of the cell. Eg- sebaceous glands.
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. How are cells arranged in epithelial tissue?
A. loosely packed B. closely packed in continuous sheets
C. arranged in discontinuous form D. both A and C
2. What is the function of epithelial tissue?
A. dehydration B. protection of underlying structures
C. absorption D. all of the above
3. Match the following-
a) transitional epithelium 1. Different cells in apical layer
b) simple columnar 2. Single layer of column like cells
c) stratified squamous 3. Several layers of cells and flat cells in apical surface
d)stratified cuboidal 4. Several cells but cube shaped cell in apical surface
4. Where is the stratified cuboidal epithelium present?
A. heart B. kidneys
C. spinal cord D. lymphatic tissue
5. Which type of cell is present in the apical surface of the transitional epithelium?
a. columnar B. squamous
C. cuboidal D. both B and C
6. What is the function of simple squamous epithelium?
a. protection B. negligible secretion
C. permits distension D. none of the above
7. Which of the following statement is true?
A. epithelial tissue has its own blood vessels and nerves
B. the basement membrane is present between the epithelium and adjacent connective tissue
c. cuboidal cells are present in transitional epithelium when stretched
D. the matrix lies on the apical surface
8. where is the keratinized squamous epithelium present?
A. skin B. blood vessels
C. urethra D. spinal cord
9. Which hormone is not the example of exocrine glands?
A. sebaceous glands B. adrenal glands
C. sweat glands D. salivary glands
10. Where is the simple squamous epithelium found?
A. skin B. blood vessels
C. urethra D. spinal cord
ANSWERS:-
1. closely arranged in continuous sheets
2. all of the above
3. a) – 1 b) – 2 c) – 3 d) – 4
4. kidneys
5. both B and C
6. none of the Above
7. the basement membrane is present between the epithelium and the adjacent connective tissue
8. skin
9. adrenal glands
10. blood vessels
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Refrences:-Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 112-121.
The post Epithelial Tissue and MCQ for NEET, GPAT, NET JRF, GATE, Staff Nurse and Pharmacist Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>The post Cardiac Cycle and Question Answer for NEET, GPAT, Nursing, Pharmacist and Lab Technician Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
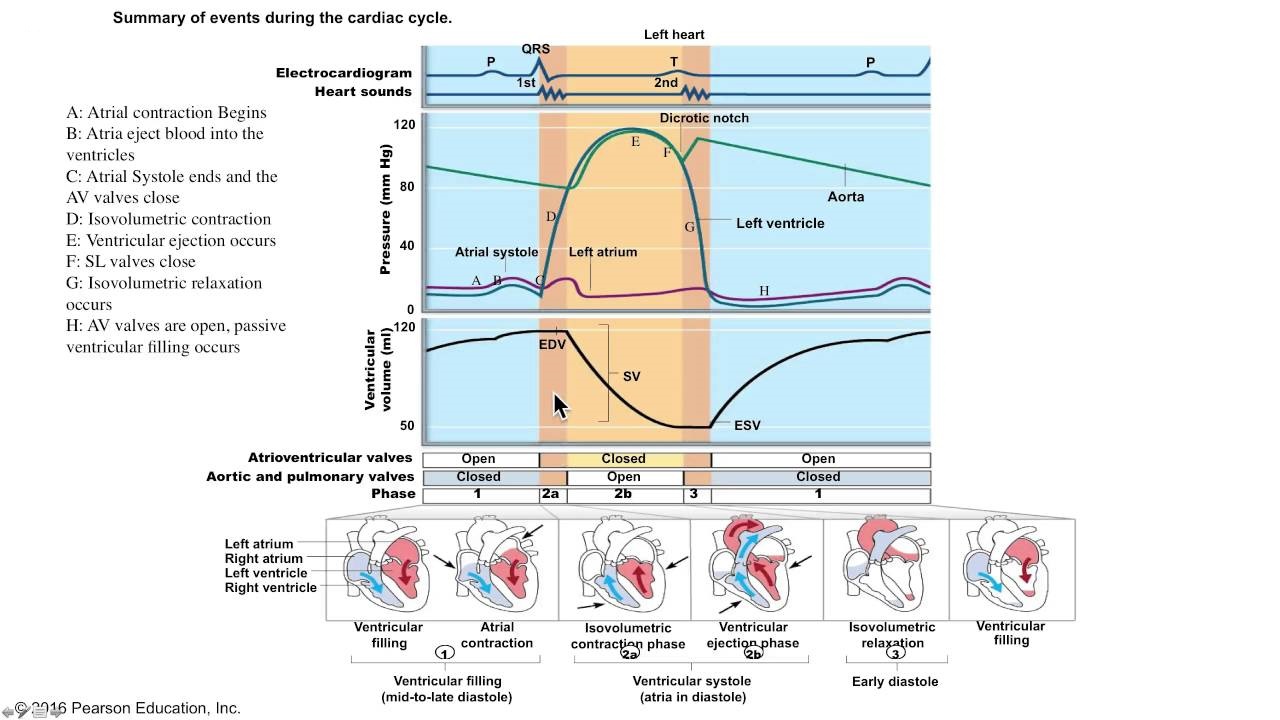
]]>The cardiac cycle is defined as a cycle which includes all the events associated with one heart beat. cardiac cycle consist of contraction(systole) and relaxation(diastole) of both atria and ventricles.
In each cardiac cycle, the atria and ventricles contract and relax. This alternating contraction and relaxation forces the blood to move from high pressure areas to the areas of low pressure. When a chamber of heart contracts, it develops pressure within the chamber and the blood moves to low pressure areas. When heart rate is 75 beats/min, the cardiac cycle is of 0.8 sec. The events associated with cardiac cycle are-
Atrial Systole
The atrial systole is for 0.1 sec; during this period the atria contract and ventricles relax.
- depolarization of SA node causes the atrial depolarization; which is marked by P wave in the ECG.
- Atrial depolarization causes atrial systole. As the atria contract, they exert pressure within; this causes the blood to move through the AV valves.
- Due to atrial systole, the total volume of 25ml of blood reaches to the ventricles which already contains 105ml of blood within it.
- At the end of atrial systole, which is also the end of ventricular diastole; the ventricles contain 130ml of blood. This volume of blood is known as end diastolic volume (EDV).
Ventricular Systole
The ventricular systole is for 0.3 sec; during this period, the ventricles contract and the atria are relaxed.
5. The QRS complex of ECG marks the ventricular depolarization on the ECG. The ventricular depolarization causes ventricular systole.
6. As the ventricles contract, pressure rises within the ventricles and pushes the blood up against the AV valves forcing them to shut. for about 0.005 sec, both the AV valves and semilunar valves are closed; this period is known as isovolumetric contraction.
7. When the left ventricle crosses the pressure of 80mmHg and the right ventricle crosses the pressure of 20mmHg; both the aorta and pulmonary trunk opens. This period is known as ventricular ejection and is for 0.25 sec.
8. The ventricles eject about 70ml of blood after contractions within it. The volume that remains after ejection is known as end systolic volume(ESV); which is about 60ml.
9. The stroke volume(SV) equals to SV=EDV-ESV, that is 130-60ml=70ml.
Relaxation period
This period is for 0.4 sec. During this period, both the atria and ventricles relax. Ventricular repolarization causes ventricular relaxation. This is marked by T wave on the ECG.
The relaxation period is for longer time than the contraction period because if the cardiac muscles relaxes for longer duration, more powerful and forceful is the next contraction. this results in more stroke volume; hence more cardiac output.
Multiple choice questions(MCQs)
1. What is cardiac cycle?
A. blood ejected from the ventricles to the body
B. blood ejected from atria to the ventricles
C. events associated with each heart beat
D. event associated with each heart rate
2. For how long is the cardiac cycle, if the heart rate is 75 beats/min?
A. 0.7 sec B. 0.8 sec
C 0.5 sec D. 0.4 sec
3. Which event is associated with cardiac cycle?
A. atrial systole B. ventricular systole
C. relaxation period D. all of the above
4. The atrial depolarization is marked by which wave on the ECG?
A. P wave B. QRS complex
C. T wave D. U wave
5. Match the following-
A. cardiac cycle 1. 0.3 SEC
B. atrial contraction 2. 0.8 SEC
C. ventricular contraction 3. 0.1 SEC
D. ventricular relaxation 4. 0.4 SEC
6. After the contraction of atria, how much volume of blood flows from atria to the ventricles through AV valves?
A. 30ml B. 25ml
C. 15ml D. 22ml
7. What is the time period for ventricular systole?
A. 0.3 sec B. 0.1 sec
3. 0.4 sec D. 0.5 sec
8. Which of the following statement is true?
A. Blood flows from lower pressure areas to higher pressure areas
B. EDV is about 140ml for heart rate of 75beats/min
C. left ventricle crosses pressure of 80mmHg to open the aorta
D. ventricular ejection is for 0.005 sec
9. Why the relaxation period is longer than contraction period?
A. more time for the cardiac muscles to relax before contraction
B. no specific reason to it
C. so that more forceful is next contraction
D. both A and C
10. What is the accurate formula of stroke volume?
A. EDV+ESV B. EDV*ESV
C. ESV-EDV D. none of the above
ANSWERS:-
1. events associated with each heart beat
2. 0.8 sec
3. all of the above
4. P wave
5. A – 2 B – 3 C – 1 D – 4
6. 25ml
7. 0.3 se
8. left ventricle crosses pressure of 80mmHg to open the aorta
9. Both A and C
10. none of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Reference:-Gerard J. Tortora -Principles of anatomy and physiology; edition twelfth ; page no.-: 7738-739.
The post Cardiac Cycle and Question Answer for NEET, GPAT, Nursing, Pharmacist and Lab Technician Exam appeared first on Gpatindia: Pharmacy Jobs, Admissions, Scholarships, Conference,Grants, Exam Alerts.
]]>