Antibiotic Drug Resistance and Its Mechanism, Cross Resistance, Prevention of Drug Resistance and MCQ for GPAT, NEET, NORCET
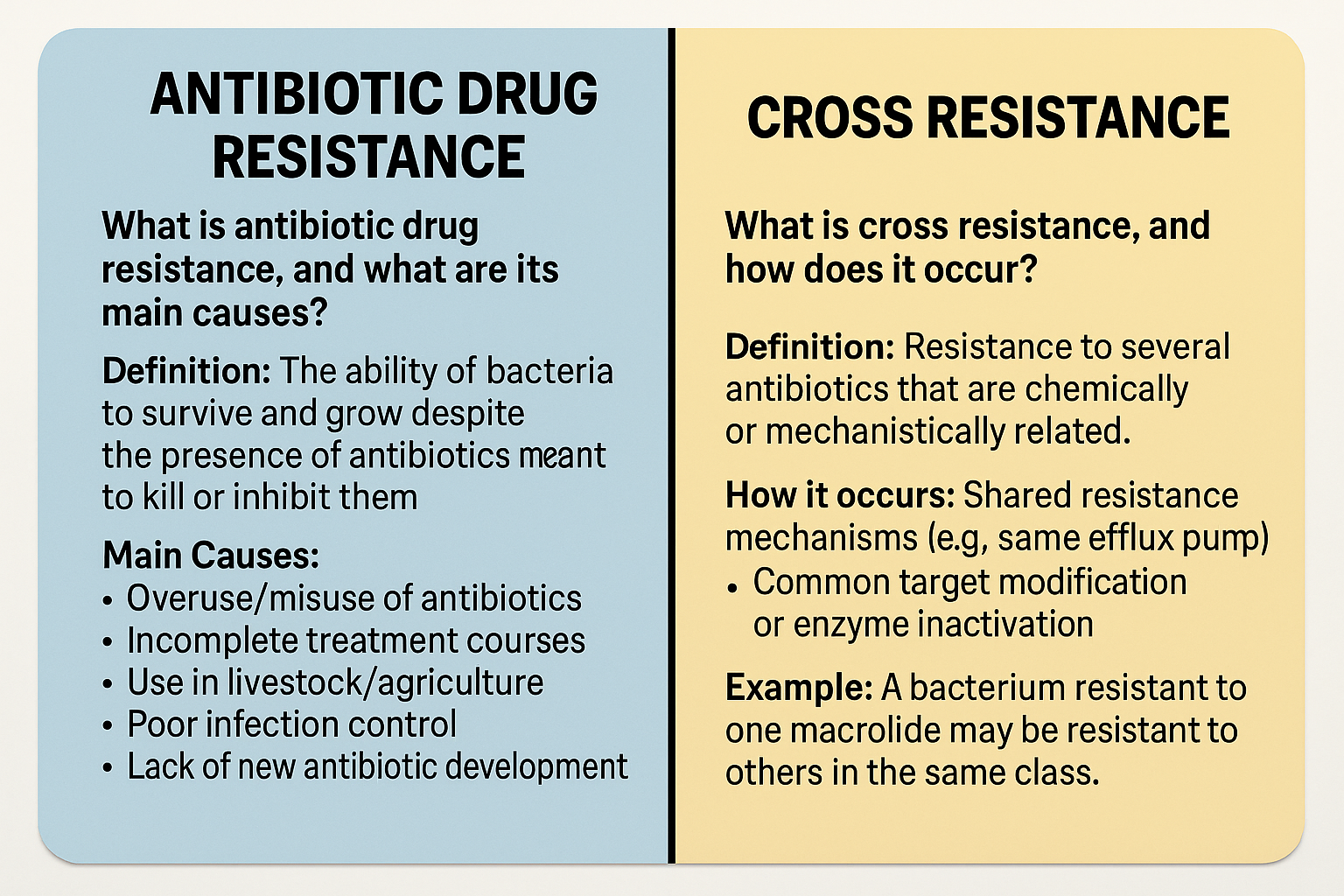
Antibiotic Drug Resistance
-
Definition: The ability of bacteria to withstand the effects of an antibiotic that would normally kill them or inhibit their growth.
-
Causes:
-
Overuse or misuse of antibiotics
-
Incomplete antibiotic courses
-
Use of antibiotics in livestock and agriculture
-
Poor infection control in hospitals
-
Lack of new antibiotic development
-
-
Mechanisms of Resistance:
-
Enzymatic degradation (e.g., β-lactamase enzymes breaking β-lactam antibiotics)
-
Altered target sites (e.g., MRSA altering penicillin-binding proteins)
-
Efflux pumps that expel the antibiotic
-
Reduced permeability of bacterial cell walls
-
2. Cross Resistance
-
Definition: Resistance to multiple antibiotics that are structurally or functionally related.
-
Examples:
-
A bacterium resistant to one tetracycline may also resist others in the same group.
-
MRSA is often resistant to multiple β-lactam antibiotics.
-
-
Mechanism: Often due to shared resistance genes or mechanisms (e.g., same efflux pump or enzyme degrading multiple drugs)
- Participate in GPAT MOCK TEST
3. Prevention of Drug Resistance
-
Rational Antibiotic Use:
-
Prescribe antibiotics only when necessary.
-
Choose the correct antibiotic based on culture/sensitivity reports.
-
-
Public Health Measures:
-
Improve infection control (e.g., hand hygiene in hospitals)
-
Surveillance of antibiotic resistance
-
-
Patient-Level Interventions:
-
Educate patients to complete the full course of antibiotics.
-
Avoid self-medication.
-
-
Agricultural Interventions:
-
Limit antibiotic use in livestock.
-
-
Development Strategies:
-
Encourage research on new antibiotics and alternative therapies (e.g., bacteriophages)
-
✅ MCQs
1. Which of the following is a major cause of antibiotic resistance?
A. Taking multivitamins
B. Completing the full course of antibiotics
C. Overuse of antibiotics
D. Eating processed food
Answer: C
2. Cross resistance refers to:
A. Resistance developed due to poor diet
B. Resistance to unrelated classes of antibiotics
C. Resistance to multiple antibiotics with similar structures or mechanisms
D. Resistance that crosses over from animals to humans
Answer: C
3. Which mechanism involves pumping the antibiotic out of the bacterial cell?
A. Enzymatic degradation
B. Efflux pump
C. Target site alteration
D. Permeability barrier
Answer: B
4. One way to prevent antibiotic resistance at the patient level is:
A. Stopping antibiotics as soon as symptoms disappear
B. Saving antibiotics for future use
C. Completing the prescribed antibiotic course
D. Sharing antibiotics with family
Answer: C
5. MRSA shows resistance by:
A. Inhibiting protein synthesis
B. Producing β-lactamase only
C. Altering penicillin-binding proteins
D. Increasing cell wall thickness only
Answer: C