BISOPROLOL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
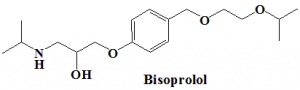
Bisoprolol
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol.
Classification
Bisoprolol is a cardioselective ß1-adrenergic antagonist
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 325.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 100°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 0.0707 mg/ml in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.2 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Bisoprolol acts as an antagonist for ß1-adrenergic receptors which results in the lowering of the blood pressure through reduction in the cardiac output.
- It also reduces the output of rennin in the kidneys
- Bisoprolol diminishes the sympathetic nervous system output from the brain, which also reduces the blood pressure and heart rate. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Increasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
- Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
- Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
- Aryloxypropanolamines are more potent than aryloxyethanolamines. [2]
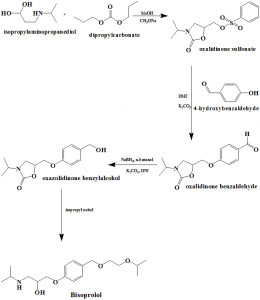
Method of synthesis
i. Isopropylaminopropanediol reacts with dimethylcarbonate to produce oxalidinone sulphonate.
ii. Oxalidinone sulphonate reacts with 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde to give oxalidinone benzaldehyde.
iii. Oxaldinone benzaldehyde is converted into oxalidinone benzylalcohol.
iv. Oxalidinone benzylalcohol is reacted with isopropyl oxitol to form bisoprolol.
Therapeutic Uses
Bisoprolol is used for treatment of:
- High blood pressure
- Prevention of strokes
- Prevention of heart attacks
- Prevention of kidney problems
Side Effects
Side effects of Bisoprolol are:
- Dryness or burning of eyes
- Nausea
- Decreased libido
- Anxiety
- Dizziness
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Diarrhea
- Slower heart rate
- Headache
- Cold or flu symptoms
- Swellings
- Allergic reactions like skin rashes
- Breathing problems
- Confusion
- Sweating
- Tremors
- Vomiting
MCQs
Q.1 “(RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Bisprolol
b) Methysergide
c) Phentolamine
d) Carvediol
Q.2 Melting point of Bisoprolol is?
a) 250°C
b) 250°C
c) 100°C
d) 225°C
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Bisoprolol | A. Ergot alkaloid |
| ii. Methysergide | B. ß2-adrenergic agonist |
| iii. Isoproterenol | C. ß1-adrenergic antagonist |
| iv. Dobutamine | D. ß1-adrenergic agonist |
a) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
c) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
Q.4 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug Bisoprolol
I. Blocking of ß1-adrenergic receptors
II. Blocking of ß2-adrenergic receptors
III. Reduction in the cardiac output
IV. Lowering of blood pressure
a) I – III – IV
b) II – III – IV
c) III – I – IV
d) III – II – IV
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug bisoprolol?
- Decreasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
- Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
- Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
- Aryloxypropanolamines are less potent than aryloxyethanolamines.
a) TFFT
b)FFTT
c) FTTF
d) TTTF
Q.6 Oxalidinone benzylalcohol is reacted with isopropyl oxitol to form?
a) Amphetamine
b) Metaraminol
c) Bisoprolol
d)Oxymetazoline
Q.7 The drug Bisoprolol is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of high blood pressure
b) Treatment of hypotension
c) Increasing the libido
d) Prevention of gonorrhea
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-d
4-a
5-c
6-c
7-a