5-FLOUROURACIL (5-FU) Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Therapeutic Uses, Chemical Property
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)
IUPAC nomenclature
5-Fluoro-1H,3H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione
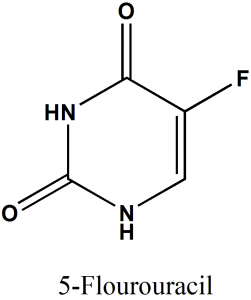
Classification
5-Fluorouracil falls under the category of pyrimidine antagonist antimetabolite.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 130.08 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 283 °C |
| 4 | Solubility | Sparingly soluble in water.
Slightly soluble in alcohol. Soluble in methanol-water mixtures. |
| 5 | Octanol water partition coefficient | -0.89 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Pyrimidine ring system |
Mechanism of Action
i. 5-Fluororacil binds with thymidylate synthase enzyme to form a ternary complex system.
ii. Formation of thymidylate form uracil is inhibited due to the complex formation.
iii. In the absence of thymidylate, DNA and RNA synthesis are inhibited.
iv. The drug can also get inserted in the place of UTP in the RNA, which result in the inhibition of the protein synthesis in the cell.
v. This overall mechanism leads o the death of the cell. [1]
Structural Activity Relationship
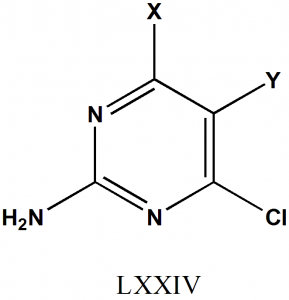
- The molar refractivity of the Y substituent will produce increase in the activity of drug.
- Substituent at Y with (CH2)3NRiR2 with R2 = COCH3, COC6H5, or COOCeH5 will produce a negative effect on the activity of the drug.
- SH at 4th position will increase the activity of drug.
- Substituent which are bulky in nature at Y position will produce negative effect on activity due to steric hindrance.
- Electron withdrawing groups at 5th position will increase the activity of drug. [2]
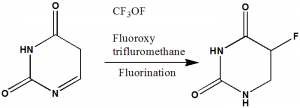
Methods of Synthesis
Fluorine is reacted with Uracil to give 5-Fluouracil.
Therapeutic Uses
- Colon anal and rectal cancer
- Breast cancer
- GIT cancers
- Bladder and Hepatobiliary cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Thymic cancer
- Squamous cell and neuroendocrine tumors.
Side Effects
- Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, mouth sores, photophobia, low blood counts and taste changes.
- Less common side effects include skin reactions, hair thinning, discoloration of nails and PPE.
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct IUPAC nomenclatures
| i. 6-MP | A. 3,7-dihydropurine-6-thione
|
| ii. 6-TG | B. 5-Fluoro-1H,3H-pyrimidine-2,4-dione
|
| iii. 5-FU | C. 3,7-dihydropurine-6-thione
|
| iv. Mtx | D. (2S)-2-[[4-[(2,4-diaminopteridin-6-yl)methyl-methylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid
|
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-C, ii-D, iii-B, iv-A
d) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
Q.2 How many statements below are true with respect to the SAR of the drug 5-Flourouracil?
- SH at 4th position will decrease the activity of drug.
- Substituent which are bulky in nature at Y position will produce negative effect on activity due to steric hindrance.
- Electron withdrawing groups at 5th position will increase the activity of drug.
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.3 The drug 5-Flourourcil is found in which form?
a) Yellow liquid form
b) White buffy powder form
c) Reddish brown crystal form
d) White crystalline form
Q.4 Which is the correct statements with respect to the method of synthesis of the drug 5-Flourouracil?
a) Florine is reacted with uracil
b) Florine is reacted with benzil
c) Chlorine is reacted with uracil
d) Chlorine is reacted with benzil
Q.5 Which amongst the following is NOT a therapeutic use of drug 5-FU?
a) Colon cancer treatment
b) Anal cancer treatment
c) GIT cancer treatment
d) Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment
Q.6 The correct classification of the drug 5-Flourouracil can be?
a) Nitrogen mustard
b) Vinca alkaloids
c) Antiandrogens
d) Antimetabolite
Q.7 How many number of rings are found in the chemical structure of the drug 5-Flourouracil?
a) 3
b) 2
c) 1
d) 0
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-d
4-a
5-d
6-a
7-c
REFERENCES
[1] Parker WB, Cheng YC. Metabolism and mechanism of action of 5-fluorouracil. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 1990 Jan 1;48(3):381-95. [2] Gupta SP. Quantitative structure-activity relationship studies on anticancer drugs. Chemical reviews. 1994 Sep;94(6):1507-51.