CHLORAMBUCIL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ and Chemical Structure
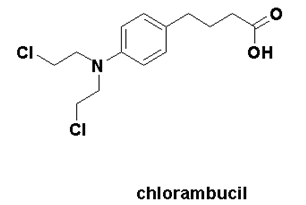
Chlorambucil
IUPAC nomenclature
4-[bis(2-chlorethyl)amino]benzenebutanoic acid
Classification
Chlorambucil can be classified as an alkalyting agent.
Physiochemical Properties
S. NO. |
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
| 1 | Molecular weight | 304.2g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | White colored granular powder powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 65-69 °C |
| 4 | Solubility | 7429 mg/L in water |
| 5 | Octanol water partition coefficient | 1.7 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | benzene |
Mechanism of Action
Chlorambucil interferes with DNA replication and damages the cell. It leads to the accumulation of cytosolic p53 which results in the cell cycle arrest and ultimately the apoptosis.
Chlorambucil shows its effect via three different ways:
- It alkylates the DNA which leads to the fragmentation of the DNA by the repair enzymes, and hence, DNA and RNA synthesis is affected.
- It can also forms the cross linkages in the DNA which will interfere with the DNA transcription.
- It will induce the mispairing of the nucleotides and hence, the translation activities will be affected. [1]
Structural Activity Relationship
- Replacement of the sulfur atom by nitrogen will lower the toxicity.
- 2-chloroethyl group is essential for the activity as the aziridine cation is formed by this only. Aziridine cation will attach with the alkylates of the DNA later.
- Binding with the amino group will increase the oral route availability o the drug
- The introduction of the substituted phenyl group will also increases the oral route availability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring introduction will increase the stability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring will further increase the distribution of the drug throughout the body.
- Benzimidazole ring can provide the local and faster action of the drug.
- Benzimidazole will further decrease the half life of compound. [2]
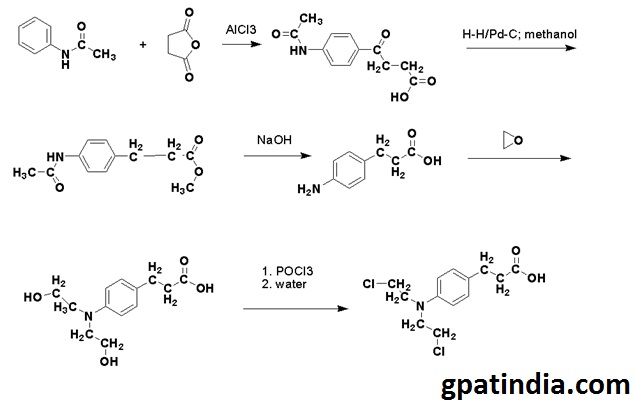
Methods of Synthesis
- Acetanilide is acylated by succinic anhydride.
- The keto group of the compound is then reduced by the hydrogen in a methanol solution using palladium on carbon as a catalyst.
- Methyl ester so formed is then treated with an alkali for hydrolyzing of amide and ester parts of the molecule.
- The compound so formed is then reacted with ethylene oxide and then by using the phosphoryl chloride, all the hydroxyl groups are replaced to give chlorambucil.
Therapeutic Uses
- Treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- polycythemia vera
- Trophoblastic neoplasms
- Ovarian carcinoma
- As an immunosuppressive drug for various autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. [3]
Side Effects
- Anemia
- Neutropenia
- Thrombocytopenia
- GIT distress
- Skin reactions
- Hepatoxicity
- Infertility
- Hair loss
- CNS disorders such as tremors, seizures confusion, etc.
MCQs
Q.1 Chlorambucil is a/an
a) alkylating agent
b) vinca alkaloid
c) antibiotic
d) progestin
Q.2 Chlorambucil produces its action through
a) alkalyting the DNA
b) introducing the cross linkages between the DNA
c) inducing the mispairing of the nucleotide
d) all of the above
Q.3 4-[bis(2-chlorethyl)amino]benzenebutanoic acid is the IUPAC name of
a) flutamide
b) finasteride
c) chlorambucil
d) busulfan
Q.4 chlorambucil can be synthesized from
a) acetanilide and phenol
b) acetanilide and succinic anhydride
c) succinic anhydride and methyl salicylate
d) methyl salicylate and phenol
Q.5 How many statements given below are true?
i. chlorambucil is given for the treatment of leukemia
ii. introduction of the aromatic ring will increase the stability of chlorambucil
iii. chlorambucil can help in the growth of hair
iv. 4-chlorethyl amino benzenebutanoic acid is the correct IUPAC name of chlorambucil
a). 1 statement is true
b). 2 statements are true
c).3 statements are true
d).4 statements are true
Q.6 which drugs are under the category of akalyting agents
a) topotecan and chlorambucil
b) chlorambucil and ifofsamide
c) mechlorethamine and methotrexate
d) methotrexate and topotecan
Q.7 Drug of choice for the treatment of Hodgkin’s disease is
a) methotreaxate
b) chlorambucil
c) ifofsamide
d) decarbazine
Answers
1- a
2- d
3- c
4- b
5- b
6- b
7- b
References
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of medical pharmacology. JP Medical Ltd; 2013 Sep 30.: p.822. [2] Pires J, Kreutz OC, Suyenaga ES, Perassolo MS. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROFILE AND STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP OF ALKYLATING AGENTS USED IN CANCER TREATMENT. [3] Wilson CO, Beale JM, Block JH. Wilson and Gisvold’s textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,; 2011: pp.360-362.