FESOTERODINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
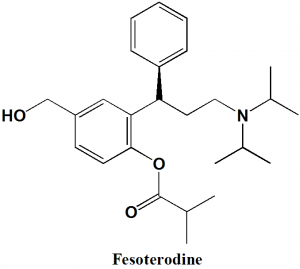
Fesoterodine
IUPAC nomenclature
[2-[(1R)-3-(Di(propan-2-yl)amino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl] 2-methylpropanoateClassification
Fesoterodine is an acetylcholine antagonist. It is a muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 411.6 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 104-107°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Highly soluble |
| 5 | Presence of ring | Benzene |
| 6 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
Fesoterodine converts into its active metabolite, 5-hydroxymethyltolterodine. The active metabolite acts as a muscarinic antagonist, which helps in inhibition of bladder contraction and decreases the detrusor pressure. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
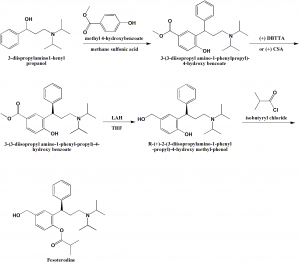
Method of synthesis
i. Reaction of methyl-4-hydroxy benzoate with 3-diisopropylamino-1-phenyl propanol in presence of methane sulfonic acid to give 3-(3-diisopropyl amino-1-phenylpropyl)-4-hydroxy benzoate.
ii. Resolution of the above formed product with(+)2,3-dibezoyl-D-tartaric acid in ethanol produces (+)2,3-dibenzoyl –D-tartaric acid of 3-(3-diisopropyl amino-1-phenyl-propyl)-4-hydroxy benzoate.
iii. The product is then reduces with Lithium aluminum hydride to give R-(+)-2-(3-diisopropylamino-1-phenyl-propyl)-4-hydroxy methyl-phenol.
iv. On reaction of the latter compound with isobutyl chloride produces Fesoterodine. [2]
Therapeutic Uses
Fesoterodine is used for:
- Treatment of overactive bladder
- Reducing the frequent trips to bathroom
- Reducing the urge for frequent voids
- Reducing the leakage of urine
Side Effects
Side effects of Fesoterodine are:
- Constipation
- Headache
- Dry mouth
- Blurred vision
- Dry eyes
MCQ
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug fesoterodine-
| i. When X is an ester | A. Maximum potency |
| ii. Distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon unit | B.Minimum potency |
| . | C. Least potent derivative |
| D. Most potent derivative |
a) i-A, ii-D
b) i-A, ii-C
c) i-B, ii-C
d) i-C, ii-D
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Benztropin: (3-endo)-3-(Diphenylmethoxy)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane
- Fesoterodine: [2-[(1R)-3-(Di(propan-2-yl)amino)-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl] 2-methylpropanoate
- Flurazepam: 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine
- Midazolam: 7-Chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
a) TFTF
b) TTFF
c) FFTT
d) TTFT
Q.3 Number of chiral carbons present in the structure of Fesoterodine?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 The active metabolite of fesoterodine, 5-hydroxymethyltolterodine acts as??
a) Mixed agonist
b) Nicotinic antagonist
c) Muscarinic antagonist
d) ß-inhibitor
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug fesoterodine?
a) Treatment of Insomia
b) Treatment of Alzhiemer’s disease
c) Treatment of Overactive bladder
d) Treatment of Asthma
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Benztropin: acetylcholine antagonist
II. Fesoterodine: Nitrogen mustard
III. Flurazepam: benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
IV. Midazolam: Acetylcholine Nicotinic receptor antagonist
a) I, III
b) I, III, IV
c) II, IV
d) I, II, III, IV
Q.7 Type of ring present in the structure of fesoterodine is?
a) Benzene
b) Pyrimidine
c) Pyrolopyrimidine
d) Not present
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT, Pharmacist,Drug Inspector
ANSWERS
1-a
2-b
3-b
4-c
5-c
6-a
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Vella M, Cardozo L. Review of fesoterodine. Expert opinion on drug safety. 2011 Sep 1;10(5):805-8. [2] Arava V, Bandatmakuru S. Synthesis of fesoterodine: An enantiopure active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research. 2016;8(8):518-38.