Black Pepper Biological Source, Morphology, Chemical Constituents, Uses
BLACK PEPPER
1.BIOLOGICAL SOURCES: Piper nigrum, also known as black pepper is the member of Piperaceae family. It is cultivated for getting its fruit which works as a spice and seasoning agent in many food items.
2.MORPHOLOGICAL FEATURES:
- It is a woody climber
- Height may reach upto 10m by using its aerial roots.
- Each slender spike having 40-50 blossoms of the small flowers.
- Their appearance changes to yellowish-red upon maturity, at that time, it bears a single seed [1].
- It is having drupe fruit which is called peppercorn having diameter equal to 5mm.
- Black pepper contains essential oils which is having the aromatic odour.
3.CHEMICAL CONSTITUENTS
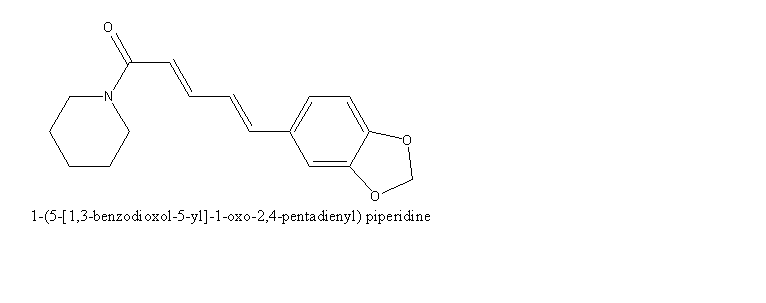
- Black pepper contains Piperine. Molecular formula for Piperine is C17H19NO3.
- The most important candidate of p. nigrum is piperine, its concentration varies in different species of p. nigrum. For example the amount of piperine in long pepper varies upto 1-2% and in white and black pepper, it varies upto 5-10% .
- The reason behind its very essential therapeutic use is that due to presence of piperine, it increases the bioavaibility of many nuitrients and drugs by inhibiting various metabolizing enzymes .thus it play an essential role in regulating obesity induced dyslipidemia.
- Piperine can be extracted from the unripe fruit of black pepper. It is present in the concentration of 6-9% in the black pepper. In addition to Piperine, it also contains beta-carotene, lauric-acid, palmitic acid, and pepper phellandrene.
- piperine is such a dominant constituent of p. nigrum that it is responsible for its pungency i.e. its strong odor and taste property. Also with addition of chavicine, which is an alkaloid with diastereomeric geometric isomers of piperine ,have a synergistic effect on its pungency.
- Essential compounds such as steroid, alkaloid, flavonoid ,phenolics ,chalcones and various lignans derivatives ,in addition with terpenes isolated from black pepper.
4.USES
In pharmaceutical sciences, its applications are as follows:
- It works as an analgesic, antipyretic and antioxidant.
- It utilizes as a rubefacient.
- It is also used as a preservative.
- It has application in cosmetic industries and also in the preparation of insecticides.
- It improves appetite, increases digestive power and also has antimicrobial activities.[2]
- It is used in the treatment of fever, colic, dysentery, piles and infections of worms.
- In reduces inflammatory responses by inhibiting lipopolysaccharides.
- Also used as a cure of cold, cough and dysponea and other diseases of the throat.
- It has a protective effect on the key liver enzymes. [3]
5.MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
A)Biological name of black pepper is
- Mangifera indica
- Piper nigrum
- Centella asiatica
- Pisum sativam
B)Black pepper is which type of fruit?
- Dried and unripe fruit
- Ripe and dried fruit
- It is a drupe fruit
- Both a) and c)
C)Which body function is improved by black pepper?
- Respiration
- Reproduction
- Digestion
- Urinary system
D)What is the size of the fruit of black pepper?
- 10mm
- 5mm
- 5inches
- 5cm
E)Types of roots present in pepper plant?
- Aerial roots
- Haustorial roots
- Epiphytic roots
- None of the above
F)Number of seeds fruit of black pepper contains at maturity mostly?
- Two seeds
- Single seed
- More than 5 seeds
- Sometime 4 seeds and sometimes 6 seeds
G)Main chemical constituent of black pepper?
- Piperine
- Omega 3 fatty acids
- Triglycerides
- L-citronellol
H)Molecular formula of piperine?
- C10H15NO3
- C17H19NO3
- C15H15NO3
- C2H5NO3
I)What are the therapeutical uses of black pepper
- Rubefacient
- Antioxidant
- Antipyretic
- All of the above
J)Concentration of piperine in black pepper?
- 15-18%
- 4-5%
- 10-11%
- 6-9%
ANSWERS:
A)Piper nigrum
B)Both a and c
C)Digestion
D)5mm
E)Aerial roots
F)Single seed
G)Piperine
H)C17H19NO3
I)All of the above
J)6-9%
REFERENCES
[1] Ravindran PN, Babu KN, Sasikumar B, Krishnamurthy KS. Botany and crop improvement of black pepper. InBlack pepper 2000 Aug 7 (pp. 43-164). CRC Press. [2] Singh G, Marimuthu P, Catalan C, DeLampasona MP. Chemical, antioxidant and antifungal activities of volatile oil of black pepper and its acetone extract. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 2004 Nov;84(14):1878-84. [3] Pino J, Rodriguez‐Feo G, Borges P, Rosado A. Chemical and sensory properties of black pepper oil (Piper nigrum L.). Food/Nahrung. 1990;34(6):555-60.