Oxytocin & its function | Birth Hormone | Milk Ejection Hormone | Notes on Posterior Pituitary Hormone
Oxytocin Functions:
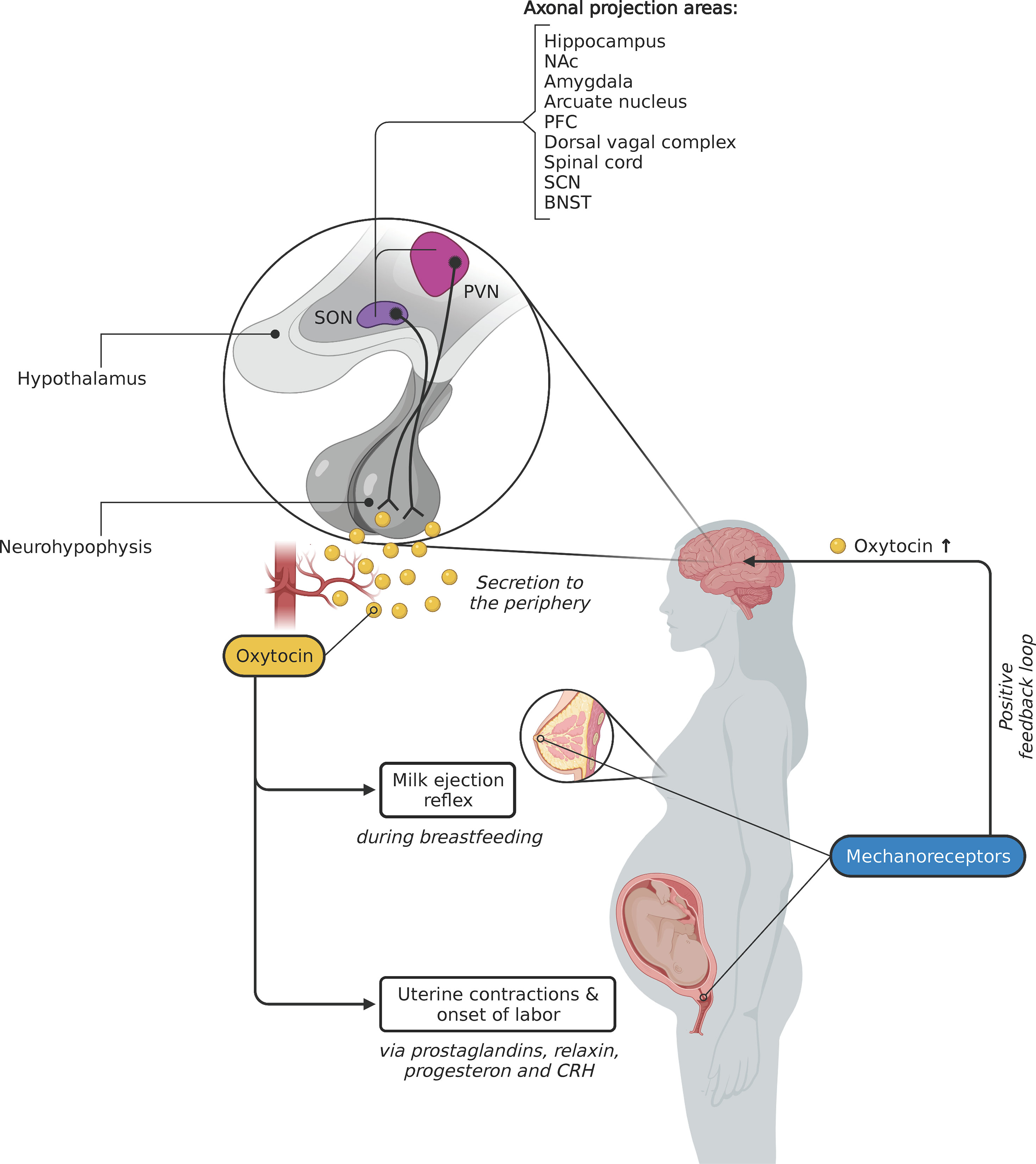
- During and after delivery of a baby, oxytocin affects two target tissues: the mother’s uterus and breasts.
- During delivery, oxytocin enhances contraction of smooth muscle cells in the wall of the uterus; after delivery, it stimulates milk ejection (“letdown”)
from the mammary glands in response to the mechanical stimulus provided by a suckling infant. - The function of oxytocin in males and in nonpregnant females is not clear. Experiments with animals have suggested that it has actions within the brain that foster parental caretaking behavior toward young offspring.
- It may also be responsible, in part, for the feelings of sexual pleasure during and after intercourse
Clinical Connection of Oxytocin
Years before oxytocin was discovered, it was common practice in midwifery to let a first-born twin nurse at the mother’s breast to speed the
birth of the second child. Now we know why this practice is helpful—it stimulates the release of oxytocin. Even after a single birth, nursing promotes expulsion of the placenta (afterbirth) and helps the uterus regain its smaller size. Synthetic OT (Pitocin) often is given to induce labor or to increase uterine tone and control hemorrhage just after giving birth.
Oxytocin Regulation
MCQ on Oxytocin
Q.1 OXYTOCIN is released by
A. Anterior Pituitary
B. Posterior Pituitary
C. BOTH
D. NONE
Q.2 OXYTOCIN is ALSO KNOWN as
A. Birth Hormone
B. Milk ejection Hormone
C. BOTH
D. NONE
Q.3 OXYTOCIN function is
A. help in uterus contraction
B. help in milk ejection
C. help in development of childcare behavior in parents
D. ALL
Q.4 During Labor pain OXYTOCIN provide
A. Positive feedback
B. Negative feedback
C. Both
D. None