FLUTAMIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Flutamide
IUPAC nomenclature
2-Methyl-N-[4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]propanamide.
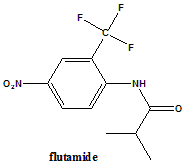
Classification
Flutamide is an antiandrogen. [1]
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 276.21 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 111.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | 9.45 mg/L |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.35 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Aryl ring |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
Flutamide blocks the action of both endogenous and exogenous testosterone by binding to the androgen receptor.
Further , the drug is a potent inhibitor to testosterone-stimulated prostatic DNA synthesis.
It is also capable of inhibiting prostatic nuclear uptake of androgen. [2]
Structural Activity Relationship
- 2- hydroxyl derivative is an active metabolite.
- Electron-withdrawing substituents in the aromatic rings increases the activity.
- A branched alkyl chain alpha to the amide carbonyl have increased activity.
- Compounds with two electron-withdrawing substituents on the aromatic gave a better potency than the one substituent.
- When the CF3 group was introduced at the C2 position of anilide having only one electronwithdrawing substituent, antiandrogenic activity of compound increased by five-fold [3]
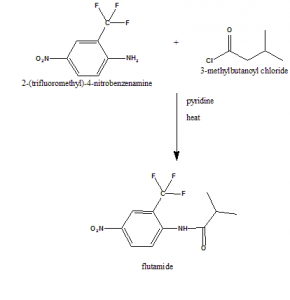
Method of synthesis
2-(trifluoromethyl)-4-nitrobenzamine is reacted with 3-methylbutanoyl chloride to give flutamide.
Therapeutic Uses
The drug used for the treatment of:
- Advanced prostate cancer at stage D2, when there is evidence of metastases.
Side Effects
- Common side effects of flutamide include diarrhea, impotency, nipple discharge, decreased libido, swelling of the breast and hot flashes.
- Less common side effects are yellow-green discoloration of urine, increased blood tests measuring liver function, nausea and vomiting.
MCQs
Q.1 “2-Methyl-N-[4-nitro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]propanamide” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Flutamide
b) Daunorubicin
c) Anastrozol
d) Thiotepa
Q.2 How many statements below are true with respect to the SAR of the drug?
- 2- hydroxyl derivative is an active metabolite.
- Electron-withdrawing substituents in the aromatic rings increases the activity.
- A branched alkyl chain alpha to the amide carbonyl have increased activity.
- Compounds with two electron-withdrawing substituents on the aromatic gave a better potency than the one substituent.
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Q.3 The drug flutamide has how many chiral centers?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Q.4 The melting point of flutamide is?
a) 50 °C
b) 111 °C
c) 150 °C
d) 211 °C
Q.5 Flutamide is used as
a) An antimalarial drug
b) An anti-cancer drug
c) Sedative
d) None of the above
Q.6 The correct classification of the drug Flutamide can be?
a) Progestins
b) Aromatase inhibitors
c) Taxanes
d) Antiandrgens
Q.7 How many number of rings are found in the chemical structure of the drug Flutamide?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
ANSWERS
1-a
2-d
3-a
4-b
5-b
6-d
7-a
REFERENCES
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 6thEdn. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. 2008: 820. [2] Labrie F. Mechanism of action and pure antiandrogenic properties of flutamide. Cancer. 1993 Dec 15;72(S12):3816-27. [3] Singh SM, Gauthier S, Labrie F. Androgen receptor antagonists (antiandrogens) structure-activity relationships. Current medicinal chemistry. 2000 Feb 1;7(2):211-47.