IFOSFAMIDE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ and Chemical Structure
Ifosfamide
IUPAC nomenclature
N,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1,3,2-oxazaphosphinan-2-amide 2-oxide
Classification
Ifosfamide falls under the category of alkalyting agents and from nitrogen mustard family.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 261.1g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | White colored crystalline powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 39-41 °C |
| 4 | Solubility | 3780 mg/L in water |
| 5 | Octanol water partition coefficient | 0.86 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | oxazaphosphorine ring |
Mechanism of Action
1. In the liver, biotransformation of the drug takes place by the mixed-function oxidases.
2. Metabolites so formed are the active forms of the drug.
3. Metabolites binds with the nucleic acids along with other essential cell component.
4. In the DNA strand, alkylation takes place on the N-7 position of the guanine
5. This results in the formation of cross linkages between the DNA strands results in the death of cell. [1]
Structural Activity Relationship
- Replacement of the sulfur atom by nitrogen will lower the toxicity.
- 2-chloroethyl group is essential for the activity as the aziridine cation is formed by this only. Aziridine cation will attach with the alkylates of the DNA later.
- Binding with the amino group will increase the oral route availability o the drug
- The introduction of the substituted phenyl group will also increases the oral route availability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring introduction will increase the stability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring will further increase the distribution of the drug throughout the body.
- Benzimidazol ring can provide the local and faster action of the drug.
- Benzimidazol will further decrease the half life of compound. [2]
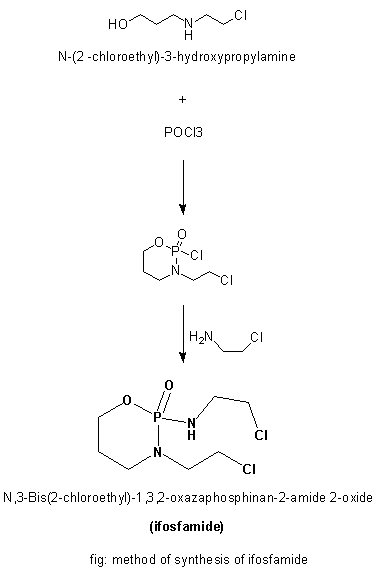
Methods of Synthesis
i. N-(2 –chloroethyl)-3-hydroxypropylamine hydrochloride is treated with POCl3.
ii. The product so formed is reacted with 2-chloroethlamine hydrochloride to give ifosfamide.
iii. The whole reaction takes place in the presence of triethylamine.
Therapeutic Uses
Cancers: testicular cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, osteosarcome, bladder cancer, lung cancer, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer
Side Effects
- Hemorrhagic cystitis [3]
- Encephalopathy
- Interferes with neurologic development in children
- Also affects the peripheral nerves of the patient
MCQs
Q.1 What is the correct IUPAC name of ifosfamide?
a) N,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1,3,2-oxazaphosphinan-2-amide 2-oxide
b) (RS)-N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1,3,2-oxazaphosphinan-2-amine 2-oxide
c) 2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethan-1-amine
d) 1,3,2-oxazaphosphinan-2-amine 2-oxide
Q.2 Ifosfamide produces action through?
a)cell membrane destruction
b)DNA damage
c)cell wall dissolution
d)inhibiting the ETC cycle
Q.3 Aromatic ring substitution on N,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1,3,2-oxazaphosphinan-2-amide 2-oxide will
a) increase the stability of drug
b) decrease the stability of drug
c) decreases the distribution of drug in body
d) none of the above
Q.4 Side effect of Ifosfamide includes
a) Hemorrhagic cystitis
b) Encephalopathy
c) Interferes with neurologic development in children
d) All of the above
Q.5 Ifosfamide is used for the treatment of
a) auto immune disorder
b) cancer
c)both a and b
d) cardiac arrhythmia
Q.6 Classification of the ifosfamide is?
a) antibacterial drug
b) calcium channel blockerc)
c)COX-2 inhibitors
d) alkalyting agent
Q.7 Which type of ring is present in the ifosfamide?
a) indole ring
b) benzene ring
c) oxazaphosphorine ring
d) none of the above
Answers
1- a
2- b
3- a
4- d
5- b
6- d
7- c
References
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of medical pharmacology. JP Medical Ltd; 2013 Sep 30.: p.822.
[2] Pires J, Kreutz OC, Suyenaga ES, Perassolo MS. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROFILE AND STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP OF ALKYLATING AGENTS USED IN CANCER TREATMENT.
[3] Wilson CO, Beale JM, Block JH. Wilson and Gisvold’s textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,; 2011: pp.360-362.