Pilocarpus Biological Sources, Chemical Constituents, Uses, Morphology and MCQ,
PILOCARPUS
1. Biological sources :
• Pilocarpus is the genus having 13 species of plants within it .(pilocarpus genus).
• The biological source of pilocarpin is the leaves of closely related plants of this genus.
• The order of pilocarpin is rutaceae.
• The genus have various plants such as
- Pilocarpus jaborandi,
- Pilocarpus pennatifolius,
- Pilocarpus microphyllus,
- Pilocarpus selloanus,
- Pilocarpus trachylophus,
- Pilocarpus spicatus.
• The major biological source of pilocarpin is the leaves of Pilocarpus microphyllus.
• They also known as jaborandi, arruda do mato, arruda brava, jamguarandi , juarandi.
2. Morphological features :
• The leaves of this plant (p. microphyllus) are imparipinnate compound leaves with about 7 leaflets.
• In this plants, the leaflets are attached to the winged rachis which are almost glabrous .
• They have an occasional fruit.
• The leaflets are 2-5 cm long and 1-3 cm broad.
• The shape of leaflets are oval, symmetrical and have a petiolule 5-15 mm long, with a winged margin which passes imperceptibly into lamina.
• Some leaflets are asymmetrical, obovate and sessile in nature.
• The right side of leaves and left side of leaves are differenciate on the basis of the fact that the broader side each leaflet lies away from the rachis.
• The veins are pinnate and anastomose near the margin.
• The color is grayish – green to greenish – brown .
• The texture is brittle.
• When crushed , they have aromatic odour.
• Leaves of p. jaborandi are imparipinnate with 1-9 leaflets .
• Leaflets are 4-12 cm long and 2-4 cm broad.
• The height of the shrub is 4-5 feet.
• The bark is smooth.
• Flowers of this plant are small, thick, reddish-purple in color.
3. Chemical constituents :
• leaves of this plant contain 0.7-0.8 % of imidazole alkaloid,pilocarpin,isopilocarpin.
• They also have pilosin and isopilosin.
• They contain about 0.5 % of volatile oil.
• In volatile oil they composed of monoterpenes( for example, limonene, sabiene, alpha-pinene), sesquiterpenes(caryophyllene).
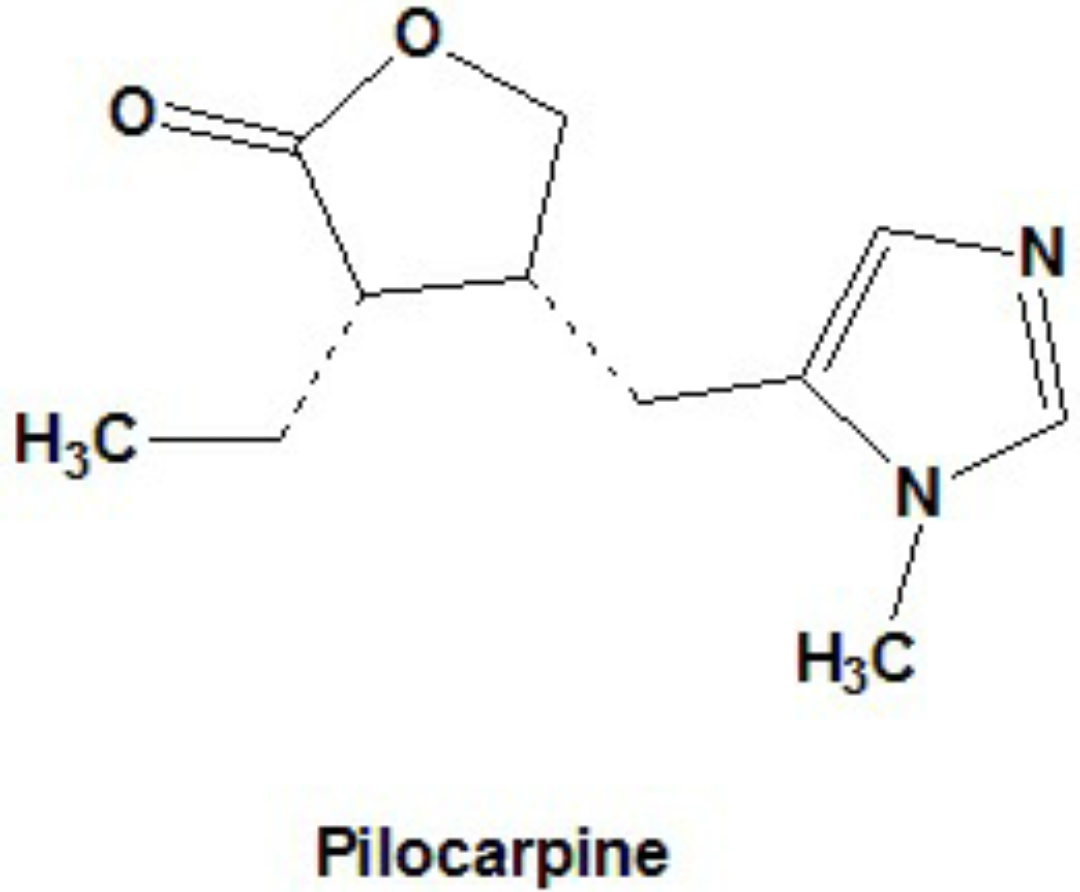
• Pilocarpine, the lactone of pilocarpic acid ,composed of glyoxaline nucleus .
• Pilocarpine is the most important chemical constituent of this pilocarpus.
4. Adulterants:
• It has been adulterated with species of piper, which are not pellucid-punctate, with laurus nobilis.
5. Uses:
• Due to its antagonistic nature to atropine, it stimulate the nerve ending paralysed by that drug and contract the pupil of the eye, this nature of this drug is used as powerful and rapid diaphoretic.
• It have property of inducing free salivation and stimulate gland(sweat gland) secretion mostly.
• It is also used in ophthalmic practice in the treatment of glaucoma.(causes contraction of pupil of eye)
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :
1. The biological source of pilocarpin
(a) Leaves of plant
(b) Flowers of plant
(c) Fruit of plant
(d) All of the above
2. The major biological source of pilocarpin
(a) Pilocarpus microphyllus
(b) Pilocarpus jaborandi
(c) Pilocarpus selloanus
(d) Pilocarpus trachylophus
3. Pilocarpin belongs to the order
(a) Asterales
(b) Scourfieldiales
(c) Rutaceae
(d) proteales
4. The leaflets of Pilocarpus microphyllus
(a) 5-6 cm long and 2-3 cm broad
(b) 6-7 cm long and 4-5 cm broad
(c) 10-11 cm long and 5-6 cm broad
(d) 2-5 cm long and 1-3 cm broad
5. The leaftets of P. microphyllus are
(a) Oval and symmetrical
(b) Lobed and asymmetrical
(c) Unifoliolate and symmetrical
(d) Lobed and symmetrical
6. Amount of imidazole alkaloid p. microphyllus plant contain
(a) 0.6-0.9 %
(b) 0.4-0.2%
(c) 0.7-0.3%
(d) 0.7-0.8%
7. P. microphyllus contain which Chemical constituents
(a) Pilosin
(b) Isopilosin
(c) Pilocarpin
(d) All of the above
8. P. microphyllus contain how much approximate Amount of volatile oil as a chemical constituent
(a) 0.4%
(b) 0.8%
(c) 0.5%
(d) 0.7%
9. Pilocarpin is used as
(a) In ophthalmic practice
(b) Secretion of glands such as sweat gland
(c) Induce salivation
(d) All of the above
10. Pilocarpin show adulteration with
(a) Glycoside
(b) Alkaloid
(c) Species of piper
(d) All of the above
ANSWERS:
1. Leaves of plant
2. Pilocarpus microphyllus
3. Rutaceae
4. 2-5 cm long and 1-3 cm broad
5. Oval and symmetrical
6. 0.7-0.8%
7. All of the above
8. 0.5%
9. All of the above
10. Species of piper
REFERENCE:
Evans W.C, Editors. Trease and Evans Pharmacognosy. New York, Saunders Elsevier, 2009. P. 407.