CIMETIDINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
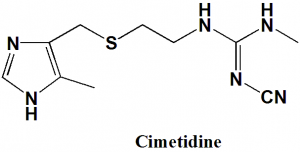
Cimetidine
IUPAC nomenclature
1-cyano-2-methyl-3-[2-[(5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)methylsulfanyl]ethyl]guanidine
Classification
- H2-antihistamine
- Antiulcer drug
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 252.34g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 142oC |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in alcohol |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 0.4 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Imidazole |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Cimetidine binds with H2 receptors present on the basolateral membrane of the gastric parietal cells.
- This results in blockage of histaminic effects.
- Due to this, there is reduction in gastric acid secretion and thus, reduction in acidity and gastric volume.
Structure Activity Relationship
General structure activity of H2-antihistamines antiulcer drugs can be summarized as:
- Structure of the drug should closely resemble to the structure of histamine.
- Imidazole ring is maintained for affinity at H2 receptor site.
- Substitution at C-4 site helps in H2-selectivity of the drug.
- Sulfur atom increases potency than nitrogen or oxygen atoms.
- Replacement of N-cyanoamino group with nitromethylene increase the potency.
- Guanidines with electron withdrawing groups substitutions have decreased basicity than guanidine.
- Replacement of imidazole ring with other aromatic rings gives other useful products. [1]
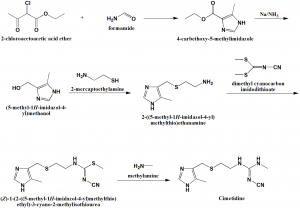
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of 2-chloroacetoacetic ether with 2 mole of formamide to get 4-carbethoxy-5-methylimidazole.
ii. Reducing the carbethoxy group by sodium in liquid ammonia produces 4-hydroxymethyl-5-methylimidazole.
iii. Hydrochloride of the resulting alcohol is reacted with 2-mercaptoethylamine hydrochloride to give 4-(2-aminomethyl)-thiomethyl-5-methylimidazole dihydrochloride.
iv. On reacting the above formed compound with –cyanimido-S,S-methylamine produces cimetidine. [1]
Medicinal Uses
Cimetidine is used for treatment of:
- Stomach ulcers
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Heart burn with sour stomach
- Acid indigestion
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Erosive esophagitis
Side Effects
Side effects of Cimetidine are:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Drowsiness
- Diarrhea
- Agitation
- Confusion
- Depression
- Hallucinations
- Troub;e urinating
- Muscle pain
- Breast swellings
- Decreased libido
- Allergic reactions
MCQs
Q.1 Mechanism of action of Cimetidine drug includes?
a) Binds with H2 receptor
b) Binds with H1 receptors
c) Antagonistic effects at H1 receptor for histamine
d) Agonist effects H1 receptor for Histamine
Q.2 Medicinal use of drug Cimetidine is/are?
a) Stomach ulcers
b) Acid indigestion
c) Erosive esophagitis
d) All of the above
Q.3 The type of ring which should be maintained for affinity at H2 receptor site in cimetidine ring is?
a) Piperazine
b) Pyridine
c) Cyclohexane
d) Imidazole
Q.4 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of Cimetidine is?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug cimetidine can be?
- Molecular weight: 252.34 gm/mol
- Physical appearance: Oil
- Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.4
a) TTT
b) TFT
c) FFT
d) TFF
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the drugs are?
I. Cimetidine: 1-cyano-2-methyl-3-[2-[(5-methyl-1H-imidazol-4-yl)methylsulfanyl]ethyl]guanidine
II. Rabeprazol: (RS)-2-([4-(3-Methoxypropoxy)-3-methylpyridin-2-yl]methylsulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole.
III. Amiodarone: Ethyl-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-dimethylazanium
IV. Clonidine: 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-1,1-dioxo-N-pyridin-2-ylthieno[2,3-e]thiazine-3-carboxamide
a) I, II
b) III, IV
c) IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Dimenhydrinate | A. H2-antagonist |
| ii. Cimetidine | B.Vasodilator |
| iii. Thioguanine | C. Antimetabolite |
| iv. Isosorbide | D. H1-receptor antihistamine |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-B, iii-A, iv-C
d) i-B, ii-D, iii-A, iv-C
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test
ANSWERS
1-a
2-d
3-d
4-a
5-b
6-a
7-b