DOPAMINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
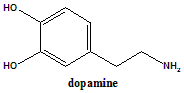
Dopamine
IUPAC nomenclature
4-(2-Aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol.
Classification
Dopamine is a ß1-adrenergic agonist. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 153.18 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in form of stout prisms |
| 3 | Melting point | 128°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Freely soluble in water, methanol and 95% hot ethanol. |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Benzene ring present |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Dopamine exerts an agonist action on ß-adrenoceptors and also causes release of the norepinephrine from the storage sites in sympathetic nerve endings. This results in the positive chronotropic and inotropic effects on the myocardium which increases the heart rate and cardiac contractility.
- It acts as agonist on five receptor subtypes in the brain, namely, D1, D2, D3, D4 and D5.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Primary or secondary aliphatic amine separated by two carbons from a substituted benzene ring is essential for the high agonist activity.
- The hydroxyl substituted carbon must be in the R configuration for the maximal direct activity.
R1 substitution:
- When R1 is increased in size, activity of alpha receptors decreases and activity of the beta receptors increases
- Activity of both alpha and beta receptors is maximum when R1 is methyl group.
- Alpha agonist activity decreases when R1 is larger than methyl, and went negligible when R1 is isopropyl.
- Large lipophillic groups can afford compounds with alpha blocking activity.
- N-substituent provides selectivity for different receptors.
- Arylalkyl group can provide beta selectivity, increased cell penetration and increased lipophillicity for the longer duration of action.
R2 substitution:
- Ethyl group can eliminate the alpha activity of the drug.
- Erythrostero isomers have maximal activity.
- The additional methyl group makes the drug more selective for the alpha2
R3 substitution on the aromatic ring:
- 3’,4’-dihydroxy substituted benzene ring has poor oral activity.
- 3’, 5’-dihydroxy compounds are orally active.
- At least one of the groups is required which can form hydrogen bonds. And if only one group is present then it is preferred at 4’ position to retain the beta2
- If phenyl group has no phenolic substituent then it may act directly or indirectly.[2]
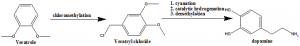
Method of synthesis
i. Veratrole undergos chloromethylation to form veratryl chloride.
ii. The compound undergoes cyanation, catalytic hydrogenation and demethylation to form Dopamine.
Therapeutic Uses
The drug used for the treatment of:
- Low blood pressure
- Slow heart rate
- Cardiac arrest
Side Effects
Side effects of dopamine include irregular heartbeats and abnormal kidney functions.
MCQs
Q.1 “ 4-(2-Aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Dopamine
b) Methyldopa
c) Bitolterol
d) Naphazoline
Q.2 Type of ring present in Dopamine?
a) Imidazoline
b) Naphthalene
c) Benzene
d) No ring structure present
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Albuterol | A. ß1-adrenergic agonist |
| ii. Dopamine | B. nonselective adrenergic agonist |
| iii. Clonidine | C. ß2-adrenergic agonist |
| iv. Epinephrine | D. Selective α2-adrenergic agonist |
a) i-B, ii-D, iii-C, iv-A
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
d) i-D, ii-B, iii-C, iv-A
Q.4 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug dopamine are?
I. Action on ß-adrenoceptors and release of norepinephrine from storage sites.
II. Increase in heart rate and cardiac contractility.
III. Positive chronotropic and inotropic effects
a) I –III – II
b) III –II – I
c) II – I – III
d) I – II – III
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug Dopamine-
- Primary or secondary aliphatic amine separated by two carbons from a substituted benzene ring is essential for the high agonist activity.
- When R1 is increased in size, activity of alpha receptors increases and activity of the beta receptors decreases
- Alpha agonist activity increases when R1 is larger than methyl
- Ethyl group can eliminate the alpha activity of the drug
a) TTFF
b) TFTF
c) FTFT
d) TFFT
Q.6 Veratrole undergoes………….to form dopamine
a) Chloromethylation- cyanation- hydrogenation- demethylation
b) Bromination- hydrolysis- demethylation
c) Nitration- chloromethylation-hydrolysis-cyanation
d) Dehalogination-Bromination-Cyanation-Hydrogenation
Q.7 The drug dopamine is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of low blood pressure
b) Treatment of cancer
c) As a decongestant
d) None of the above
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-c
4-a
5-d
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 340 [2] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 348-352