MELPHALAN Synthesis, SAR, MCQ and Chemical Structure
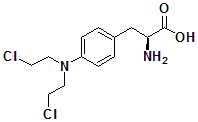
Melphalan
It is a Anticancer Drug.
IUPAC nomenclature
4-[bis(2-Chloroethyl)amino]-L-phenylalanine
Classification
Melphalan falls under the category of Nitrogen mustard alkalyting agents.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 305.2 g/mol |
| 2 | Appearance | White to buff colored powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 182.5°C |
| 4 | Solubility | < 1 mg per ml at NTP |
| 5 | Octanol water partition coefficient | -0.52 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Phenyl ring |
Mechanism of Action
- Alters Guanine nucleotide in DNA through alkylation
- Causes linkages between strands of DNA.
- DNA and RNA synthesis are inhibited.
- Cytotoxicity occurs in both dividing and non-dividing tumors.[1]
Structural Activity Relationship
- Replacement of the sulfur atom by nitrogen will lower the toxicity.
- 2-chloroethyl group is essential for the activity as the aziridine cation is formed by this only. Aziridine cation will attach with the alkylates of the DNA later.
- Binding with the amino group will increase the oral route availability of the drug
- The introduction of the substituted phenyl group will also increases the oral route availability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring introduction will increase the stability of the drug.
- Aromatic ring will further increase the distribution of the drug throughout the body.
- Benzimidazole ring can provide the local and faster action of the drug.
- Benzimidazol will further decrease the half life of compound. [2]
Methods of Synthesis
- 4-Nitro-L-phenylalanine is converted to its phthalimide by heating with phthalic anhydride. It is converted to ethyl ester.
- Corresponding aniline is produced through catalytic hydrogenation
- It is then heated in acid with oxirane
- Then it is treated with phosphorous oxichloride.
- After removal of the protecting groups by heating in presence of HCl produces Melphalan.
Therapeutic Uses
- Breast cancer
- Neuroblastoma
- Ovarian cancer
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Multiple myeloma
Side Effects
- Most commonly, people experiences low blood count, nausea and vomiting.
- In some patients it produces allergic reactions, moth soares, diarrhea, loss of fertility, hair loss, nephrotoxicity and arrthmias.
- There is very low probability of developing blood cancer.
- Bone marrow depression is the most important toxicity.[3]
MCQs
Q.1 Which amongst the following terms is not related with melphlan?
a) Alkeran
b) Sarcolysin
c) Evomela
d) Carpine
Q.2 Predict the correct sequence for the action of Melphalan
i. Cytotoxicity occurs in both dividing and non-dividing tumors
ii. DNA and RNA synthesis are inhibited.
iii. Causes linkages between strands of DNA
iv. Alters Guanine nucleotide in DNA through alkylation
a) iii – iv – i – ii
b) i – ii – iv – iii
c) iv – iii – ii – i
d) iv – ii – iii – i
Q.3 Oral route availability of melphalan can be increased through
a) Binding with amino group
b) binding with benzimidazole ring
c) binding with substituted phenyl group
d) both a) and c)
Q.4 What is the starting product for the synthesis of melphalan?
a) 4-Nitro-L-phenylalanine
b) methanol
c) ethylene oxide
d)ammonia
Q.5 Melphalan is mainly used for the treatment of
a) acute gout
b) prostatic cancer
c) leukemia
d) multiple myelomas
Q.6 An important side effect of melphalan is
a) rhabdomyosarcoma
b) ovarian cancer
c) bone marrow depression
d) all of the above
Q.7 Which type of ring is present in the melphalan?
a) indole ring
b) benzene ring
c) cycloalkane
d) phenyl ring
ANSWERS
1-d
2-c
3-d
4-a
5-d
6-c
7-d
References
[1] Tripathi KD. Essentials of medical pharmacology. JP Medical Ltd; 2013 Sep 30.: p.822. [2] Pires J, Kreutz OC, Suyenaga ES, Perassolo MS. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROFILE AND STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIP OF ALKYLATING AGENTS USED IN CANCER TREATMENT. [3] Wilson CO, Beale JM, Block JH. Wilson and Gisvold’s textbook of organic medicinal and pharmaceutical chemistry. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,; 2011: pp.360-362.