Notes of Scrotum Anatomy, Parts, and Function and MCQ on Reproductive system for NEET, GPAT, CUET, BSc, Nursing exams
Definition:
The scrotum is a pouch of skin located posterior to the penis, containing and supporting the testes. It plays a vital role in temperature regulation and protection of the testes.
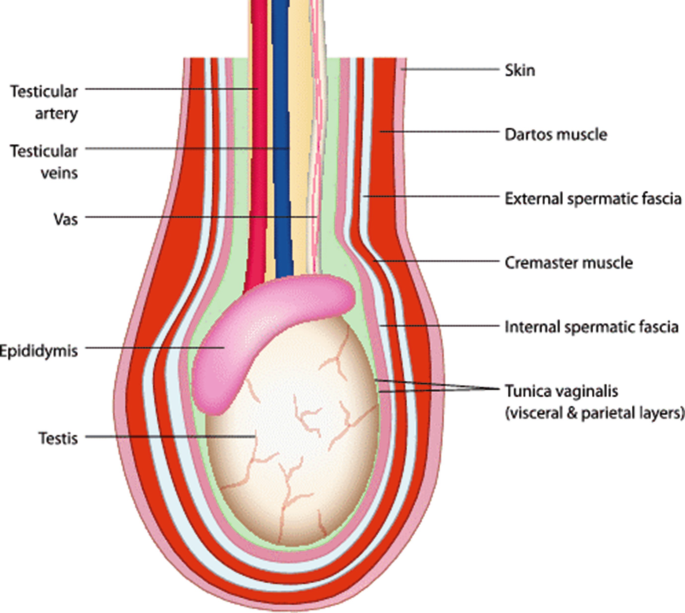
🧬 Anatomical Structure (Layers – from superficial to deep):
| Layer | Derived from | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Skin | Ectoderm | Contains sweat & sebaceous glands; dark and pigmented |
| Dartos muscle/fascia | Superficial fascia (Colles’) | Smooth muscle; wrinkles scrotal skin; regulates temperature |
| External spermatic fascia | External oblique aponeurosis | Protective covering of spermatic cord |
| Cremaster muscle & fascia | Internal oblique muscle | Raises/lowers testes (reflex) |
| Internal spermatic fascia | Transversalis fascia | Deepest covering of cord/testes |
| Tunica vaginalis | Peritoneum | Serous sac around testes (visceral and parietal layers) |
🧩 Parts of the Scrotum:
-
Median Raphe – External ridge dividing the scrotum into two compartments.
-
Scrotal Septum – Internally divides the scrotum into two sacs, each containing one testis.
-
Each Compartment Contains:
-
One testis
-
One epididymis
-
Part of the spermatic cord
-
⚙️ Functions of the Scrotum:
| Function | Details |
|---|---|
| Thermoregulation | Maintains temperature ~2–4°C below body temp for optimal spermatogenesis |
| Protection of Testes | Acts as a physical barrier and shock absorber |
| Sperm Maturation Environment | Supports testicular function for sperm development |
| Reflex Contraction | Cremaster and dartos muscles contract to regulate position & temperature |
✅ Quick Revision Chart:
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Skin | Protection, thermoregulation via sweat glands |
| Dartos Muscle | Wrinkling skin to conserve heat |
| Cremaster Muscle | Raises testes to body in cold/stress |
| Septum | Separates testes, prevents infection spread |
| Tunica Vaginalis | Reduces friction around testes |
📝 MCQs on Scrotum Anatomy
1. The dartos muscle in the scrotum is responsible for:
A. Producing testosterone
B. Raising the testis toward the abdomen
C. Wrinkling the scrotal skin
D. Supporting the spermatic cord
→ Correct Answer: C
2. The cremaster muscle is derived from which abdominal muscle?
A. Transversus abdominis
B. External oblique
C. Internal oblique
D. Rectus abdominis
→ Correct Answer: C
3. Which structure forms the innermost covering of the spermatic cord?
A. Dartos fascia
B. External spermatic fascia
C. Cremasteric fascia
D. Internal spermatic fascia
→ Correct Answer: D
4. The primary function of the scrotum is:
A. Hormone production
B. Urine excretion
C. Temperature regulation of testes
D. Formation of semen
→ Correct Answer: C
5. Which layer of the scrotum is directly derived from the peritoneum?
A. Dartos fascia
B. Cremaster muscle
C. Tunica vaginalis
D. Internal spermatic fascia
→ Correct Answer: C