Notes on Spermatogenesis, Chart of Various steps and MCQ for NEET, GPAT, CUET, UGC NET for Male Reproductive system
Spermatogenesis is the process by which spermatozoa (mature male gametes) are produced from spermatogonial stem cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
-
Begins at puberty under the influence of hormones (especially FSH and testosterone).
-
Takes approximately 64–74 days in humans.
-
Occurs in the seminiferous epithelium, with support from Sertoli cells.
📊 Chart: Stages of Spermatogenesis
| Stage | Cell Type | Ploidy | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
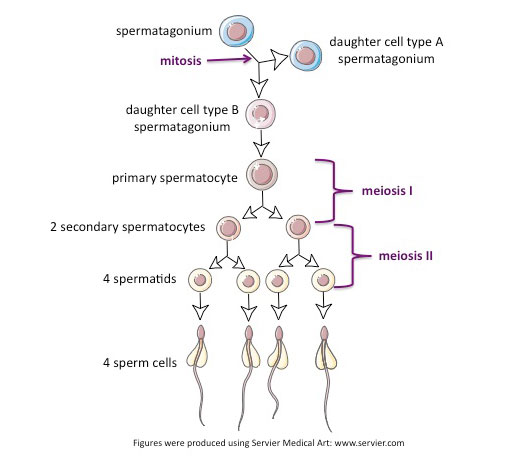
| 1. Spermatocytogenesis | Spermatogonia | Diploid (2n) | Mitotic division of stem cells into Type A (renewal) and Type B (committed) |
| Primary Spermatocyte | Diploid (2n) | Type B spermatogonia differentiate into primary spermatocytes | |
| 2. Meiosis I | Secondary Spermatocyte | Haploid (n) | Primary spermatocyte undergoes first meiotic division |
| 3. Meiosis II | Spermatids | Haploid (n) | Secondary spermatocytes divide into spermatids |
| 4. Spermiogenesis | Spermatozoa | Haploid (n) | Morphological transformation into mature sperm (head, tail, acrosome formation) |
🔬 Important Supporting Cells
| Cell Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Sertoli Cells | Nourish developing spermatogenic cells, form blood-testis barrier, produce inhibin |
| Leydig Cells | Produce testosterone in response to LH |
🧪 Hormonal Regulation
| Hormone | Produced by | Function |
|---|---|---|
| GnRH | Hypothalamus | Stimulates FSH and LH release from anterior pituitary |
| FSH | Anterior Pituitary | Acts on Sertoli cells to support spermatogenesis |
| LH | Anterior Pituitary | Stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone |
| Testosterone | Leydig cells | Promotes spermatogenesis and secondary sexual characteristics |
| Inhibin | Sertoli cells | Inhibits FSH release (negative feedback) |
❓ MCQs on Spermatogenesis
-
Which cell undergoes the first meiotic division in spermatogenesis?
A. Spermatogonium
B. Primary spermatocyte
C. Secondary spermatocyte
D. Spermatid
✅ Answer: B. Primary spermatocyte -
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating Sertoli cells?
A. LH
B. Testosterone
C. FSH
D. GnRH
✅ Answer: C. FSH -
Which of the following is the correct sequence of stages in spermatogenesis?
A. Spermatogonia → Spermatids → Secondary spermatocytes → Primary spermatocytes
B. Spermatogonia → Primary spermatocytes → Secondary spermatocytes → Spermatids
C. Spermatids → Secondary spermatocytes → Primary spermatocytes → Spermatozoa
D. Primary spermatocytes → Spermatids → Spermatogonia → Secondary spermatocytes
✅ Answer: B. Spermatogonia → Primary spermatocytes → Secondary spermatocytes → Spermatids -
Which cells form the blood-testis barrier?
A. Leydig cells
B. Sertoli cells
C. Spermatocytes
D. Epididymal cells
✅ Answer: B. Sertoli cells -
How many functional sperm cells are formed from one primary spermatocyte?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
✅ Answer: C. 4