Gas CHROMATOGRAPHY INSTRUMENTATION AND APPLICATION; Questions with Answers
INSTRUMANTION OF GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY :-
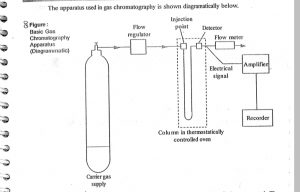
- carrier gas :- Transmits the sample form the point of introduction through the column to the detector. examples of carrier gas is hydrogen, helium, or nitrogen flow rate is depends upon column i.d.→2mm/min, i.d.→15-20mm/min
- purification gas :- two stage of purification is recommended i.e. 1. a sintered metal filter to remove particulate matter and 2. a drying cartridge containing a desiccant to remove water vapor from the CG cartidge also contains a molecular sieve which remove small and trace molecules such as water and low MW hydrocarbons.
- sample injection device :- it will be receive sample vaporize, it instantly and deliver the sample to the head of the column in a sharp concentrated band with minimum fronting or tailing. usually sample in liquid state is introduced by microsyring/hypodermic syring(sample size 1 to 50 μl). the gaseous sample can be introduced in the same way(0.5 to 5 ml) with the help of microsyringe or loop injector.
- columns :- important of GC it is made up of glass or stainless steel.
columns can be classfied
- depending on its use :-
- analytical column :- 1-1.5 meters length and 3-6 mm d.m.
- preparative column :- 3-6 meters length and 6-9 mm d.m.
- depending on its nature :-
- packed column :- column are available in a packed manner .
s.p for GLC :- polyethylene glycol, esters, anides
2. open tubular or capillary column or golay column :-
- long capillary tubing 30-90 m in length
- uniform & narrow d.m of 0.025-0.075 c.m
- made up of stainless steel & from of a coil
3. SCOT column (support coated open tubular column)
- improved version of golay / capillary columns have small sample capacity
- made by depositing a micron size porous layer of supporting material on the inner wall of the capillary column
- Then coated with a thin film of liquid phase.
5. DETECTOR :- decides sensitivity of GC
- Working principal :- difference in property of CG alone and CG with solute is measured.
- TCD(thermal conductivity detector /hot – wire detector):-
- based on a principal that thermal conductivity will vary with the composition of GC.
- the actual detecting elements may be either an electrically heated wire filament or thermister. they both function by detecting change in electrical resistance which can be ultimately measured by WB circuit.
- temp. change→ change in resistance→ measured by wheatstone bridge
- CG should be of high thermal conductivity: H/He
- TC is expressed as caloria/ cm
- used for measurement of trace amount of water
- FID (Flame ionization detector):-
• Burning of compounds in a flame will lead to ion poduction which are collected at opposite electrodes → current produced is directly proportional to concentration of solute.
• Burning H2 is provided as fuel which is supported by air in the form of pure oxygen.
• C.G + OXYGEN → few electron
• C.G + sample + oxygen → more ions → more electron
• About 90% of drug GC analysis are analysis are analyzed by FID.
6. FLOW METER :- Measure flow of CG limit is 20-60 ml\min. Soap bubble flow meter is most commonly used.
7. MODIFICATION IN GC :-
DERIVATIZATION :- To convert polar to non polar , to increase the thermal stability , to increase the ability of detection, Aid in identification.
Temperature programming :- when the mixture contain compounds of widely differing volatility use of chromatograph in iso thermal condition gives unsatisfactory results.
- High volatility compound are eluted first , where as the rest need more time for elution leading to band broadning.
- If separation is carried out at high temperature , the lower B.P compound will be co-eluted & over lapping peaks would be obtained.
- to avoid these problem temperature programming is done where increase in temp is regulated systematically.
APPLICATION OF GC :-
- Quality control and analysis of drug products like anti biotics (penicilin), anti viral (amantidine), general anesthetics, etc.
- ASSAY of drugs – purity of a compound can be determined for drugs like :-
- ATROPINE SULPHATE
- CLOVE OIL
- STEARIC ACID
- in determining the levels of metabolites in body fluids like plasma, urine, serum etc.
3. miscellaneous :-
- analysis of food likes carbohydrates, proteins,lipdis , vitamins, steroids ,and trace elements
- polluent like formaldehyde, carbon monoxide , benzene , DDT etc.
MCQ
1. Which of the following is not a feature of carrier gas used in gas chromatography?
a) It must be chemically inert
b) It should be suitable for the detector employed
c) It should not be completely pure :
d) It should be cheap
2. In which of the following methods are liquid samples injected into the column in gas chromatography?
a) Gas tight syringe
b) Micro-syringe:
c) Rotary sample valve
d) Solid injection syringes
3. Which of the following is the commonly used support material for the packed column in gas chromatography?
a) Glass
b) Metal
c) Diatomaceous earth:
d) Stainless steel
4. Which of the following is the disadvantage of coiled or helical shaped packed chromatographic column?
a) It cannot be packed uniformly
b) It cannot be repacked easily:
c) It is not compact
d) It is not easy to heat it evenly
5. Which detector is not used in GC ?
a. FID
b. TCD
c.A &B
d. TMD
6.which is not application of GC chromatography?
a.Quality control and analysis of drug products like anti biotics (penicilin), anti viral (amantidine), general anesthetics, etc.
b.polluent like formaldehyde, carbon monoxide , benzene , DDT etc.
c.ASSAY of drugs – purity of a compound can be determined for drugs like :-ATROPINE SULPHATE
d. It is purified water.
answer key
1.c
2.b
3.c
4.b
5.d
6.d
REFERNCE:-
TEXT BOOK OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS THIRD EDITION OF DR. RAVI SANKAR (17.1 TO 17.20)
TEXT BOOK OF PHARMACEUTCAL ANALYSIS FOUR EDITION OF DAVID.G.WATSON (261-290)