MECHLORETHAMINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ and Chemical Structure
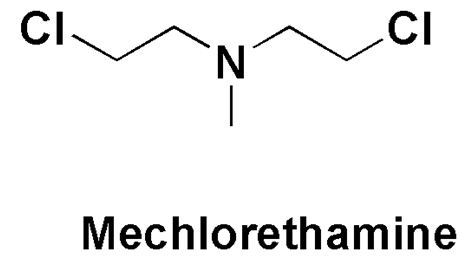
Mechlorethamine
IUPAC nomenclature
2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
Classification
Mechlorethamine falls under the category of Nitrogen mustard alkalyting agents.
Physiochemical Properties
S. NO. |
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|
| 1 | Molecular weight | 156.05 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | Mobile liquid, pale yellow when fresh |
| 3 | Melting point | 109-110°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very slightly soluble in water |
| 5 | Dissociation constant (pKa) | 6.43 at 25°C |
| 6 | Presence of ring | No rings present |
Mechanism of Action
The drug binds with the Guanine nitrogen base pair and this results in the fragmentation of the DNA by the repair enzymes. This leads to the prevention of the DNA synthesis. This also affects the RNA transcription in the cells.[1]
Structural Activity Relationship
- Replacement of the sulfur atom by nitrogen will lower the toxicity.
- 2-chloroethyl group is essential for the activity as the aziridine cation is formed by this only. Aziridine cation will attach with the alkylates of the DNA later.
- Binding with the amino group will increase the oral route availability o the drug
- The introduction of the substituted phenyl group will also increases the oral route availability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring introduction will increase the stability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring will further increase the distribution of the drug throughout the body.
- Benzimidazole ring can provide the local and faster action of the drug.
- Benzimidazol will further decrease the half life of compound. [2]
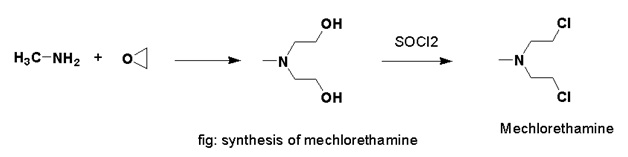
Methods of Synthesis
Ethylene oxide is treated with methanamine. Product so formed is further treated with SOCl2 to obtain mechlorethamine.
Therapeutic Uses
- Treatment of prostatic cancer by modification of the drug into estrogen analogues
- During the world wars, it was used in the form of mustard gas which was powerful and vesicant.
- It was also used for the treatment of Hodgkin’s disease, lymphosarcoma, chronic myelocytic leukemia, polycythemia vera, brochgenic carcinoma.
- It is very powerful and thus, it is usually referred for oral administration only, but where it is necessary, it is directly injected to the tumor cells.
Side Effects
- It is very toxic and should not be administered to the pregnant women.
- May produce the acute effects like nausea, vomiting ad hemodynamic changes.
- When the drug is administered intravenously, it may produce sloughing.
- On longer administration, the level of RBCs, WBCs and blood platelets may decrease, which suppresses the immune system of the patient and the patient will beat higher risk of other diseases.
- When any surface of the body/skin comes in contact with the drug, irritation starts and the sensory ability of that organ may be damaged. [3]
MCQs
Q.1 What is the correct IUPAC name of mechlorethamine?
a)2-Chloro-N,N-bis-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
b)3-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
c)2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
d)2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethylmethane-1-amine
Q.2 Mechlorethamine produces action through?
a)cell membrane destruction
b)DNA damage
c)cell wall dissolution
d)inhibiting the ETC cycle
Q.3 Match the following with respect to the drug mechlorethamine (nitrogen mustard alkylating agents)-
| i. introduction of substituted phenyl group | A. local and faster action of the drug |
| ii. binding of drug with amino group | B. increase the oral route availability |
| iii. introduction of aromatic ring | C. increase the stability of the drug |
| iv. introduction of benzimidazol ring | D. increase oral route availability |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
c) i-D, ii-C, iii-A, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-B, iii- C, iv-A
Q.4 What is the starting product for the synthesis of mechlorethamine?
a) ammonia and thiazide
b) methanol and ethane
c) ethylene oxide and methanamine
d)ammonia and methanamine
Q.5 Mechloroethanamine is used for the treatment of
a) acute gout
b) prostatic cancer
c) leukemia
d) cardiac arrhythmia
Q.6 Which amongst the following compounds were used in the formulation of war gases.?
a) nitrogen gas
b) mechlorethamine
c) pyridine
d) chlorine gas
Q.7 Which type of ring is present in the Mechlorethamine?
a) indole ring
b) benzene ring
c) cycloalkane
d) none of the above
ANSWERS
1-d
2-b
3-d
4-c
5-b
6-b
7-d
References
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of medical pharmacology. JP Medical Ltd; 2013 Sep 30.: p.822. [2] Pires J, Kreutz OC, Suyenaga ES, Perassolo MS. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROFILE AND STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP OF ALKYLATING AGENTS USED IN CANCER TREATMENT. [3] Wilson CO, Beale JM, Block JH. Wilson and Gisvold’s textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,; 2011: pp.360-362.