HPLC-Procedure, Application and Important question for GPAT, GATE, NET, & Pharmacist exam
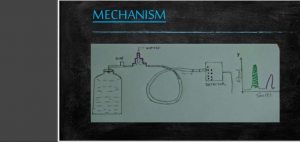
PROCEDURE OF HPLC:-
The sample is introduced through an injection system into the entrance to the column.
The stationary phase is porous silica.
mobile phase can either be aqueous or organic solvent
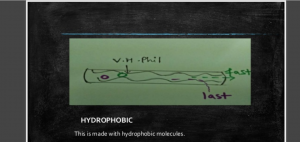
In interaction between mobile and stationary phase, two types of scenarios can result.

APPLICATION OF HPLC :-
The main purpose of the HPLC technique is to identify, quantify and purify a particular analyte or compound. Both quantitative and qualitative analysis can be done. HPLCs can be used in the following applications:
- Water purification
- Detection of impurities in pharmaceutical industries
- Pre-concentration of trace components
- Ligand-exchange chromatography
- Ion-exchange chromatography of proteins
- High-pH anion-exchange chromatography of carbohydrates and oligosaccharides
- NO.1 seperation method of pharmacopoeias assay :- >90% drugs, particle size is decreased from 50-70μ to 3-10μ which is increases the resolution.
MCQ
1. Degassing of the mobile phase can be done by all of the following except
A. Distillation
B.Sparging
C.Reverse Osmosis
D.Vacuum Pumping
(A) To increase the resolution
(B) To increase the detectability of a compound
(C) To decrease the retention time
(D) All of the above
3.Which of the following will improve the efficiency of the separation process in liquid chromatography?
a) Increase in sample size, increase in column diameter
b) Reduction in sample size, increase in column diameter
c) Increase in sample size, reduction in column diameter
d) Reduction in sample size, reduction in column diameter
4. Which of the following columns are not used in liquid or high performance liquid chromatography?
a) Analytical column
b) Separation column
c) Guard column
d) Capillary column
5.Which of the following types of liquid chromatography uses immobilized biochemical as a stationary phase?
a) Ion exchange chromatography
b) Exclusion chromatography
c) Affinity chromatography
d) Gel permeation chromatography
6. In reversed phase HPLC, there is a
a. Non-polar solvent/polar column
b. Polar solvent/ Non polar column
c.polar solvent/polar column
d. All of the above
7. For a typical adsorbent such as silica gel, the most popular pore diameter are,
a. 60&100 A°
b. 70& 120A°
c.89 & 110 A°
d.ALL OF THE ABOVE
8. Which of the following is not application of HPLC ?
a. Pre-concentration of trace components
b. Ligand-exchange chromatography
c.Ion-exchange chromatography of protein
d. identification of polysacharide
ANSWER KEY
1.C
2.D
3.D
4.D
5.C
6.B
7.A
8.D
REFERENCE :-
TEXT BOOK OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS THIRD EDITION DR.S.RAVI SANKAR.(18.1 TO 18.15)
TEXT BOOK OF DAVID G. WATSON FOURTH EDITION (296 TO 344)