BITOLTEROL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
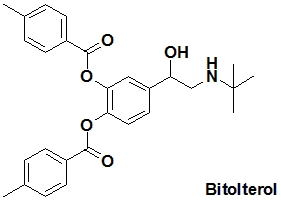
Bitolterol
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-[4-(1-Hydroxy-2-tert-butylamino-ethyl)-2-(4-methylbenzoyl)oxy-phenyl] 4-methylbenzoate.
Classification
Bitolterol is ß2-adrenergic agonist. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 461.5g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Off-white solid |
| 3 | Flash point | 341.2 |
| 4 | Solubility | Water solubility is 0.00048 mg / ml |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 5.8 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene ring present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
Relaxation of the smooth muscles surrounding the air flow tubes through agonsim of ß2 adrenergic receptors. This result in increase in the diameter of the air flow tubes and thus, ease in breathing.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Primary or secondary aliphatic amine separated by two carbons from a substituted benzene ring is essential for the high agonist activity.
- The hydroxyl substituted carbon must be in the R configuration for the maximal direct activity.
R1 substitution:
- When R1 is increased in size, activity of alpha receptors decreases and activity of the beta receptors increases
- Activity of both alpha and beta receptors is maximum when R1 is methyl group.
- Alpha agonist activity decreases when R1 is larger than methyl, and went negligible when R1 is isopropyl.
- Large lipophillic groups can afford compounds with alpha blocking activity.
- N-substituent provides selectivity for different receptors.
- Arylalkyl group can provide beta selectivity, increased cell penetration and increased lipophillicity for the longer duration of action.
R2 substitution:
- Ethyl group can eliminate the alpha activity of the drug.
- Erythrostero isomers have maximal activity.
- The additional methyl group makes the drug more selective for the alpha2
R3 substitution on the aromatic ring:
- 3’,4’-dihydroxy substituted benzene ring has poor oral activity.
- 3’, 5’-dihydroxy compounds are orally active.
- At least one of the groups is required which can form hydrogen bonds. And if only one group is present then it is preferred at 4’ position to retain the beta2
- If phenyl group has no phenolic substituent then it may act directly or indirectly.[2]
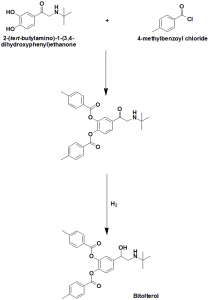
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethanone and 4-methylbenzoyl chloride gives compound (1).
ii. Reduction of compound (1) produces Bitolterol.
Therapeutic Uses
Bitolterol is given for the relief of bronchospasm during asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases.
Side Effects
Some of the side effects of bitolterol are
- tremors,
- nervousness,
- headache,
- lightheadedness,
- dizziness,
- paresthesia,
- somnolence, etc.
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug Bitolterol-
| i. Large lipophillic groups at R1 | A. Elimination of α-activity |
| ii. N-substituent at R1 | B. Afford compounds with α-blocking activity. |
| iii. Ethyl group at R2 | C. Provides selectivity for different receptors |
| iv. 3’, 5’-dihydroxy compounds | D. Orally active drug |
a) i-A, ii-D, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
d) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
Q.2 correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Bitolterol: (RS)-[4-(1-Hydroxy-2-tert-butylamino-ethyl)-2-(4-methylbenzoyl)oxy-phenyl] 4-methylbenzoate
- Naphazoline: 2-[(4-tert-butyl-2,6-dimethylphenyl)methyl]- 4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole
- Xylometazoline: 3-(4,5-Dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-ylmethyl)-2,4-dimethyl-6-tert-butyl-phenol
- Oxymetazoline: 2-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole
a) TFTF
b) FFFT
c) TFFF
d) FFTT
Q.3 Water solubility of Bitolterol is?
a) 0.00048 mg/ml
b) 48 mg/ml
c) 2 mg/ml
d) 480 mg/ml
Q.4 Agonism of ß2-adrenergic receptors by Bitolterol leads to?
a) Relaxation of smooth muscles surrounding air flow
b) Increase in diameter of the air flow tubes.
c) Ease in breathing
d) All of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug Bitolterol?
a) Relief in bronchospasm
b) For treatment of ulcers
c) Treatment of insomia
d) None of the above
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Flutamide: Progestin
II. Etoposide: Epipodophyllotoxin
III. Bitolterol: Nonselective adrenergic agonist
IV. Methamphhetamine: Mixed acting sympathomimetics
a) II, III
b) I, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) I
Q.7 Bitolterol can be synthesized by the reaction of-
a) 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethanone and 4-methylbenzoyl chloride; followed by reduction
b) 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethanone and 4-methylbenzoyl chloride; followed by hydrolysis
c) (1-naphthyl)acetonitrile and ethnol; followed by reduction
d) (1-naphthyl)acetonitrile and ethanol; followed by hydrolysis
ANSWERS
1-b
2-c
3-a
4-d
5-a
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 340 [2] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 348-352