DIAZEPAM Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Diazepam
IUPAC nomenclature
7-Chloro-1,3-dihydro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-3H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
Classification
Diazepam is a benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 284.74 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Colorless to yellow crystalline compound |
| 3 | Melting point | 132°C |
| 4 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.44 |
| 5 | Solubility | 1 gm in 2 ml of chloroform; 1 gm in 39 ml of ether. |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Diazepine, benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
i. Diazepam binds with different receptors present in the brain and spinal cord.
ii. This increases the inhibitory effects of the GABA.
iii. GABA involves in sleep induction, control of hypnosis, memory, anxiety, epilepsy and neuronal excitability. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Ring A should include an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring for binding with 5-phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives.
- An electronegative group at 7-position of the ring A increases the functional anxiolytic activity.
- Substitutions at 6, 8 or 9 position with electronegative group on ring A will decrease the functional anxiolytic activity.
- When Heterocycles used as ring A, drug shows poor pharmacological activity.
- A proton-accepting group is essential on Ring B for binding with GABAA
- When the proton accepting group is present on the 2-position of the ring B, and is in coplanar spatial orientation with Ring A, maximum activity is observed.
- Replacement of oxygen with sulfur in ring B results in alteration in the selectivity for binding with GABA BZR subpopulations, but anxiolytic properties are maintained.
- There is no effect on agonist activity, but the antagonist activity dereases when methylene 3-position or imine nitrogen of the ring B is substituted.
- Derivatives having the 3-hydroxy moiety are fast excreted.
- Sterically large substituents on ring B, like tert-butyl group reduces the receptor affinity and the in vivo activity.
- 4,5-double bond and 4-position nitrogen is not essential for anxiolystic activity.
- BZR affinity is decreased if C=N bond is replaced with C-N bond.
- 5-phenyl ring C is not necessary for the binding with BZR.
- Substitution at the para position of the ring C decreases the agonist activity of the drug.
- There is no change observed in the agonist property of the drug when there is substitution at ortho position.
- When 1,2-bond f the ring C is annelated with an additional electron rich ring such as imidazole, affinity of the BZR increases. [2]
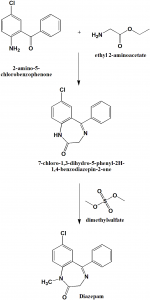
Method of synthesis
i. 2-amino-5-chlorobenzophenone undergoes cyclocondensation with the ethyl ester of glycine hydrochloride produces 7-chloro-1,3-dihydro-5-phenyl-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one.
ii. Methylation of the above formed compound with dimethylsulfate leads to the formation of diazepam. [3]
Therapeutic Uses
Diazepam is used for:
- Treatment of anxiety
- Treatment of seizures
- Treatment of Acute alcohol withdrawal
- Relieving fear
- Relieve muscle spasm
- For sedation before medical procedures
Side Effects
Side effects of diazepam are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Unsteadiness
- Mood changes
- Memory weakness
- Hallucinations
- Confusion
- Restlessness
- Depression
- Speech problem
- Trouble in walking
- Muscle weakness
- Tremors
- Trouble in urination
- Pale skin and eyes
- Fever
- Chills
- Shallow breathing
- Allergic reactions
MCQ
Q.1 Binding of Diazepam with acetylcholine muscarinic receptors results in?
a) agonizing effect on muscarinic receptors
b) Antagonizing effect on muscarinic receptors
c) Do not produce any significant effect
d) Do not bind with muscarinic receptor
Q.2 Therapeutic use of drug Diazepam is/are?
a) Treatment of Acute alcohol withdrawal
b) Treatment of seizures
c) Treatment of anxiety
d) All of the above
Q.3 Which amongst the following are the correct statements with respect to the SAR of drug Diazepam?
I. Ring A should include an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring for binding with 5-phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives.
II. An electronegative group at 7-position of the ring A increases the functional anxiolytic activity.
III. Substitutions at 6, 8 or 9 position with electronegative group on ring A will decrease the functional anxiolytic activity.
IV. When Heterocycles used as ring A, drug shows poor pharmacological activity.
a) I, IV
b) I, II, IV
c) I, II, III, IV
d) II, III, IV
Q.4 Type of ring structures present in the structure of diazepam?
a) Quiniclidine
b) Quinoline
c) Diazepine
d) All of the above
Q.5 Correct sequence for the True/False for the physiochemical properties of the drug solifenacin?
I. Molecular weight is 284.74 gm/mol
II. Colorless to yellow crystalline compound
III. Melting point is between 132°C
IV. Diazepine ring is present
a) TFTF
b) TTTT
c) FFFF
d)FFFT
Q.6 Correct statements for the IUPAC nomenclatures of the are?
I. Solifenacin: (3R)-1-Azabicyclo[2 2 2]oct-3-yl (1S)-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboxylate
II. Zaleplon: N-(3-(3-cyanopyrazolo[1,5-a] pyrimidin-7-yl)phenyl)-N-ethylacetamide
III. Alprazolam: 7-Chloro-1,3-dihydro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-3H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
IV. Diazepam: 8-Chloro-1-methyl-6-phenyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine
a) II, IV
b) I, II
c) I, III, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Match the following drugs with their correct classifications-
| i. Solifenacin | A. Barbiturate sedative-hypnotic |
| ii. Thiobarbital | B. Benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic |
| iii. Diazepam | C. Acetylcholine antagonist |
| iv. Zaleplon | D. Nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic |
a) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
c) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
d) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-d
2-d
3-c
4-c
5-b
6-b
7-a