BETAXOLOL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Betaxolol
IUPAC nomenclature
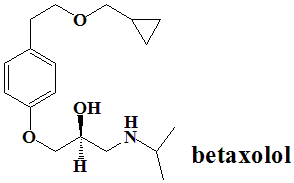
(RS)-1-{4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]-phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol.
Classification
Atenolol is a cardioselective ß1-adrenergic antagonist
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 307.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 71°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 451 mg/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.81 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene, cyclopropane |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 2 |
Mechanism of Action
- Betaxolol selectively binds with ß2-receptors in heart and vascular smooth muscles and blocks them.
- This results in the reduction of heart rate, cardiac output, systolic and diastolic pressure and reflex orthostatic hypotension.
- Betaxolol also causes bronchospasm by competitively blocking ß2-adrenergic receptors in bronchial and vascular smooth muscles.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Increasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
- Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
- Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
- Aryloxypropanolamines are more potent than aryloxyethanolamines.
Method of synthesis
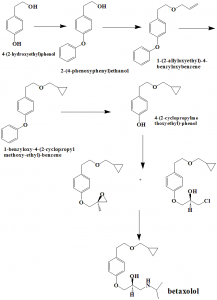
i. Condenstation of 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl-ethanol) with benzyl halide in thepresence of base, a phase transfer catalyst and organic solvent to get 2-(4-benzyloxyphenyl-ethanol).
ii. The latter compound on further condensation with an allyl halide in the presence of base and an organic solvent gives 1-(2-allyloxyethyl)-4-benzyloxybenzene.
iii. By using the Simmon smith reaction and Furukawa modification, cyclopropanating of the above formed compound will produce 1-benzyloxy-4-(2-cyclopropyl methoxy-ethyl)-benzene.
iv. Deprotecting of the above formed compound by hydrogenation gives 4-(2-cyclopropylmethoxyethyl)-phenol.
v. O-alkylation of the latter compound by treating it with R-(-) epichlorohydrin in the presence of alkali to give a mixture of compounds, which on further treatment of isopropylamine will give betaxolol.
Therapeutic Uses
Betaxolol is used for treatment of:
- Glaucoma
- High blood pressure
- Prevention of heart attacks
- Prevention of kidney problems
Side Effects
Side effects of betaxolol are:
- Weakness
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Dry eyes
- Coldness in feet and palm
- Sore throat
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Stomach upset
- Decreased libido
- Insomia
- Headache
- Drowsiness
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
MCQs
Q.1. Betaxolol decreases the blood pressure through?
a) Agonism of α1-adrenergic receptors
b) Agonism of α2-adrenergic receptors
c) Antagonism of ß2-adrenergic receptors
d) α-adrenergic antagonism
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug betaxolol is/are?
a) Glaucoma
b) Hypertension
c) Prevention of heart attacks
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of drug betaxolol-
I. Increasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
II. Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
III. Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
IV. Aryloxypropanolamines are more potent than aryloxyethanolamines.
a) I, II, III
b) I, III, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) II, IV
Q.4 The starting chemicals required for the synthesis of drug betaxolol.?
a) 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl-ethanol) and benzyl halide
b) Benzyl halide and epoxide
c) Ethanol and 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl-ethanol)
d) None of the above
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug betaxolol-
I. Molecular weight = 307.4 gm/mol.
II. Melting point = 71°C
III. Octanol/water partition coefficient = 2.81
a) TFT
b) FFT
c) TTT
d) FTT
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drugs are?
I. Betaxolol: (RS)-1-{4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]-phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol
II. Carvedilol: (RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol
III. Bisoprolol: (±)-[3-(9H-carbazol-4-yloxy)-2-hydroxypropyl][2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amine
IV. Propranolol: (RS)-1-(1-methylethylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol.
a) I, II, IV
b) I, IV
c) III, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Betaxolol | A. ß1-ADRENERGIC AGONIST |
| ii. Carvedilol | B. MIXED ACTING SYMPATHOMIMETICS |
| iii. Epinephrine | C. MIXED α/ß BLOCKER |
| iv. Amphetamine | D. NONSELECTIVE ADRENERGIC AGONISTS |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-B, iii-C, iv-A
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
ANSWERS
1-c
2-d
3-c
4-a
5-c
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Reiss GR, Brubaker RF. The mechanism of betaxolol, a new ocular hypotensive agent. Ophthalmology. 1983 Nov 1;90(11):1369-72. [2] [2] Lemke TL, Williams DA, Foye WO. Principles of medicinal chemistry. Williams & Wilkins; 2017, 356. [3] Joshi RA, Murugan M, Garud DR, Borikar SP, Gurjar MK, inventors; Council of Scientific, Industrial Research (CSIR), assignee. Process for preparation of S-(-)-betaxolol and salts thereof. United States patent US 7,019,172. 2006 Mar 28.