Classification of Cephalosporins and MCQ for GPAT, NEET PG and NORCET
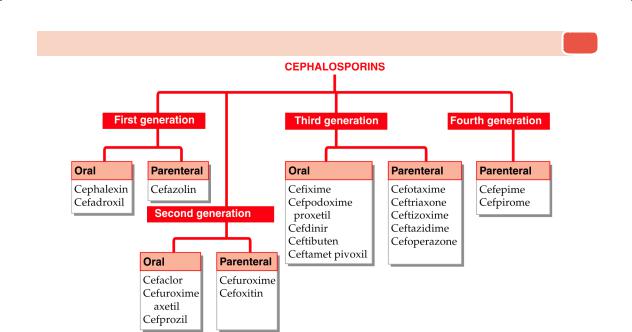
Cephalosporins are classified into generations (1st to 5th) based on their antimicrobial spectrum and chronological development.
| Generation | Examples | Spectrum / Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Generation | Cefazolin, Cephalexin | Good Gram-positive coverage (e.g., Staph, Strep); limited Gram-negative |
| 2nd Generation | Cefuroxime, Cefaclor, Cefoxitin | Better Gram-negative (e.g., H. influenzae); less Gram-positive than 1st generation |
| 3rd Generation | Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime, Ceftazidime | Stronger Gram-negative activity; some cross blood-brain barrier (good for meningitis) |
| 4th Generation | Cefepime | Broad-spectrum; excellent Gram-negative including Pseudomonas, retains Gram-positive |
| 5th Generation | Ceftaroline | Active against MRSA; broad-spectrum including resistant Gram-positive organisms |
| Other (Advanced) | Ceftolozane + Tazobactam, Ceftazidime + Avibactam | Used for multidrug-resistant organisms including ESBL and CRE |
❓ MCQs on Cephalosporin Classification
-
Which of the following is a first-generation cephalosporin?
A. Cefepime
B. Cefuroxime
C. Cefazolin
D. Ceftaroline
Answer: C. Cefazolin -
Which generation of cephalosporins has good activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
A. First
B. Second
C. Third
D. Fourth
Answer: D. Fourth -
Which cephalosporin is effective against MRSA?
A. Ceftriaxone
B. Cefuroxime
C. Ceftaroline
D. Cephalexin
Answer: C. Ceftaroline -
Ceftriaxone belongs to which generation of cephalosporins?
A. First
B. Second
C. Third
D. Fourth
Answer: C. Third -
Which of the following is a second-generation cephalosporin?
A. Cefotaxime
B. Cefoxitin
C. Ceftazidime
D. Ceftolozane
Answer: B. Cefoxitin