Lincosamide Antibiotics Notes and MCQ for GPAT, NEETPG , BPharmacy, Nursing and BPT
Overview:
-
Lincosamides are a class of antibiotics that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis.
-
They are bacteriostatic and primarily effective against Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes.
🔬 Common Drugs
-
Clindamycin (most commonly used)
-
Lincomycin (older, less used)
🔬 Mechanism of Action
-
Binds to the 50S ribosomal subunit, inhibiting peptidyl transferase.
-
Prevents peptide chain elongation during protein synthesis.
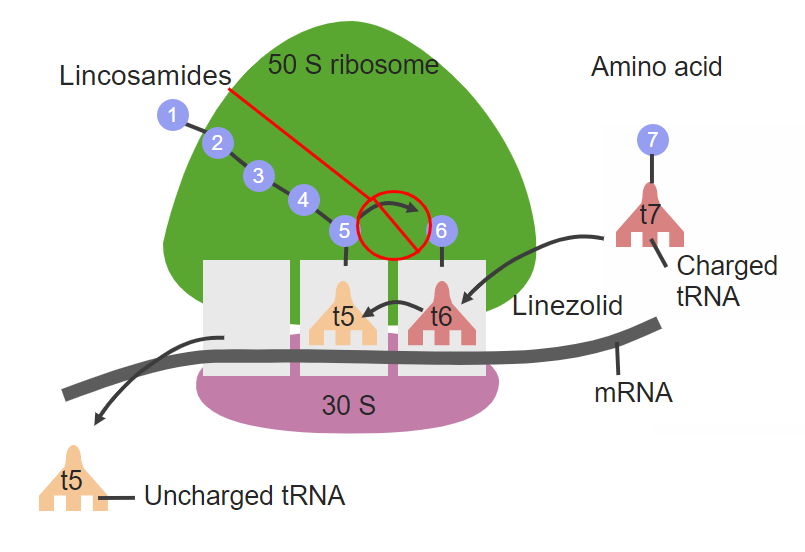
💉 Spectrum of Activity
-
Effective against:
-
Gram-positive cocci (Staphylococcus, Streptococcus)
-
Anaerobes (e.g., Bacteroides fragilis)
-
-
Not effective against most Gram-negative aerobes.
Participate in GPAT MOCK TEST: Click Here
📌 Clinical Uses
-
Anaerobic infections (e.g., aspiration pneumonia)
-
Skin and soft tissue infections (especially MRSA)
-
Dental infections
-
Alternative in penicillin-allergic patients
-
Pelvic inflammatory disease (with gentamicin)
⚠️ Side Effects
-
Pseudomembranous colitis (C. difficile overgrowth)
-
GI upset: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
-
Hepatotoxicity
-
Rash
⚠️ Drug Interactions
-
Antagonism with macrolides/chloramphenicol (compete for 50S site)
-
May enhance neuromuscular blockade (caution with anesthesia/muscle relaxants)
📊 Summary Chart: Lincosamide Antibiotics
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | Inhibits 50S ribosomal subunit → blocks protein synthesis |
| Side Effects | Diarrhea, pseudomembranous colitis, rash, hepatotoxicity |
| Uses | Anaerobic infections, MRSA, dental infections, penicillin allergy |
| Drug Interactions | Avoid with macrolides, chloramphenicol; caution with neuromuscular blockers |
📝 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of lincosamides?
A. Inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase
B. Inhibits 50S ribosomal subunit
C. Inhibits 30S ribosomal subunit
D. Inhibits folate synthesis
Answer: B. Inhibits 50S ribosomal subunit
2. Clindamycin is primarily effective against which group of organisms?
A. Gram-negative aerobes
B. Mycobacteria
C. Anaerobes and Gram-positive cocci
D. Spirochetes
Answer: C. Anaerobes and Gram-positive cocci
3. A major and potentially life-threatening side effect of clindamycin is:
A. Ototoxicity
B. Pseudomembranous colitis
C. Nephrotoxicity
D. Bone marrow suppression
Answer: B. Pseudomembranous colitis
4. Which of the following drugs may have antagonistic interaction with clindamycin due to binding the same ribosomal site?
A. Penicillin
B. Tetracycline
C. Macrolides
D. Fluoroquinolones
Answer: C. Macrolides
5. Which of the following is NOT a typical use of clindamycin?
A. MRSA skin infections
B. Gram-negative sepsis
C. Dental abscess
D. Aspiration pneumonia
Answer: B. Gram-negative sepsis