FLAVOXATE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
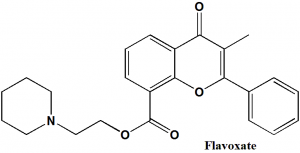
Flavoxate
IUPAC nomenclature
2-(1-piperidyl)ethyl 3-methyl-4-oxo-2-phenylchromene-8-carboxylate
Classification
Flavoxate is an acetylcholine antagonist. It is a muscarinic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 391.5 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 246-248 |
| 4 | Solubility | 10 mg/ml |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.1 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Chromine, benzene and piperidine |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
Flavoxate acts as a direct antagonist for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. It reduces the tonus of smooth muscles in the bladder and thus, reduces the frequent urge for micturition.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Either R1 or R2 must be heterocyclic or carbocyclic.
- The R3 group can be hydrogen, hydroxyl, hydroxymethyl or amide.
- Most potent derivatives has X as an ester.
- X can also be either oxygen or absent completely.
- The N substituent can be quaternary ammonium salt or tertiary amine or both with different alkyl groups.
- Maximum potency obtained when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is 2 carbon units.
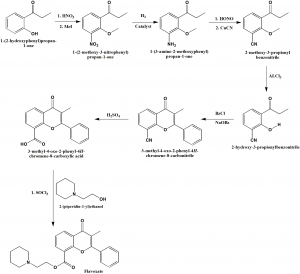
Method of synthesis
i. 1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one undergoes nitration in presence of methyl iodide to give 1-(2-methoxy-3-nitrophenyl propan-1-one.
ii. It then undergoes reduction to produce 1-(3-amino-2-methoxyphenyl) propan-1-one.
iii. On reeaction with nitrous acid followed by reaction with copper cyanide, 2-methoxy-3-propionylbenzonitrile is produced.
iv. Treatment with aluminium chloride produces 2-hydroxy-3-propionylbenzonitrile.
v. The above formed compound on reaction with benzylchloride in presence of sodium benzoate produces 3-methyl-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromene-8-carbonitrile.
vi. The latter compound on reduction and followed by reaction with SOCl2 and 2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethanol, produces flavoxate.
Therapeutic Uses
Flavoxate is used for:
- Help in reducing the leakage of urine
- Reducing the feeling to urinate right away
- Reducing the conditions of frequent trips to bathroom
- Bladder pain
Side Effects
Side effects of flavoxate are:
- Dry mouth
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Nervousness
- Nausea
- Drowsiness
MCQ
Q.1 Correct statements related to the physicochemical properties of drug flavoxate are?
I. Molecular weight: 391.5 gm/mol
II. Present in solid form.
III. Octanol/water partition coefficient is 5.4
IV. Five chiral carbon atoms are present in structure
a) I, II
b) I II, III
c) II, IV
d) II, IV
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Flavoxate | A. 2-(1-piperidyl)ethyl 3-methyl-4-oxo-2-phenylchromene-8-carboxylate |
| ii. Eszopiclone | B. 7-Chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one |
| iii. Chlordiazepoxide | C. 7-Chloro-2-methylamino-5-phenyl-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine-4-oxide |
| iv. Lorazepam | D. (S)-(+)-6-(5-Chloro-2-pyridinyl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl-4-methyl-1-piperazinecarboxylate |
a) i-B, ii-C, iii-A, iv-D
b) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
c) i-A, ii-B, iii-C, iv-D
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-C, iv-B
Q.3 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug Flavoxate?
I. Antogonizes muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
II. Antagonizes nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
III. Decreases the tonus of smooth muscles in the bladder
IV. Increases the tonus of smooth muscles in the bladder
a) I – III
b) I – IV
c) II – III
d) II – IV
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Flavoxate: Nicotinic acetylcholine antagonist
- Aszopiclone: nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic
- Chlordiazepoxide: Muscarinic acetylcholine antagonist
- Lorazepam: Benzodiazepine sedative hypnotic
a) TTFT
b) FFTT
c) FTFT
d) TFTT
Q.5 Maximum potency obtained of flavoxate when the distance between the ring substituted carbons is how many carbon units.
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Q.6 Types of ring structure present in flavoxate?
I. Chromine
II.Benzine
III. Piperidine
IV. Pyrrolopyrimidine
a) I, II, III, IV
b) III, IV
c) I, III
d) I, II, III
Q.7 Side effect of drug Flavoxate?
a) Dizziness
b) Constipation
c) Blurred vision
d) All of the above
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-a
2-d
3-a
4-c
5-b
6-d
7-d