DARIFENACIN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Darifenacin
IUPAC nomenclature
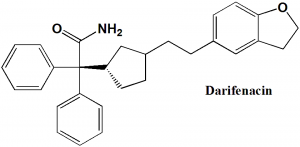
(S)-2-[1-[2-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)ethyl] pyrrolidin-3-yl] -2,2-diphenyl-acetamide
Classification
Darifenacin is an acetylcholine antagonist. It is a muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 426.5 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | White crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | More than 230°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Slightly soluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 4.5 |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Dihydrobenzofuran, cyclopentyle, phenyl |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 2 |
Mechanism of Action
Darifenacin acts as selective antagonist for the muscarinic receptors (M3). M3 receptors are involved in contraction of bladder, and hence, the drug helps in relaxing bladder. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
Method of synthesis
Reaction of 3-(S)-(-)-(1-carbamoyl-1,1-diphenylmethyl)- pyrrolidine with 5-(2-bromoethyl)benzo[2,3-b]furan in presence of anhydrous K2CO3 in acetonitrile to get darifenacin. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Darifenacin is used for:
- Treatment of overactive bladder
- Reducing the frequent trips to bathroom
- Reducing the urge for frequent voids
- Reducing the leakage of urine
Side Effects
Side effects of Darifenacin are:
- Constipation
- Headache
- Dry mouth
- Blurred vision
- Dry eyes
- Tiredness
- Weakness
- Stomach upset
- Stomach pain
MCQ
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Darifenacin?
a) (S)-2-[1-[2-(2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-yl)ethyl] pyrrolidin-3-yl] -2,2-diphenyl-acetamide
b) (S)-2-[3-(Diisopropylamino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-methylphenol.
c) 7-Chloro-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid
d) N,N-Dimethyl-2-[6-methyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl]acetamide hemitartrate
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of Darifenacin?
I. Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
II. The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
III. Poorest derivatives has X as an ester.
IV. ‘X’ can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
a) I, II
b) III
c) III, IV
d) II
Q.3 Darifenacin can be obtained by reaction of 3-(S)-(-)-(1-carbamoyl-1,1-diphenylmethyl)- pyrrolidine with?
a) 5-(2-bromoethyl)benzo[2,3-b]furan
b) 1-phenylpropyl-4-methylphenol
c) 1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid
d) None of the above
Q.4 Side effects of drug darifenacin is/are?
a) Constipation
b) Headache
c) Dry mouth
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct molecular weights-
| i. Darifenacin | A.426.5 gm/mol |
| ii. Tolterodine | B.307.4gm/mol |
| iii. Chlorazepate | C. 325.5 gm/mol |
| iv. Zolpidem | D. 314.72 gm/mol |
a) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-B, iii-D, iv-A
c) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
d) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
Q.6 An example of drug from class Acetylcholine antagonist?
a) Zolpidem
b) Chlorazepate
c) Amphetamine
d) Darifenacin
Q.7 The type of ring system found in the structure of darifenacin?
a) Dihydrobenzofurane
b) Pyrrolopyrimidine
c) Naphthalene
d) Pyrrolopyrrole ring
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT, Pharmacist,Drug Inspector
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-a
4-d
5-c
6-d
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Steers WD. Darifenacin: pharmacology and clinical usage. Urologic Clinics. 2006 Nov 1;33(4):475-82. [2] Vasantha M, Lakshmanarao V, Rao SY, Devi SA, Suryanarayana VM. Synthesis/Isolation of darifenacin hydrobromide by-products.