CLONIDINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
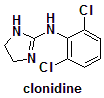
Clonidine
IUPAC nomenclature
N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-4,5–1H-imidazol-2-amine.
Classification
Clonidine is an α2-Adrenergic agonist. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 230.09 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in solid crystal form |
| 3 | Melting point | 130°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Insoluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.59 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Imidazoline ring |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- The α2-adrenoceptor is coupled with the G-proteins G0 and G1. G1 inhibits the adenyl cyclase and activates opening of a potassium channel that causes hyperpolarization.
- Clonidine also reduces the binding affinity of the G-protein for the GDP, by binding with the α2-adrenoceptors.
- Hypnotic effects of the clonidine are due to stimulation of α2-adrenoceptos in the locus cioeruleus.
- Clonidine is also helpful in reduction of transmission of the pain signals at te spine.
- In the medulla, clonidine can affect the regulation of the blood pressure in the ventromedial and rostral-ventrolateral areas of the medulla.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Primary or secondary aliphatic amine separated by two carbons from a substituted benzene ring is essential for the high agonist activity.
- The hydroxyl substituted carbon must be in the R configuration for the maximal direct activity.
R1 substitution:
- When R1 is increased in size, activity of alpha receptors decreases and activity of the beta receptors increases
- Activity of both alpha and beta receptors is maximum when R1 is methyl group.
- Alpha agonist activity decreases when R1 is larger than methyl, and went negligible when R1 is isopropyl.
- Large lipophillic groups can afford compounds with alpha blocking activity.
- N-substituent provides selectivity for different receptors.
- Arylalkyl group can provide beta selectivity, increased cell penetration and increased lipophillicity for the longer duration of action.
R2 substitution:
- Ethyl group can eliminate the alpha activity of the drug.
- Erythrostero isomers have maximal activity.
- The additional methyl group makes the drug more selective for the alpha2
R3 substitution on the aromatic ring:
- 3’,4’-dihydroxy substituted benzene ring has poor oral activity.
- 3’, 5’-dihydroxy compounds are orally active.
- At least one of the groups is required which can form hydrogen bonds. And if only one group is present then it is preferred at 4’ position to retain the beta2
- If phenyl group has no phenolic substituent then it may act directly or indirectly.[2]
Method of synthesis
i. 2,3-dichloroanilline reacts with ammonium thiocyanate to give thiourea.
ii. Thiourea is treated with methy iodide to give S-methylthiouronium salt.
iii. Latter compound is treated with ethylenediamine to give clonidine.

Therapeutic Uses
The drug used for the treatment of:
- High blood pressure
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- Menopausal flushing
- Diarrhea
- Some pain conditions
Side Effects
Common side effects of clonidine are dizziness, hypotension, skin reactions, fatigue, headaches, dry mouth, erectile dysfunction, pain below ear, weight changes rashes, malaise, nausea and vomiting.
Some of the less frequent side effects are urticaria, pruritus, Raynaud’s phenomenon, sinus bradycardia, paresthasia, nightmare, hallucination, delusions, gynaecomastia and nasal dryness.
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug Clonidine-
| i. When R1 increase in size | A. Activity of both α ns ß receptors are at maximum |
| ii. When R1 is methyl group | B. Increase in cell penetration |
| iii. Arylalkyl group substitution at R1 | C. Elimination of the α-activity |
| iv. Ethyl group at R2 substitution | D. Activity of α-receptors decreases |
a) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-A, ii-B, iii-D, iv-C
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- “ N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-4,5–1H-imidazol-2-amine” is for Clonidine
- “4-(2-Aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol” is for Dopamine
- “(RS)-4-(2-{[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butan-2-yl]amino}ethyl)benzene-1,2-diol” is for Dobutamine
- “ N-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amine” is for Methyldopa
a) TTFT
b) TTTF
c) FFTF
d) TFTF
Q.3 Number of chiral centers in the structure of clonidine is?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 Clonidine produces its action through binding with?
a) α1-adrenergic receptors
b) α2-adrenergic receptors
c) ß1– adrenergic receptors
d) ß2 – adrenergic receptors
Q.5 Which amongst the following is not a therapeutic use of drug Clonidine?
a) Treatment of low blood pressure
b) treatment of Attention Deficit disorder
c) Treatment of menopausal flushing
d) None of the above
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Vincristine: Vinca alkaloids
II. Flutamide :Nitrosaureas
III. Clonidine: Selective α2-adrenergic agonist
IV. Epinephrine: ß-adrenergic antagonist
a) II, IV
b) I, III
c) I, II, IV
d) I, IV
Q.7 S-ethylthiouronium can be converted to clonidine by reaction with?
a) Methyliodide
b) Ethylenediamine
c) Sufuric acid
d) Tryptophan amino acid
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-a
4-b
5-a
6-b
7-b
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 340 [2] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 348-352