MASS SPECTROSCOPY PART -2- Ionization Technique, Source, MCQ
Mass spectroscopy is significantly depends upon the ionization method. Ionization can be categorized into two part
- Hard ionization technique :- High energy, Increased fragmentation
- Soft ionization technique :- Low energy, Decreased fragmentation
IONIZATION TECHNIQUES :-
- FOR VOLATILE COMPOUNDS :-A. ELECTRON IMPACT , B. CHEMICAL IONIZATION, C.FIELD IONIZATION
- FOR NON VOLATILE COMPOUNDS :-A.Field desorption
B. Desorption ionization by particle/radiation
1. Laser desorption (MALDI)
2. FAST ATOM BOMBARDMENT (FAB)
3.ION MASS SPECTROSCOPY (SIMS)
4. PLASMA DESORPTION
5. CALIFORNIUM PLASMA DASORPTION
6. ELECTRON SPRAY IONIZATION(ESI)
7. THERMO SPRAY IONIZATION (TSI)
SOURCES OF IONS :-
APCI (Atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation):- Ionisation by reaction with reagent formed with a plasma discharge in air.
CALIFORNIUM FISSION IONISATION :- Ionisation as a result of impact with fission fragments from 252Cf.
Ci(chemical ionisation):- ionisation by reaction with gaseous reagent.
Di(desorption ionisation):- This is a general term encompassing all form of direct ionisation from a solid or liquid sample.
ESI(ELECTROSPRAY IONISATION):- Ionisation produced by spraying a sample solution through a conducting capillary tube at a high potential.
EI(ELECTRON IONISATION):- Ionisation in the gas phase by interaction with a beam of electrons.
FAB (FAST ATOM BOMBARDMENTS):- Ionisation by impact of a beam of energetic atoms and/or ions from an ion gun into a liquid matrix and the subsequent transfer of energy from the matrix to the analyte.
MALDI (MATRIX ASSISTED LASER IONISATION):- Ionisation by effect illumination with a beam of laser generated light into a matrix containing a small proportion of analyte.
SOFT IONISATION :- methodes leading to the formation of ions with low internal energies.
TI(THERMAL IONISATION):- Ionisation induced at high temp. in a gaseous sample with a microwave or an inductively coupled plasma.
TSP (THERMOSPRAY IONISATION):- IONISATION FROM A SOLUTION OF ANALYTE BY PASSING THROUGH A HEATED TUBE.
IONIZATION TECHNIQUE SUMMARY :-
| IONIZATION | VOLATILE | THERMAL | SIZE | AMOUNT |
| EI | YES | STABLE | SMALL | 1-2mg |
| CI | YES | STABLE | SMALL | 1-2mg |
| FI | YES | STABLE | SMALL | 1-2mg |
| FAB | NO | LABILE | MEDIUM | 50μ-1mg |
| FD | NO | LABILE | MEDIUM | 1-2 mg |
| MALDI | NO | LABILE | LARGE | 250-500μg |
| ESI | NO | LABILE | LARGE | 1-300μg |
TYPES OF PEAKS :-
- PARENT PEAK, MASS PEAK OR MOLECULAR ION PEAK :- The peak normally with highest m/e value is called as M+
- BASE PEAK :- The most intense peak (tallest on y – axis) is called as base peak.
- M+1 peak :- It occurs due to the presence of 13C,2H,15N,33S.
- m+2 peak :- It occurs due to the presence of 18O,34S,37Cl,81Br.
APPLICATION OF MS :-
1.Structure elucidation :– Using nitrogen rule, peak matching fragmentation pattern of compound and % abundance of isotopes structure elucidation of organic compound can be done.
2.Detection of impurities :– Impurities present can be detected by the additional peaks, highest value of mass peak than compound itself and from the fragmentation pattern.
3. Quantitaive analysis :– The intensity of peak correspond to the proportion of fragments. By comparing with standard drug the quantity of sample can be estimated.
4.Drug metabolism studies :- By recording the mass spectrum of metabolite and that of pure drug the metabolism of the drug can be known.
5.Clinical,toxicological and forensic application :– Very minute quantites of the drug can be used to find out mass and hence the substance can be identified from the mass spectral pattern.
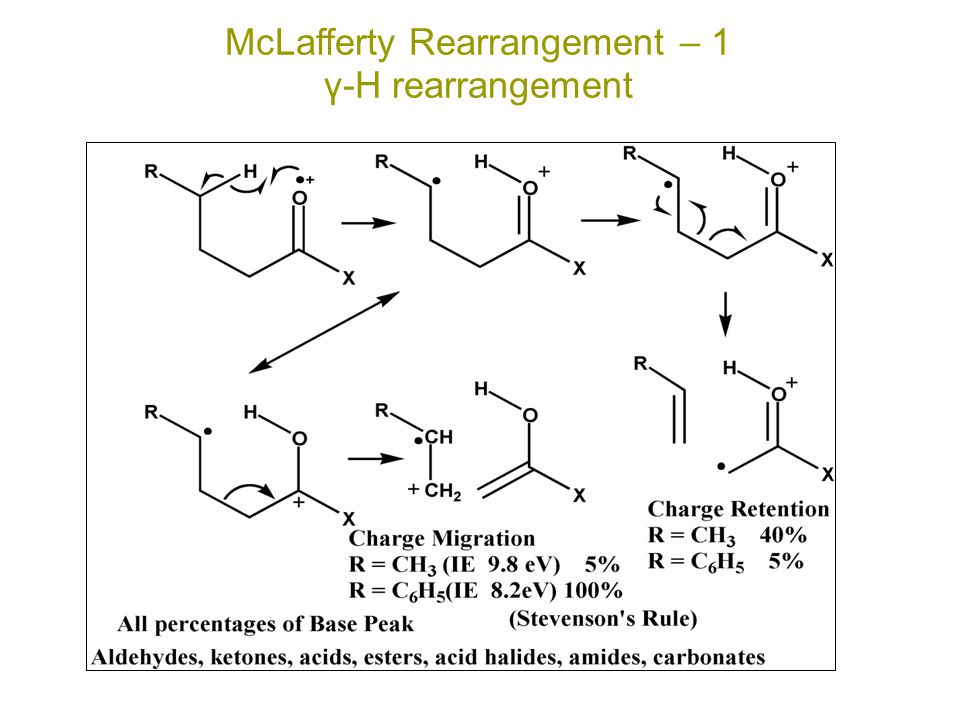
MCLAFFERTY REARRANGEMENT :-
The loss of an alkene fragment by cyclic rearrangements of a carbonyl compound unsaturated compound with γ-hydrogens under go mc-lafferty rearrangements.
MECHANISM :-
Fragmentation take place only at γ-hydrogen
↓
Then this hydrogen is obstructed by oxygen of carbonly group or unsaturated compound
↓
Carbonyl group is converted to hydroxyl group
↓
bond break down between α and β carbon resulting in liberation.
REACTION :-
MCQ:-
1.which molecules shows m+1 peak ?
A.34S
B.81Br
C.18O
D.33S
2.which ionization technique is not used for a VOLATILE compound ?
A.CI
B.FAB
C.FI
D.EI
3.How many mg sample is required for FAB methode ?
A.1-2 mg
B.3-4 mg
C.50μ-1mg
D.10-20 mg
4.MALDI is methode of which spectroscopy ?
A. UV SEPCTROSCOPY
B.IR SEPCTROSCOPY
C.MS SEPCTROSCOPY
D.NMR
5.Which is sample destructive technique ?
A. UV SEPCTROSCOPY
B.IR SEPCTROSCOPY
C.MS SEPCTROSCOPY
D.NMR
6. in which technique heated tube are used for ionization of sample?
A.TSP
B.MALDI
C.CI
D. EI
ANSWER KEY
1.D
2.B
3.C
4.C
5.C
6.A
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
REFERENCE :-
TEXT BOOK OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS THIRD EDITION OF Dr.s.ravi sankar (pg.no.8.1 to 8.5)
TEXT BOOK OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS FOURTH EDITION DAVID G WASTON (PG.NO. 200 TO 244)