CHLOROQUINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
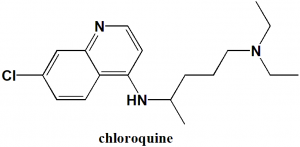
Chloroquine
IUPAC nomenclature
(RS)-N’-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)-N,N-diethyl-pentane-1,4-diamine.
Classification
Chloroquine is an aminoquininoline derivative. It belongs to class known as antimalarials.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 319.9g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White to slightly yellow crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 87°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very slightly soluble in water |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Quinioline |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Chloroquine prevents the conversion of heme to hemazoin by inhibiting the heme polymerase in the malarial trophozoites. The accumulation of the toxic heme kills the parasite.
- Chloroquine diffuses into through the cell membrane and into the cell organelles like endosomes, lysosomes, glogi vesicles, and raises the pH of the surrounding. This prevents the virus to to utilize their activity for fusion and entry into cell.
- Chloroquine also inhibits the terminal glycosylation of ACE2, the receptors through which SARS-CoV and SARS CoV-2 uses for entering into the cell. Due to this, the ACE2 less efficiently interacts with the spike proteins of the SARS CoV-2, which further prevents the viral entry.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Chloroquine is crucial for heme binding.
- Nitrogen of the amine attached with the chloroquine entity is responsible for the basic nature of the drug.
- There is no major role of having the secondary alkyl group attached with the carbon next to the amino group near the chloroquine entity.
- Tertiary amine at the terminal is very important for the activity of the drug.
- The length of spacer between the terminal nitrogen and 4-amino group is sensitive towards the parasite resistance. Compounds having shorter chains or longer chains retains the activity against the resistant species of the parasite.
- Small electron withdrawing group at 7th position of the quinoline ring is important for the inhibition of hmozoin formation. [1]
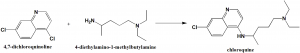
Method of synthesis
Chloroquine can be synthesized by reaction of 4,7-dichloroquinoline with 4-diethylamino-1-methylbutylamine at 180 °C [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Chloroquine is used for:
- Prevention and treatment of malaria.
- Useful in treatment of corona virus infection, However use based on risk & benefit ratio
Side Effects
Side effects of Chloroquine are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Abdominal cramps
Serious side effects include:
- Bradycardia
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling of ankles and feet
- Tiredness
- Weight gain
- Anxiety
- Hearing loss
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts
- Hallucinations
- Liver diseases
- Muscle weakness
- Change in skin and hair color
MCQ
Q.1 ‘(RS)-N’-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)-N,N-diethyl-pentane-1,4-diamineethanol’ is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Chloroquine
b) Beclomethasone
c) Triptorelin
d) Albuterol
Q.2 Physical appearance of chloroquine is?
a) Brown crystals
b) White to slightly yellow crystalline powder
c) Present in liquid form at room temperature
d) Amorphous solid
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Tiotropium | A. HIV protease inhibitor |
| ii. Darunavir | B. Antimuscarinic |
| iii. Chloroquine | C. Fusion inhibitor |
| iv. Enfuvirtide | D. Antimalarial drug |
a) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
b) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
Q.4 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug Chloroquine?
I. Inhibition of the parasite heme polymerase.
II. Destruction of parasite
III. Accumulation of ß-hematin in parasite.
a) II – I – III
b) I –III – II
c) III – II – I
d) II – III – I
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug chloroquine
- Nitrogen of the amine attached with the chloroquine entity is responsible for the acidic nature of the drug.
- There is no major role of having the secondary alkyl group attached with the carbon next to the amino group near the chloroquine entity.
- Tertiary amine at the terminal is not so important for the activity of the drug.
- Small electron withdrawing group at 7th position of the quinoline ring is important for the inhibition of hmozoin formation.
a) FFTF
b) FTFT
c) FTTT
d) TFFT
Q.6 Chloroquine can be synthesized by reaction of 4-diethylamino-1-methylbutylamine with?
a) 4,7-dichloroquinoline
b) α-naphthol
c) ß-naphthol
d) None of the above
Q.7 The drug chloroquine is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of viral synptoms
b) Treatment of AIDS
c) Treatment of malaria
d) All of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-d
4-b
5-b
6-s
7-c
REFERENCES
[1] Muraleedharan KM, Avery MA. In Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry II. Therapeutic Areas II: Cancer, Infectious Diseases, Inflammation, Immunology and Dermatology; Taylor JB, Triggle DJ, Eds. [2] Vardanyan R, Hruby V. Synthesis of essential drugs. Elsevier; 2006 Mar 10.