BENZTROPINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
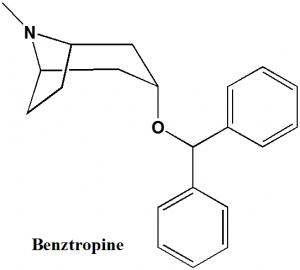
Benztropine
IUPAC nomenclature
(3-endo)-3-(Diphenylmethoxy)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane
Classification
Benztropine is an acetylcholine antagonist. It is a muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 307.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to off-white powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 135°C. |
| 4 | Solubility | 24.9mg/L in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 4.27 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Bicycle ring and benzene rings |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 3 |
Mechanism of Action
Benztropine inhibits uptake of dopamine and thus, helps in reducing the symptoms of Parkinson’s diseases.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
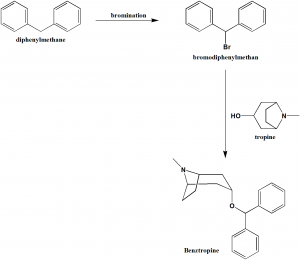
Method of synthesis
i. Diphenylmethane undergoes bromination to form bromodiphenylmethane.
ii. It is followed by condensation with tropine and purification to get benztropin.
Therapeutic Uses
Benztropine is used for:
- Treatment of symptoms of Parkinson’s disease
Side Effects
Side effects of benztropine are:
- Dry mouth
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Nervousness
- Nausea
- Flushing
MCQ
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug benztropine-
| i. When X is an ester | A. Maximum potency |
| ii. Distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon unit | B.Minimum potency |
| C. Least potent derivative | |
| D. Most potent derivative |
a) i-A, ii-D
b) i-A, ii-C
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-C, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Benztropine: (3-endo)-3-(Diphenylmethoxy)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane
- Fesoterodine: [2-[(1R)-3-(Di(propan-2-yl)amino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl] 2-methylpropanoate
- Flurazepam: 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine
- Midazolam: 7-Chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
a) TFTF
b) TTFF
c) FFTT
d) TTFT
Q.3 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of Benztropine?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 Benztropine helps in reducing the symptoms of Parkinson’s diseases by?
a) Stimulating the uptake of dopamine
b) Binding with GABA receptor complex
c) Inhibiting the uptake of dopamine
d) Both a) and b)
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug benztropine?
a) Treatment of Insomnia
b) Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
c) Treatment of Parkinson’s disease
d) Treatment of Asthma
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Benztropine: acetylcholine antagonist
II. Fesoterodine: Nitrogen mustard
III. Flurazepam: benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
IV. Midazolam: Acetylcholine Nicotinic receptor antagonist
a) I, III
b) I, III, IV
c) II, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 When bromodiphenyl methane undergoes condensation with tropine, the drug formed is?
a) Midazolam
b) Fesoterodine
c) Benztropine
d) Methysergide
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT, Pharmacist,Drug Inspector
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-d
4-c
5-c
6-a
7-c