ESMOLOL Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Esmolol
IUPAC nomenclature
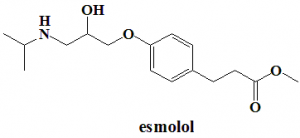
Methyl (RS)-3-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl}propanoate.
Classification
Esmolol is a cardioselective ß1-adrenergic antagonist
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 295.37 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 90°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Very soluble in hydrochloride salt |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1.7 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
- Esmolol competitively binds with ß1-receptors in cardiac tissues and blocks the agonist effect of sympathetic neurotransmitters.
- It blocks the adrenergic stimulation of cardiac pacemaker potential and produces antiarrhythemic activity. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Increasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
- Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
- Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
- Aryloxypropanolamines are more potent than aryloxyethanolamines. [2]
Method of synthesis
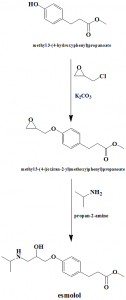
i. Methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate reacts with 2-(chloromethyl)oxirane to give methyl 3-(4-((oxirane-2-yl)methoxy)phenyl)propanoate.
ii. The latter compound is reacted with propan-2-amine to give esmolol.
Therapeutic Uses
Esmolol is used for treatment of:
- Heart rhythm disorders
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter
- Regulation of blood pressure during surgery
Side Effects
Side effects of esmolol are:
- Headache
- Hunger
- Low blood sugar
- Irritability
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Fast heart rate
- Anxiety
- Coldness in hands and feet
- Pain or swelling near the injection site
- Weak and shallow breathing
- Wheezing
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Slow heart beats
- Lightheadedness
MCQs
Q.1 What can be the correct IUPAC nomenclature of Esmolol?
a) (RS)-1-(1-methylethylamino)-3-(1-naphthyloxy)propan-2-ol.
b) Methyl (RS)-3-{4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl}propanoate
c) (RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxy}-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol
d) (RS)-1-{4-[(2-Isopropoxyethoxy)methyl]phenoxybenzamide
Q.2 Which amongst the following statements is/are incorrect related to the SAR of esmolol?
I. Increasing the chain length of the side chain prevents appropriate binding of the required functional groups to the same receptors side.
II. Side chain of aryloxypropanolamines can adopt a conformation that places the hydroxyl and amine groups into approximately the same position in space.
III. Aryloxypropalonamines permits a close overlap with the arylethanomine side chain.
a) I, III
b) II, III
c) I, II, III
d) I, II
Q.3 The correct order for the synthesis of drug esmolol from Methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate can be?
Reaction with 2-(chloromethyl)oxirane
Reaction with propan-2-amine
III. Reduction with help of Pt-Pd catalyst
a) III – II – I
b) I – III – II
c) I – II
d) III – I
Q.4 Side effects of drug Esmolol is/are?
a) Headache
b) Fast heart rate
c) Anxiety
d) All of the above
Q.5 Match the following drugs with their correct molecular weights-
| i. Propranolol | A. 295.37 gm/mol |
| ii. Esmolol | B. 309.4 gm/mol |
| iii. Bisoprolol | C. 325.4 gm/mol |
| iv. Metipranolol | D. 259.34 gm/mol |
a) i-B, ii-A, iii-D, iv-C
b) i-B, ii-A, iii-C, iv-D
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
d) i-D, ii-A, iii-C, iv-B
Q.6 An example of drug from class ß1-adrenergic antagonist?
a) Dopamine
b) Dobutamine
c) Propranolol
d) Esmolol
Q.7 The type of ring system found in Esmolol?
a) Naphthalene
b) Carbazoline
c) Imidazoline
d) Benzene
ANSWERS
1-b
2-c
3-c
4-d
5-d
6-d
7-d
REFERENCES
[1] Benfield P, Sorkin EM. Esmolol. Drugs. 1987 Apr 1;33(4):392-412. [2] Lemke TL, Williams DA, Foye WO. Principles of medicinal chemistry. Williams & Wilkins; 2017, 356.