Pituitary Gland Hormones – Study Notes for NEET, CUET, REET, GPAT, UPSC exams
Overview:
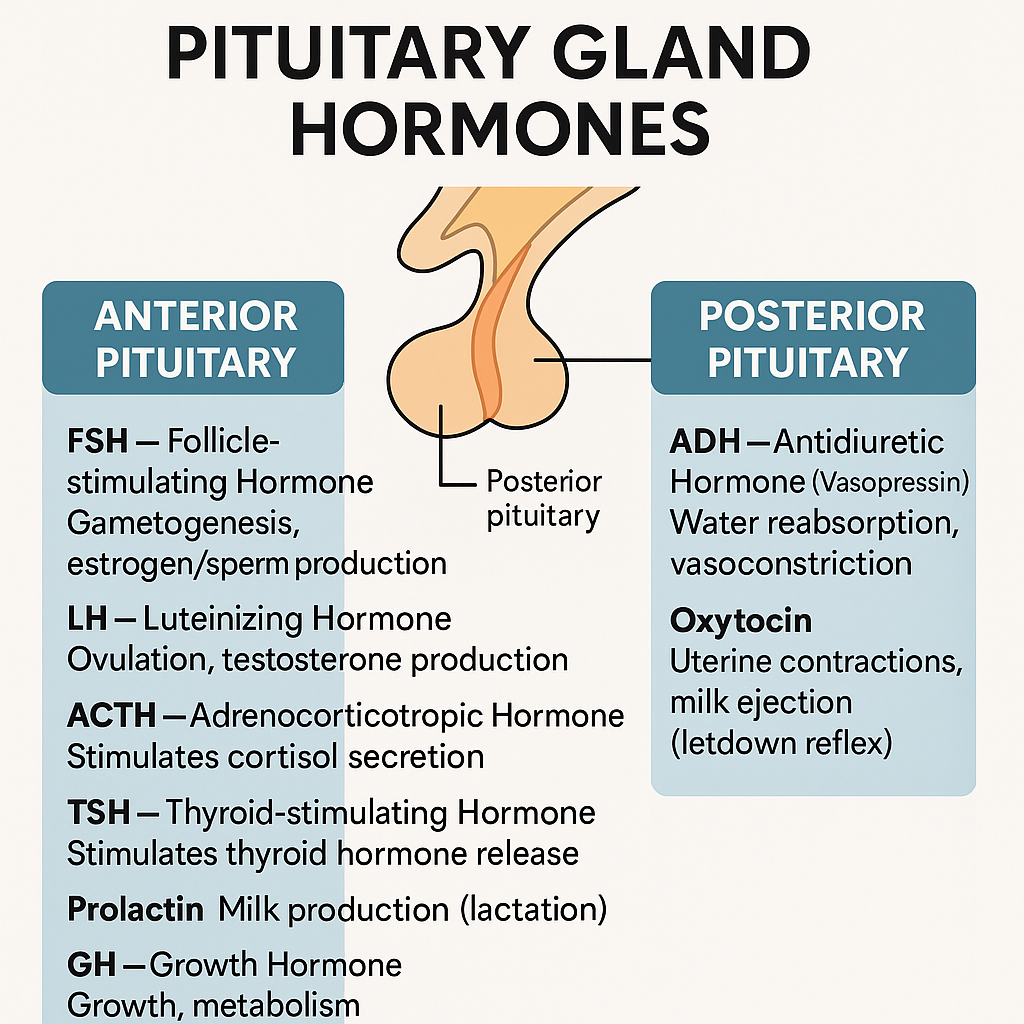
The pituitary gland (aka hypophysis) is the master endocrine gland, located at the base of the brain in the sella turcica. It is divided into:
-
Anterior pituitary (Adenohypophysis) – glandular
-
Posterior pituitary (Neurohypophysis) – neural
🔹 1. Anterior Pituitary Hormones (Adenohypophysis)
Mnemonic: “FLAT PEG” (FLAT = Tropic; PEG = Direct hormones)
| Hormone | Full Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| F | FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) | Gametogenesis, estrogen/sperm production |
| L | LH (Luteinizing Hormone) | Ovulation, testosterone production |
| A | ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) | Stimulates cortisol secretion |
| T | TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) | Stimulates thyroid hormone release |
| P | Prolactin | Milk production (lactation) |
| E | Endorphins | Pain relief (less emphasized) |
| G | GH (Growth Hormone) | Growth, metabolism |
✔️ Tropic hormones stimulate other endocrine glands
✔️ Direct hormones act on non-endocrine tissues
🔹 2. Posterior Pituitary Hormones (Neurohypophysis)
(Note: Synthesized in hypothalamus, stored/released by posterior pituitary)
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| ADH (Vasopressin) | Water reabsorption via V2 receptors (kidney), vasoconstriction via V1 |
| Oxytocin | Uterine contractions, milk ejection (letdown reflex) |
📌 Control by Hypothalamus:
-
Releasing hormones (e.g., TRH, GnRH, CRH, GHRH)
-
Inhibitory hormones (e.g., Somatostatin, Dopamine for prolactin)
🔬 Disorders:
| Hormone | Excess | Deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| GH | Gigantism (children), Acromegaly (adults) | Dwarfism |
| ACTH | Cushing’s disease | Addison’s disease (secondary) |
| TSH | Hyperthyroidism | Hypothyroidism |
| Prolactin | Galactorrhea, infertility | Poor lactation |
| ADH | SIADH | Diabetes insipidus |
✅ MCQs on Pituitary Gland Hormones
Participate in GPAT MOCK Test
🧠 Q1. Which of the following is NOT secreted by the anterior pituitary?
A. Growth Hormone
B. ADH
C. TSH
D. ACTH
Answer: ✅ B. ADH
(Secreted by the posterior pituitary)
🧠 Q2. Which anterior pituitary hormone is responsible for stimulating the adrenal cortex?
A. GH
B. TSH
C. ACTH
D. LH
Answer: ✅ C. ACTH
🧠 Q3. Excess Growth Hormone in adults leads to:
A. Gigantism
B. Acromegaly
C. Dwarfism
D. Marfan syndrome
Answer: ✅ B. Acromegaly
🧠 Q4. Which hormone is inhibited by dopamine?
A. Oxytocin
B. Prolactin
C. FSH
D. TSH
Answer: ✅ B. Prolactin
🧠 Q5. A patient with frequent urination and low urine osmolality likely has:
A. SIADH
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. Diabetes insipidus
D. Addison’s disease
Answer: ✅ C. Diabetes insipidus
(Due to ADH deficiency or resistance)