BICALUTAMIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
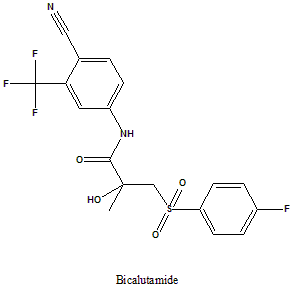
Bicalutamide
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-N-[4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-[(4-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl]-2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanamide.
Classification
Bicalutamide is an antiandrogen. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 430.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | Fine white to off white powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 191-193°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in acetone and tetrahydrofurane; insoluble in water. |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.5 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Aryl rings present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Bicalutamide competes with androgen for androgen binding receptors.
ii. The action of androgen of adrenal and testicular origin is blocked.
iii. Inhibition of growth of normal and malignant prostatic tissue.
Structural Activity Relationship
- 2- hydroxyl derivative is an active metabolite.
- Electron-withdrawing substituents in the aromatic rings increases the activity.
- A branched alkyl chain alpha to the amide carbonyl have increased activity.
- Compounds with two electron-withdrawing substituents on the aromatic gave a better potency than the one substituent.
- When the CF3 group was introduced at the C2 position of anilide having only one electronwithdrawing substituent, antiandrogenic activity of compound increased by five-fold.
- Replacement of the anilide by the alkene gave weakly active compounds. [3]
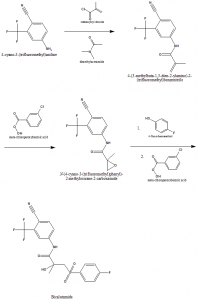
Method of synthesis
i. 4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline undergoes reaction with methacryloyl chloride in presence of dimethylacetamide to give 4-(3-methylbuta-1,3-dien-2-ylamino)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.
ii. Above formed compound is then reacted with meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid to give N-(4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2-methyloxirane-2-carboxamide.
iii. Latter compound is recated with 4-fluorobenzenethiol and then with meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid to give Bicalutamide.
Therapeutic Uses
The drug used for the treatment of:
- Advanced prostate cancer at stage D2, when there is evidence of metastases.
Side Effects
- Common side effects of bicalutamide include impotency, decreased libido, breast pain, swelling of breast and hot flashes.
- Less common side effects are increased in blood tests measuring liver functions, nausea, diarrhea and constipation.
MCQs
Q.1 Casodex is the trade name of which drug?
a) Flutamide
b) Bicalutamide
c) Finasteride
d) Letrozole
Q.2 Appearance of bicalutamide is?
a) Off white to white powder
b) Black charcoal like powder
c) Yellow crystalline powder
d) None of the above
Q.3 The drug Bicalutamide shows its action through?
a) Inhibition of purine synthesis
b) Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis
c) Blocking the androgen binding receptors
d) Through alkylation of the DNA of cells.
Q.4 The correct order for the synthesis of the drug
I. Reaction with 4-fluorobenzenethiol.
II. Reaction with meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid.
III. 4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline undergoes reaction with methacryloyl
IV. Reaction with meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid
a) III – II – I – IV
b) III – I – II – IV
c) I – II – IV – III
d) III – IV – I – II
Q.5 Predict the incorrect statements from the following with respect to the classification of the drug.
I. Methotrexate is a pyrimidine antagonist
II. Cytarabine is a purine antagonist.
III. Bicalutamide is an aromatase inhibitor.
IV. Thiotepa is an antibiotic drug.
a) I, II & IV
b) I, III & IV
c) I, II, III & IV
d) I & IV
Q.6 Bicalutamide is used for?
a) Treatment of Advanced prostate cancer
b) Treatment of Tuberculosis
c) Prevention of rabies
d) None of the above
Q.7 Number of rings present in structure of Bicalutamide is?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
ANSWERS
1-b
2-a
3-c
4-a
5-c
6-a
7-c
REFERENCES
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 6thEdn. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. 2008: 820. [2] Furr BJ, Tucker H. The preclinical development of bicalutamide: pharmacodynamics and mechanism of action. Urology. 1996 Jan 1;47(1):13-25. [3] Singh SM, Gauthier S, Labrie F. Androgen receptor antagonists (antiandrogens) structure-activity relationships. Current medicinal chemistry. 2000 Feb 1;7(2):211-47.