ELECTROCARDIOGRAM, Abnormal ECG AND MCQs based on Heart Problems
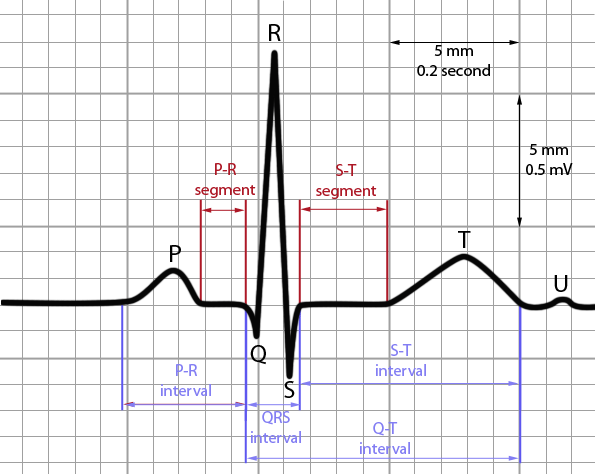
An ELECTROCARDIOGRAM is a recording of electrical signals generated by heart. The instrument used to record these signals is known as electrocardiograph. The ECG consist of different waves which are as follows-the first, known as P-wave, is a small wale of upward deflection on the ECG. This wave represents atrial depolarization that is contraction of atria. The next is the QRS complex which looks like a up-down wave, this complex represents the ventricular depolarization i.e contraction of ventricles. The last and the third is the T-wave , a downward wave representing the ventricular repolarization means relaxation of ventricles. This T wave is smaller and slight wider than other waves because heart takes more time for relaxation than contraction. This image shown above represents all these waves of an ECG in normal condition i.e when the person’s heart functions properly. Any changes in the positions of these waves shows that the person is suffering with certain type of abnormalities.
- If the P- wave is larger, it indicates enlargement of atrium
- While enlargement of Q WAVE represent myocardial infraction,
- Larger R wave shows enlarged ventricles
- If the T wave is flatter than it indicates that the heart is getting insufficient oxygen and if the T wave is elevated than in normal condition that is shows hyperkalemia.
Apart from these waves the ECG is also divided in different intervals or segments.
These segments are
- PQ segment
- ST segment
- QT segment.
The PQ segment is the time from beginning of P-wave to the beginning of QRS complex which means time from atrial excitation to ventricular excitation, and changes in this segment indicate coronary artery disease and rheumatic fever.
The ST segment begins at the end of QRS complex and ended at the beginning of T wave. The ST segment is elevated in acute myocardial infraction and depressed when oxygen supply is less to the heart muscle.
The last segment is QT segment is from beginning of ventricular contraction and ends at end of ventricular repolarization and if this segment is lengthened it shows myocardial ischemia or some conduction abnormalities.
MULTIPLE CHOISE QUESTION(MCQs)
1. ECG is used for examination of?
A. heart B. kidney
C. LUNGS D. BRAIN
Ans- heart
2.In ECG relaxation of ventricles is represented by?
A. P-wave B. T wave
C.U wave D. QRS complex
Ans- T wave
3.Match the following:
(a)represents the time from 1.QRS complex
Beginning of ventricular depolarization 2.P wave
To the end of ventricular repolarization 3. Q-T interval
(b)represents atrial depolarization 4.PQ interval
(c)represents the onset of ventricular
Depolarization
(d)represents time from beginning of atrial
excitation to the beginning of ventricular
excitation.
Ans- (a) – 3 (b) – 2 (c) – 1 (d) – 4
4. What does lengthening of P wave indicate
A. Myocardial infraction B. Enlargement of atria
C. Ventricular enlargement D. Hyperkalamia
Ans – enlargement of atria
5. What happens if T wave becomes wider?
A. CONDUCTION Abnormalities B. insufficient oxygen to heart
C. hyperkalamia D. myocardial ischemia
Ans- insufficient oxygen to heart
6. What does elevated ST segment represents?
A. insufficient oxygen B. acute myocardial infraction
C. Rheumatic fever D. ischemia
Ans- option B
7. What does enlarged R wave indicate?
A. enlarged atria B. Rheumatic fever
C. Coronary artery disease D. none of the above
Ans – none of the above
8. Which of the following statement is NOT true?
A. P wave indicate atrial contraction
B. depressed ST segment indicate hyperkalamia
C. T wave represents ventricular repolarization
d. QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization
Ans- option B
9. ECG was first developed by?
A. Steward B. Willem Einthoven
C. Koch D. Hubbert Mann
Ans- Willem Einthoven
10.Which of the following is the part of ECG?
A. QRS complex B. ST segment
C. T wave D. All of the above
Ans- all of the above
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFRENCES:- 1. ROSS and WILSON-Anatomy and physiology in health and illness; 12th edition; page no.94
2.Gerard J Tortora- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology; 12th edition; page no.735-736.