TRICHLORMETHIAZIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
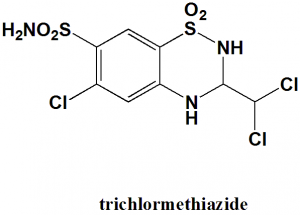
Trichlormethiazide
IUPAC nomenclature
6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[e] [1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide.
Classification
- Thiazide diuretic
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 380.7 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 270oC |
| 4 | Solubility | 1 gm is soluble in 10 ml acetone. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.62 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Benzothiazine |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Trichlormethiazide prevents active chloride reabsorption at the early distal tubule through the sodium chloride contransportor which results in an increase in the excretion of sodium, chloride and water from the body.
- The drug also binds with thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl transportor and prevents sodium ion transport across the renal tubular epithelium. This increases the potassium excretion through Na-K exchange mechanism.
- It can also mediate its actions on carbonic anhydrase in the smooth muscle or on the large-conductance KCa channel found in smooth muscle.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of thiazide diuretics can be summarized as:
- Chlorothiazide is the simplest member of the series.
- Hydrogen atom at the 2-N is most acidic due to presence of electron-withdrawing group.
- Sulfonamide group at C-7 position provides additional acidity to the drug.
- Electron withdrawing group is essential at position 6 for diuretic activity of the drug.
- Substitution on hydrogen at 6 position gives little diuretic activity, whereas, substitution with chloro and trifluoromethyl groups gives highly active compounds.
- Substitution of electron donating group at position 6 significantly reduces the diuretic activity.
- Replacement or removal of sulfonamide groups from position 7 significantly reduces the diuretic activity.
- Saturation of the double bond to give 2,4-dihydro derivative are 10-folds more active than the unsaturated compounds.
- Substitution of a lipophillic group at 3 position increases the potency.
- Substitution with the entities such as haloalkyl, aralkyl or thioether gives compounds with longer duration of action due to increased lipid solubility.
- Alkyl substitution at the 2-N position can increase the action duration. [1]
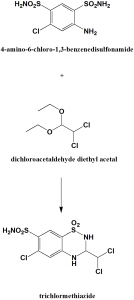
Method of synthesis
Reaction of 4-amino-6-chloro-1,3-benzenedisulfonamide with dichloroacetaldehyde diethyl acetal produces trichlormethiazide.
Medicinal Uses
Trichlormethiazide is used for:
- Reducing edema
- Treatment of hypertension
Side Effects
Side effects of trichlormethiazide are:
- Nausea
- Blurred vision
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Low blood sodium and potassium levels
- Loss of appetite
- Stomach cramps
- Photosensitivity
- Muscle cramps
- Allergic reactions
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Trichlormethiazide?
a) 6-fluoro-1,1-dioxo-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
b) 6-Chloro-3-(dichloromethyl)-1,1-dioxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[e] [1,2,4]thiadiazine-7-sulfonamide
c) 1-[(4-Chlorophenyl)(phenyl)methyl]-4-methylpiperazine
d) (RS)-3-ethyl 5-methyl 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-2,6-dimethyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are correct related to the SAR of thiazide diuretics?
I. Substitution on hydrogen at 6 position gives little diuretic activity, whereas, substitution with chloro and trifluoromethyl groups gives highly active compounds.
II. Substitution of electron donating group at position 6 significantly reduces the diuretic activity.
III. Replacement or removal of sulfonamide groups from position 7 significantly reduces the diuretic activity.
a) I, III
b) II, III
c) I, II
d) I, II, III
Q.3 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of trichlormethiazide is?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 0
Q.4 Side effects of drug Trichlormethiazide is/are?
a) Fatigue
b) Loss of appetite
c) Muscle spasms
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct Octanol water partition coefficient-
| i. Trichlormethiazide | A. 1.42 |
| ii. Methyclothiazide | B. 1.9 |
| iii. Omeprazole | C. 0.62 |
| iv. Polythiazide | D. 2.23 |
a) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
Q.6 An example of drug from class Thiazide diuretics?
a) Trichlormethiazide
b) Amplodipine
c) Hydroxyamphetamine
d) Pseudoephedrine
Q.7 The type of ring system found in the structure of drug Trichlormethiazide is?
a) Dihydroopyridine
b) Benzothiazine
c) Naphthalene
d) Pyrimidine
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-b
2-a
3-b
4-d
5-d
6-d
7-b
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Williams DA, editors. Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012 Jan 24. [2] DAS 1 147 233 (Ciba; appl. 4.10.1960; USA-prior. 8.10.1959, 16.10.1959).