EPINEPHRINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
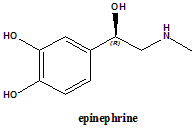
Epinephrine
IUPAC nomenclature
(R)-4-(1-Hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl)benzene-1,2-diol.
Classification
Epinephrine is a nonselective adrenergic agonist. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 183.2 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Colorless microcrystals, turn brownish on exposure to air |
| 3 | Melting point | 211.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Insoluble in ethanol; soluble in acetic acid |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Aryl ring |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Epinephrine acts on alpha-adrenergic receptors to minimize the vasodilation and increase the vascular permeability, which results in loss of intravascular fluids and hypotension.
- It acts on beta-adrenergic receptors and leads to the relaxation of the bronchial smooth muscles relaxation which results in the relief from bronchospasm, wheezing and dyspnea occurs during anaphylaxis.
- Epinephrine also relaxes the smooth muscles of bronchi and iris and is a histamine agonist, which find useful in the treatment of allergic reactions and related conditions.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Primary or secondary aliphatic amine separated by two carbons from a substituted benzene ring is essential for the high agonist activity.
- The hydroxyl substituted carbon must be in the R configuration for the maximal direct activity.
R1 substitution:
- When R1 is increased in size, activity of alpha receptors decreases and activity of the beta receptors increases
- Activity of both alpha and beta receptors is maximum when R1 is methyl group.
- Alpha agonist activity decreases when R1 is larger than methyl, and went negligible when R1 is isopropyl.
- Large lipophillic groups can afford compounds with alpha blocking activity.
- N-substituent provides selectivity for different receptors.
- Arylalkyl group can provide beta selectivity, increased cell penetration and increased lipophillicity for the longer duration of action.
R2 substitution:
- Ethyl group can eliminate the alpha activity of the drug.
- Erythrostero isomers have maximal activity.
- The additional methyl group makes the drug more selective for the alpha2
R3 substitution on the aromatic ring:
- 3’,4’-dihydroxy substituted benzene ring has poor oral activity.
- 3’, 5’-dihydroxy compounds are orally active.
- At least one of the groups is required which can form hydrogen bonds. And if only one group is present then it is preferred at 4’ position to retain the beta2
- If phenyl group has no phenolic substituent then it may act directly or indirectly.[2]
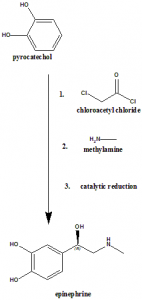
Method of synthesis
Epinephrine can be synthesized by reaction of pyrocatechol with chloroacetyl chloride and then reaction with methylamine, catalytic reduction and finally separation of racemic mixture with d-tartaric acid.
Therapeutic Uses
The drug used for the treatment of:
- Cardiac arrest
- Anaphylaxis
- Superficial bleeding
- Bronchospasm
- Low blood sugar
- Symptomic bradycardia
- Asthma
- Croup
- As a local anasthetic
Side Effects
Some of the common side effects of epinephrine are palpitations, pulmonary edema, hypertension, teremor, headache, panic attacks, arrhythmia and tachycardia.
It can also cause Takotsubo cardiomyopathy
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct IUPAC nomenclatures
| i. (R)-4-(1-Hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl)benzene-1,2-diol | A. Norepinephrine |
| ii. (R)-4-(2-amino-1-hydroxyethyl)benzene-1,2-diol | B. Phenylephrine |
| iii. (R)-3-[-1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]phenol | C. Epinephrine |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-B
b) i-A, ii-B, iii-C
c) i-C, ii-B, iii-A
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-C
Q.2 How many statements below are correct with respect to the SAR of the drug epinephrine?
- Primary or secondary aliphatic amine separated by two carbons from a substituted benzene ring is essential for the high agonist activity
- The hydroxyl substituted carbon must be in the L configuration for the maximal direct activity
- When R1 is increased in size, activity of alpha receptors increases and activity of the beta receptors decreases.
- Activity of both alpha and beta receptors is minimum when R1 is methyl group.
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Q.3 Number of chiral centers in Epinephrine is?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 Epinephrine can be synthesized from?
a) Pyrocatechol
b) Aniline
c) Corticosterone
d) None of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug epinephrine?
a) Anaphylaxis
b) Superficial bleeding
c) Bronchospasm
d) All of the above
Q.6 The correct classification of the drug epinephrine can be?
a) Selective adrenergic agonist
b) Nonselective adrenergic agonist
c) Selective adrenergic antagonist
d) Nonselective adrenergic antagonsit
Q.7 How many number of rings are found in the chemical structure of the drug……
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b (1st and 4th statements are correct)
3-b
4-a
5-d
6-b
7-b
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 340 [2] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 348-352