THIOTEPA Synthesis, SAR, MCQ and Chemical Structure
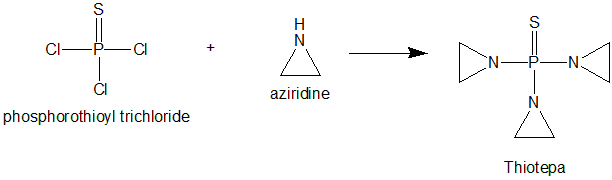
Thiotepa
IUPAC nomenclature
1,1′,1′′-Phosphorothioyltriaziridine
Classification
Thiotepa falls under the category of ethylenimine alkalyting agents.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 189.22 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 51.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 19 mg per 100 ml at NTP |
| 5 | Octanol water partition coefficient | 0.53 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Aziridine rings |
Mechanism of Action
- After administration, thiotepa converts into ethylenimine groups.
- Ethylenimine groups attaches with N7 position of guanine base pair of DNA
- This will induce the cross linkages between the ds-DNA.
- This will further interferes with the processes such as DNA replication and transcription
- This will result in the inhibition of the cell growth and apoptosis of the cell. [1]
Structural Activity Relationship
- Replacement of the sulfur atom by nitrogen will lower the toxicity.
- 2-chloroethyl group is essential for the activity as the aziridine cation is formed by this only. Aziridine cation will attach with the alkylates of the DNA later.
- Binding with the amino group will increase the oral route availability of the drug
- The introduction of the substituted phenyl group will also increases the oral route availability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring introduction will increase the stability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring will further increase the distribution of the drug throughout the body.
- Benzimidazole ring can provide the local and faster action of the drug.
- Benzimidazol will further decrease the half life of compound. [2]
Methods of Synthesis
- Ethylineimine is reacted with thiophosphoryl chloride in presence of triethyamine in dry benzene as a solvent.
Therapeutic Uses
- Breast cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Hodgkin’s lymphomas
- Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas
- Superficial tumors of bladder
Side Effects
- Most common side effect is low blood count
- Other side effects includes nausea, vomiting, mouth sores, skin allergies and bladder irritation.
MCQs
Q.1 Correct IUPAC name for thiotepa can be?
a) 1,1′,2-Phosphorothioyltriaziridine
b) 1,2,2′-Phosphorothioyltriaziridine
c) 1,1′,1′′-Phosphorothioyltriaziridine
d) 1,2,3-Phosphorothioyltriaziridine
Q.2 Predict the incorrect statement related to Thiotepa
a) It is highly toxic
b) It is seldom used now
c) It needs to be converted into its active intermediate to show its effects
d) It has aziridine rings in it
Q.3 Oral rout availability of Thiotepa can be increased through
a) Binding with amino group
b) Binding with benzimidazole ring
c) Binding with substituted phenyl group
d) Both a) and c)
Q.4 Thiotepa shows its effect through
a) Alkylation of guanine base pair of DNA
b) Altering the cell membrane structure of cancerous cells
c) Inhibiting the mitochondria to produce energy
d) Rupturing the nuclear membrane
Q.5 Classification of Thiotepa is
a) Nitrogen mustard alkalyting agent
b)Triazine alkalyting agent
c) Ethylinimine alkalyting agent
d) Nitrosoureas alkalyting agent
Q.6 An important side effect of Thiotepa is
a) Rhabdomyosarcoma
b) Ovarian cancer
c) Low blood cell count
d) Bladder cell apoptosis
Q.7 Number of aziridine rings present in Thioptepa?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 0
For More Standard and Quality Question Bank you can Join Our Test Series Programme for GPAT, NIPER JEE, Pharmacist Recruitment Exam, Drug Inspector Recruitment Exams, PhD Entrance Exam for Pharmacy: Click Here
ANSWERS
1-c
2-c
3-d
4-a
5-c
6-c
7-c
References
[1] Van Maanen MJ, Smeets CJ, Beijnen JH. Chemistry, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of N, N′, N′′-triethylenethiophosphoramide (ThioTEPA). Cancer treatment reviews. 2000 Aug 1;26(4):257-68. [2] Pires J, Kreutz OC, Suyenaga ES, Perassolo MS. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROFILE AND STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP OF ALKYLATING AGENTS USED IN CANCER TREATMENT. [3] Wilson CO, Beale JM, Block JH. Wilson and Gisvold’s textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,; 2011: pp.360-362.