AIDS: CAUSATIVE AGENT, TRANSMISSION, PATHOGENESIS,TREATMENT AND PREVENTION, MCQs
INTRODUCTION:-
1.) AIDS refers to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
2.) It is a secondary immunodeficiency disease as it arises due to the acquired suppression of immune system.
3.) AIDS is a pandemic in distribution and is seen in all continents.
CAUSATIVE AGENT:-
1.) AIDS is caused by an RNA (retrovirus) virus called the Human Immunodeficiency Syndrome (HIV).
2.) There are four members of human retroviruses into two groups :-
- Transforming viruses : these are human T – cells leukemia – lymphoma virus (HTLV) 1 and 2 and are implicated in leukemia and lymphoma.
- Cytopathic virus : this group includes HIV – 1 and HIV – 2, causing two form of AIDS.
3.) HIV – 1 viron is spherical in shape and is 100 – 140 NM in size.
4.) It contain a chore having a chore protein, chiefly P24 and P18, two strands of genomic RNA and the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
5.)The core is covered by a double layer of lipid membrane. The membrane is studded with two envelope glycoprotein, gP120 and gP41.
6.) Besides other genes, three important gene code of the respective component of viron:
- gag (group antigen) for core protein.
- pol (polymerase) for reverse transcriptase.
- env (envelope) for envelope protein.
ROTE OF TRANSMISSION:-
1.) Sexual transmission.
2.) Transmission via blood and blood products.
3.) Perinatal transmission as infection can occur from infected mother to the newborn during pregnancy transplacentally.
4.) Occupational transmission.
5.) Transmission by other body fluids.
PATHOGENESIS:-
The pathogensis of HIV infection is largely related to the depletion of CD4+ T- cells (helper T-cells) resulting in profound immunos upperession. After getting into the body of the person, the virus enter into the macrophages where RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA with the help of an enzyme reverse transcriptase. The viral DNA gets incorporated into the host cell’s DNA and directs the infected cell to produce virus particles. The macrophages continue to produce viruses and in this way it acts like a HIV factory. Simultaneously, HIV enters into upper T-lymphocyte replicates and produce progeny viruses. The progeny viruses released in the blood attack other helper T – lymphocytes. This is repeatedly leading to a progressive decrease in the number helper T-lymphocytes in the body of the infected person. During this period, the person suffers from bouts of fever, diarrhea and weight loss.
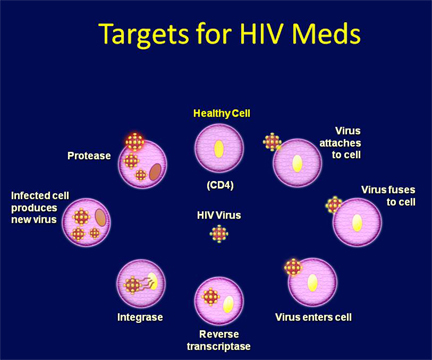
Fig : 1
DIAGNOSING TEST:-
- Screening Test : Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbant Assay also called ELISA. In ELISA, Alkaline Phosphatase and Peroxidase enzymes are used.
- Confirmatory Test : Western blot test which detects antibodies in patient’s serum.
TREATMENT:-
- Reverse transcriptase inhibitors : Zidovudin (AZT), Stavudin, DDI (didexymidine).
- Protease inhibitor : Retonavir, Nelfinavir, Saquiavir, etc.
- Integrase inhibitor : Raltegravir, Elvitegravir etc.
- HAART ( Highly Active Anti Retroviral Therapy ) or cocktail treatment includes both reverse transcriptase inhibitor and protease inhibitor drug.
- Treatment is only partially effective, only to prolong the life of the patient but cannot prevent death, which is inevitable.
PREVENTION:-
1.) As AIDS has no cure, prevention is best option.
2.) In our country the National AIDS Control Organization (NACO) and other non – governmental organizations ( NGOs) are doing a lot to educate the people about AIDS.
3.) Making blood ( from blood banks) safe from HIV.
4.) Ensuring the use of only disposable needles and syringes in public and private hospitals and clinics.
5.) Free distribution of condoms, controlling drug abuse, advocating safe sex and promoting regular check – ups for HIV in susceptible population, are some such steps taken up.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:-
Ques:1) When was HIV first recognized in U.S. ?
a.) 1970
b.) 1975
c.) 1981
d.) 1986
Ques:2.) Which of these is a symptom of HIV infection ?
a.) Swollen lymph nodes
b.) Fever
c.) Tiredness
d.) All of the above
Ques:3) A person has AIDS when which of these occurs ?
a.) HIV antibodies are found in blood
b.) Exposure to HIV
c.) The CD4+ count is lower than 200 or opportunistic infection develops in the HIV infected person
d.) A person has HIV for 5 years
Ques:4) What does HIV – Positive means ?
a.) Either antibodies against the HIV or the virus particles themselves are found in blood
b.) You have been tested for HIV
c.) Your WBC count is high
d.) You have been informed about HIV
Ques:5) HIV attack a specific kind of cell in the immune system. Which is it ?
a.) RBC
b.) WBC called T – cell
c.) Platelets
d.) Epithelial cells
Ques:6) What is the CD4+ T- cells count at which AIDS is considered to have developed ?
a.) Below 1000 per cubic millimeter
b.)Below 500 per cubic millimeter
c.)Below 200 per cubic millimeter
d.)Below 50 per cubic millimeter
Ques:7) The risk of HIV/AIDS is tied to behaviors. Which of this behavior can put you at risk ?
a.) Spending time with someone who has AIDS
b.) Not wearing latex condom during sex
c.) Injecting drugs
d.) Both (b) and (c)
Ques:8) Why is combination of medicines called a cocktail – used to treat HIV ?
a.) The virus changes (mutates) rapidly
b.) Each person responds to each medicine differently
c.) Combining medicines to triple their strength
d.) Both (a) and (b)
Ques:9) What is the best way to protect yourself against HIV ?
a.) Get yourself vaccinated for HIV
b.) Use birth control pills
c.) Use of latex condom during sexual intercourse
d.) Both (b) and (c)
Ques:10) AZT ( 3’ – azido 2’, 3’- didoxy thymine) is used in the treatment of ?
a.) Malaria
b.) AIDS
c,) Kala azar
d.) Tuberculosis
SOLUTIONS….
Sol.1] (c) 1981
Sol.2] (d)
Sol.3] (c) The CD4+ count is lower than 200 or opportunistic infection develops in a HIV – Infected person.
Sol.4] (a) Either antibodies against HIV or the virus.
Sol.5] (b) WBC called T – cells.
Sol.6] (c) Below 200 per cubic millimeter.
Sol.7] (d)
Sol.8] (d)
Sol.9] (c) Use of latex condom during sexual intercourse.
Sol.10] (b) AIDS.
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE:-
1.) Textbook of pathology by Harsh Mohan.
2.) Robbin’s Basic Pathology.