BUSULFAN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Chemical Structure and Therapeutic Uses
Busulfan
IUPAC nomenclature
Butane-1,4-diyl dimethanesulfonate
Classification
Busulfan falls under the category of alkyl sulfonate alkalyting agents.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 246.3 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 114-118°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 69000mg per litre at NTP |
| 5 | Octanol water partition coefficient | -0.52 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | No ring system |
Mechanism of Action
- After through SN2 mechanism, nucleophilic guanine N7 attacks the Carbon adjacent to mesylate leaving group.
- DNA-DNA intrastrand crosslinks formation takes place between guanine and adenine and between guanine and guanine base pairs.
- This prevents DNA replication
- Cell undergoes apoptosis [1]
Structural Activity Relationship
- Replacement of the sulfur atom by nitrogen will lower the toxicity.
- Binding with the amino group will increase the oral route availability of the drug
- The introduction of the substituted phenyl group will also increases the oral route availability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring introduction will increase the stability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring will further increase the distribution of the drug throughout the body.
- Benzimidazole ring can provide the local and faster action of the drug.
- Benzimidazol will further decrease the half life of compound. [2]
Methods of Synthesis
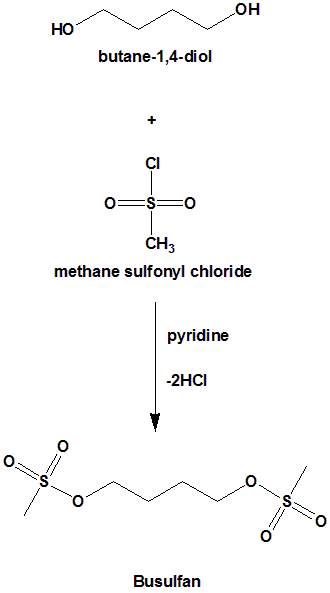
1,4-butanediol is reacted with methansulphonyl chloride to produce busulfan.
Therapeutic Uses
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia
- Blood disorders such as polysythemia vera and myeloid metaplasia
- Conditioning regimens prior to bone marrow transplant
Side Effects
- Most common side effect is low blood count
- Hyperuricaemia is common and pulmonary fibrosis is a specific adverse effect
- Other side effects includes nausea, vomiting, mouth sores, poor appetites, loss of fertility
- Discoloration of skin and skin rashes may occur in rare cases.
MCQs
Q.1 Butane-1,4-diyl dimethanesulfonate is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Thiotepa
b) Busulfan
c) Ifosfamide
d) Mechlorethamine
Q.2 Predict the incorrect statement related to Busulfan
a) It has an aziridine ring system
b) It is an example of class alkylating agents
c) It leads to apoptosis of the cell
d) Most common side effect is low blood count
Q.3 Match the following with respect to the drug busulfan
| i. introduction of substituted phenyl group | A. local and faster action of the drug |
| ii. binding of drug with amino group | B. increase the oral route availability |
| iii. introduction of aromatic ring | C. increase the stability of the drug |
| iv. introduction of benzimidazol ring | D. increase oral route availability |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-B, iii- C, iv-A
Q.4 Which amongst the following drugs shows its effect through alkylation of DNA strand?
a) Vincristine
b) Vinblastine
c) Busulfan
d) Flutamide
Q.5 Busulfan drug belongs to which class?
a) Nitrogen mustard alkalyting agent
b)Triazine alkalyting agent
c) Ethylinimine alkalyting agent
d) Nitrosoureas alkalyting agent
Q.6 Which of the following is not a side effect of Busulfan?
- a) Low blood count
- b) Hyperuricaemia
- c) Discoloration of skin
- d) Polysythemia
Q.7 Which among the following drugs is having least number of ring system in its structure-
a) Melphalan
b) Morphine
c) Busulfan
d) Cyclophosphamide
ANSWERS
1-b
2-a
3-d
4-c
5-c
6-d
7-c