NAPHAZOLINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
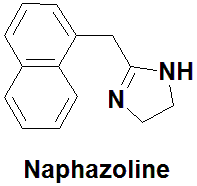
Naphazoline
IUPAC nomenclature
2-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole.
Classification
Naphazoline is a α1-adenergic agonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 210.27 |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 257°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Water solubility is 0.0381 mg / ml |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 3.88 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Naphthalene and imidazoline rings present |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | Not present |
Mechanism of Action
- Naphazoline helps in decreasing congestion at the site of administration through stimulation of the α-adrenergic receptors in the arteriols.
- It also stimulates the release of norepinephrine in the sympathetic nerves, which later binds with α-adrenergic receptors which causes vasoconstriction.
- Naphazoline also acts as mild ß-adrenergic agonist which causes vasodilation after he effect of α-adrenergic is over.
- Due to trigger of negative feedback loop, results in rhinitis medicamentosa after long time administration of Naphazoline when it is stopped.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Primary or secondary aliphatic amine separated by two carbons from a substituted benzene ring is essential for the high agonist activity.
- The hydroxyl substituted carbon must be in the R configuration for the maximal direct activity.
R1 substitution:
- When R1 is increased in size, activity of alpha receptors decreases and activity of the beta receptors increases
- Activity of both alpha and beta receptors is maximum when R1 is methyl group.
- Alpha agonist activity decreases when R1 is larger than methyl, and went negligible when R1 is isopropyl.
- Large lipophillic groups can afford compounds with alpha blocking activity.
- N-substituent provides selectivity for different receptors.
- Arylalkyl group can provide beta selectivity, increased cell penetration and increased lipophillicity for the longer duration of action.
R2 substitution:
- Ethyl group can eliminate the alpha activity of the drug.
- Erythrostero isomers have maximal activity.
- The additional methyl group makes the drug more selective for the alpha2
R3 substitution on the aromatic ring:
- 3’,4’-dihydroxy substituted benzene ring has poor oral activity.
- 3’, 5’-dihydroxy compounds are orally active.
- At least one of the groups is required which can form hydrogen bonds. And if only one group is present then it is preferred at 4’ position to retain the beta2
- If phenyl group has no phenolic substituent then it may act directly or indirectly.[2]
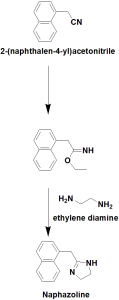
Method of synthesis
i. (1-naphthyl)acetonitrile reacts with ethanol to give an iminoester.
ii. The iminoester undergoes cyclization reaction when reacts with ethylinediamine to give naphazoline.
Therapeutic Uses
Naphazoline is used as a degongestant.
Side Effects
Some of the side effects of naphazoline are
- rhinitis medicamentosa
- several hypertensive disorders.
MCQs
Q.1 Correct statements for the Naphazoline drug are?
I. Molecular weight is 210.27gm/mol
II. Water solubility is 31 mg/ml
III. Present as yellow oily liquid at room temperature.
IV. Octanol/water partition coefficient is 3.88
a) I, III
b) I, IV
c) I, II, III
d) IV
Q.2 Match the following of the drugs with their correct IUPAC names.
| i. Naphazoline | A. (RS)-[4-(1-Hydroxy-2-tert-butylamino-ethyl)-2-(4-methylbenzoyl)oxy-phenyl] 4-methylbenzoate |
| ii. Bitolterol | B. 2-[(4-tert-butyl-2,6-dimethylphenyl)methyl]- 4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole |
| iii. Xylometazoline | C. 3-(4,5-Dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-ylmethyl)-2,4-dimethyl-6-tert-butyl-phenol |
| iv. Oxymetazoline | D. 2-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole |
a) i-D, ii-A, iii-B, iv-C
b) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-B, ii-C, iii-D, iv-A
d) i-A, ii-D, iii-, iv-B
Q.3 Correct steps for the mechanism of action of the drug Naphazoline?
I. Vasoconstriction
II. Realease of norepinephrine
III. Decrease in the congestion
IV. Stimulation of αadrenergic receptors
a) I – IV – III – II
b) III – II – I – IV
c) I – III – II – IV
d) IV – III – II – I
Q.4 Correct sequence for True/false for the classification of the drug can be?
- Terbutaline: Selective α-adrenergic agonist
- Dopamine: ß-adrenergic agonist
- Phenoxybenzamine: Nonselective adrenergic agonist
- Naphazoline: Mixed acting sympathomimetics
a) FFTF
b) FTFF
c) TFFF
d) FFFF
Q.5 Large lipophillic groups at R1 substitution can-
a) Afford compounds with α-blocking activity
b) Provides maximal direct activity
c) Increase both α and ß activity
d) None of the above
Q.6 The correct sequence for the steps for synthesis of drug naphazoline from (1-naphthyl)acetonitrile?
I. Reaction with ethanol
II. Reaction with Sulfuric acid
III. Reaction with ethylenediamine
IV. Hydrogenation
a) I – III
b) II – III
c) III – II
d) III – IV
Q.7 Side effect of drug Naphazoline includes?
a) Hair loss
b) Decrease in blood count
c) Rhinitis medicamentosa
d) Liver abnormalities
ANSWERS
1-b
2-a
3-d
4-d
5-a
6-a
7-c
REFERENCES
[1] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 340 [2] Lemke TL, Zito SW, Roche VF, Williams DA. Essentials of Foye’s principles of medicinal chemistry. Wolters Kluwer; 2017, 348-352