Notes on Testes Structure and Function and MCQ on Male Reproductive system for NEET, GPAT, CUET, DMLT, Medical, Nursing and Pharmacy Exams
1. Overview
-
The testes (testicles) are the male gonads, responsible for producing sperm (spermatogenesis) and testosterone (primary male sex hormone).
-
Located in the scrotum, which maintains temperature ~2–3°C below body temp for optimal sperm development.
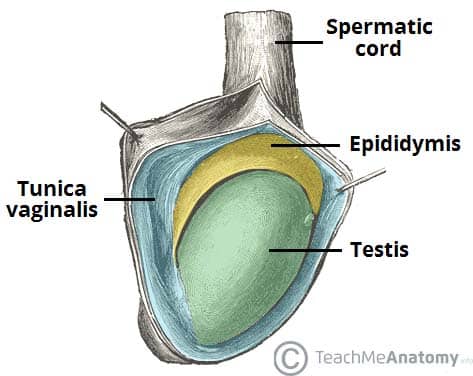
🧱 2. External Anatomy
| Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Tunica vaginalis | Outer serous membrane derived from peritoneum |
| Tunica albuginea | Tough fibrous capsule that encloses and divides testis into lobules |
| Scrotum | Pouch of skin and smooth muscle that houses the testes |
🧫 3. Internal Structure

Each testis contains:
-
~250–300 lobules, each with:
-
Seminiferous tubules – where spermatogenesis occurs
-
Interstitial (Leydig) cells – secrete testosterone
-
Sertoli cells – support and nourish developing sperm
-
🔹 Seminiferous Tubules
-
Lined by germinal epithelium
-
Contains:
-
Spermatogonia → develop into mature sperm
-
Sertoli cells → form the blood-testis barrier, provide nutrients, and secrete inhibin
-
🔹 Leydig Cells
-
Located in interstitial spaces
-
Stimulated by LH (luteinizing hormone)
-
Secrete testosterone
🔄 4. Sperm Transport Pathway
-
Seminiferous tubules
-
→ Straight tubules (tubuli recti)
-
→ Rete testis
-
→ Efferent ductules
-
→ Epididymis (sperm maturation and storage)
-
→ Vas deferens
🧠 5. Hormonal Control
| Hormone | Source | Action |
|---|---|---|
| FSH | Anterior pituitary | Stimulates Sertoli cells, spermatogenesis |
| LH | Anterior pituitary | Stimulates Leydig cells → testosterone |
| Testosterone | Leydig cells | Male secondary sex traits, spermatogenesis |
| Inhibin | Sertoli cells | Inhibits FSH release |
📌 Key Points
-
Sertoli cells = support spermatogenesis, blood-testis barrier
-
Leydig cells = testosterone production
-
Tunica albuginea = divides testes into lobules
-
Spermatogenesis occurs in seminiferous tubules
📝 MCQs on Testes Structure
1. Which of the following structures directly produces sperm?
A. Leydig cells
B. Rete testis
C. Sertoli cells
D. Seminiferous tubules
✅ Answer: D. Seminiferous tubules
2. Which hormone stimulates the Leydig cells to produce testosterone?
A. FSH
B. LH
C. Inhibin
D. GnRH
✅ Answer: B. LH
3. Which cells form the blood-testis barrier and support spermatogenesis?
A. Leydig cells
B. Spermatogonia
C. Sertoli cells
D. Myoid cells
✅ Answer: C. Sertoli cells
4. The fibrous capsule surrounding the testes is called:
A. Tunica vaginalis
B. Tunica mucosa
C. Tunica albuginea
D. Tunica media
✅ Answer: C. Tunica albuginea
5. What is the correct order of sperm flow out of the testis?
A. Rete testis → Seminiferous tubules → Efferent ductules
B. Seminiferous tubules → Rete testis → Efferent ductules
C. Epididymis → Rete testis → Seminiferous tubules
D. Efferent ductules → Seminiferous tubules → Rete testis
✅ Answer: B. Seminiferous tubules → Rete testis → Efferent ductules
6. Testosterone is secreted by:
A. Epididymis
B. Sertoli cells
C. Leydig cells
D. Spermatogonia
✅ Answer: C. Leydig cells