Emulsions Introduction, Types of Emulsions and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam
The word “emulsion” comes from the Latin word for “to milk“. An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (nonmixable or unblendable). Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Emulsion should be used when both the dispersed and the continuous phase are liquids. Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, milk, mayonnaise, and some cutting fluids for metal working. The photo-sensitive side of photographic film is an example of a colloid.
TYPES OF EMULSIONS:
1- Oil in water emulsions
2- Water in oil emulsions
3- Multiple emulsions (O/W/O) or (W/O/W)
4- Microemulsions
Table 1 – DIFFERENCE BETWEEN O/W AND W/O EMULSIONS: (o/w) (w/o)
| o/w | w/o |
| Water is the dispersion medium and oil is the dispersed phase. | Oil is the dispersion medium and water is the dispersed phase. |
| Non greasy and easily removable from the skin. | Greasy and not water washable. |
| Used externally to provide cooling effect. E.g. vanishing cream. | Used externally to prevent evaporation of moisture from the surface of skin. E.g. cold cream. |
| Preferred for internal use as bitter taste of oils can be masked. | Preferred for external use like creams. |
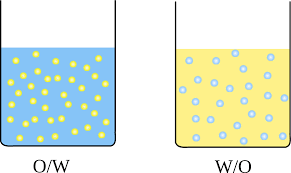
Figure 1 – O/W and W/O type emulsion
MULTIPLE EMULSIONS: Multiple emulsions are the emulsion system in which the dispersed phase contain smaller droplets that have the same composition as the external phase. The multiple emulsions are also considered to be of two types: o Oil-in-Water-in-Oil (O/W/O) emulsion system o Water-in-Oil-In-Water (W/O/W) emulsion system.
1.Oil-in-Water-in-Oil: In O/W/O systems an aqueous phase (hydrophilic) separates internal and external oil phase. In other words, O/W/O is a system in which water droplets may be surrounded in oil phase, which in true encloses one or more oil droplets.
2.Water-in-Oil-In-Water: In W/O/W systems, an organic phase (hydrophobic) separates internal and external aqueous phases. In other words, W/O/W is a system in which oil droplets may be surrounded by an aqueous phase, which in turn encloses one or several water droplets. These systems are the most studied among the multiple emulsions.
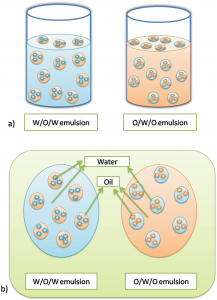
Figure 2 – Multiple emulsion
MICROEMULSIONS: Clear, stable, liquid mixtures of oil, water and surfactant, frequently in combination with a co-surfactant. In contrast to ordinary emulsion, Microemulsions form upon simple mixing of the components and do not require the high shear conditions generally used in the formation of ordinary emulsions. The two basic types of Microemulsions are (o/w) and (w/o).
Unlike the common macro emulsion in that:
1- Appear as clear transparent solution.
2- Diameter of internal phase droplets ranged between 10- 200nm.
3-Thermodynamically stable.
Multiple choice questions:
1.The word “emulsion” comes from the Latin word for
a)to milk
b)to emulsify
c)to mix
d)to grind
2.An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally
a)immiscible
b)nonmixable
c)unblendable
d)all of these
3.Emulsions are part of a more general class of ____ systems of matter called colloids.
a)single phase
b)two phase
c)both of these
d)none of these
4.Which of the following are examples of emulsions?
a)vinaigrettes
b)milk
c)mayonnaise
d)all of these
5.Types of emulsions are
a)Oil in water emulsions
b)Water in oil emulsions
c) Multiple emulsions
d)All of these
6.In O/W type emulsion oil is the dispersion medium and water is the dispersed phase.
a)true
b)false
7.Which type of emulsion is non greasy and easily removable from the skin?
a)O/W
b)W/O
c)Multiple emulsion
d)Micro emulsion
8.Which of the following is W/O type emulsion?
a)vanishing cream
b)cold cream
c)both of these
d)none of these
9.In _____ systems an aqueous phase (hydrophilic) separates internal and external oil phase.
a)O/W
b)W/O
c)W/O/W
d)O/W/O
10._____ is a system in which water droplets may be surrounded in oil phase, which in true encloses one or more oil droplets.
a)O/W
b)W/O
c)W/O/W
d)O/W/O
11.In _____ systems, an organic phase (hydrophobic) separates internal and external aqueous phases.
a)O/W
b)W/O
c)W/O/W
d)O/W/O
12.____ is a system in which oil droplets may be surrounded by an aqueous phase, which in turn encloses one or several water droplets. These systems are the most studied among the multiple emulsions.
a)O/W
b)W/O
c)W/O/W
d)O/W/O
13._____ is clear, stable, liquid mixtures of oil, water and surfactant, frequently in combination with a co-surfactant.
a)Oil in water emulsions
b)Water in oil emulsions
c) Multiple emulsions
d)Micro emulsion
14.Which of the following are types of micro emulsions?
a)O/W
b)W/O
c)W/O/W
d)a and b
15.Micro emulsions are
a)thermodynamically unstable
b)thermodynamically stable
c)no relation with thermodynamics
d)thermodynamically stable only at room temperature
Solutions:
- a)to milk
- d)all of these
- b)two phase
- d)all of these
- d)All of these
- b)false
- a)O/W
- b)cold cream
- d)O/W/O
- d)O/W/O
- c)W/O/W
- c)W/O/W
- d)Micro emulsion
- d)a and b
- b)thermodynamically stable
References:
- Gaurav K. Jain Theory and Practice of Physical Pharmacy, 1st edition 2012 Elsevier, page no. 223, 224, 237-240.
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in CSIR NET JRF Mock Test