Notes on Anti-Malarial Drugs Mechanism (via Chart) and MCQ for GPAT, NIPERJEE, NEETPG and Nursing exams
Notes on Anti-Malarial Drugs Mechanism (via Chart)
🔄 Lifecycle of Plasmodium
-
Mosquito Stage (Anopheles bite)
-
Injects sporozoites into human bloodstream.
-
-
Liver Stage (Hepatic)
-
Sporozoites → liver cells → schizonts → merozoites.
-
-
Blood Stage (Erythrocytic)
-
Merozoites infect RBCs → trophozoites → schizonts → burst and infect new RBCs.
-
Some differentiate into gametocytes.
-
-
Transmission Back to Mosquito
-
Gametocytes taken up by mosquito → sexual cycle continues.
-
Participate in GPAT MOCK TEST: Click Here
-
Mechanism of Anti-Malarial Drugs
Drug Class Mechanism Examples Artemisinin Produces free radicals → damage parasite proteins and membranes. Dihydroartemisinin, Artesunate, Artemether Chloroquine Inhibits heme polymerization → buildup of toxic heme kills parasite. Chloroquine, Quinine Atovaquone Inhibits mitochondrial electron transport → parasite can’t produce ATP. Atovaquone, Proguanil 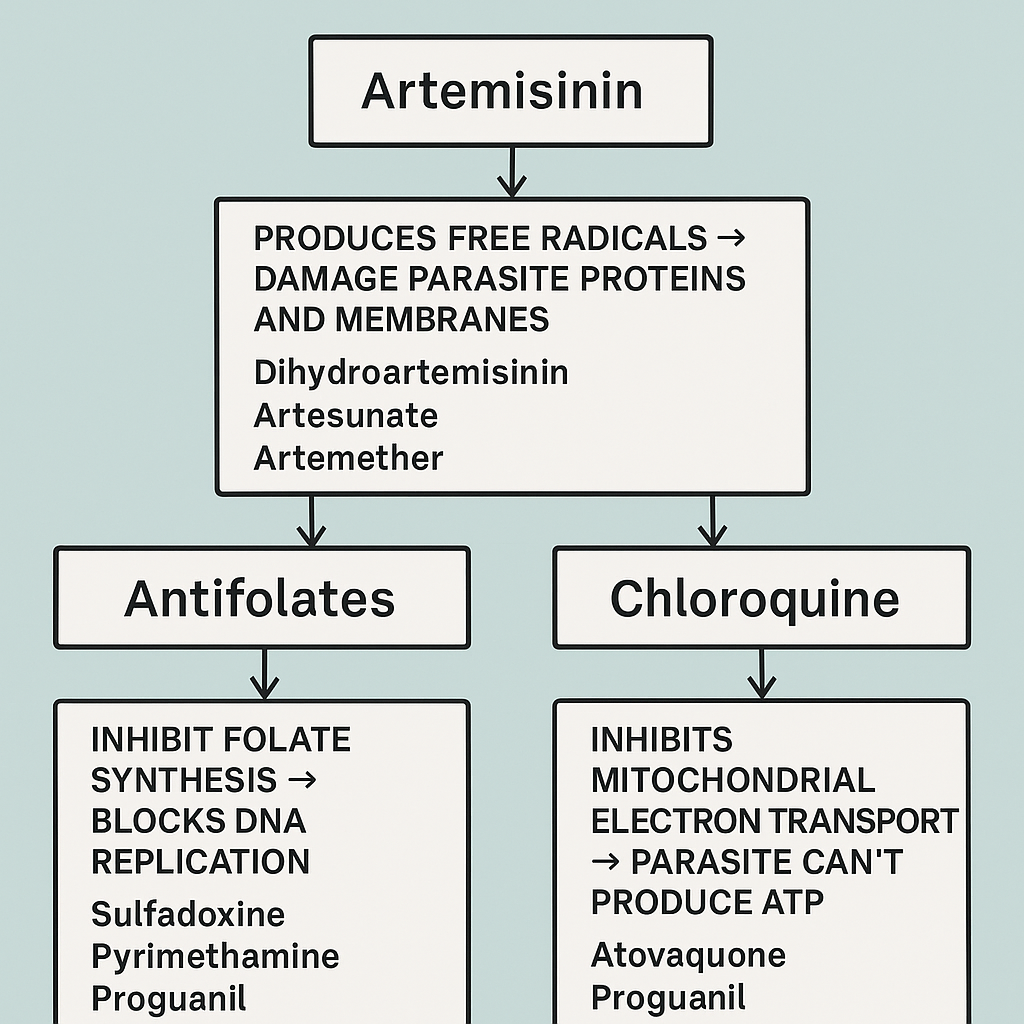
-
MCQs on Anti-Malarial Drugs
-
-
Which stage of the Plasmodium life cycle is targeted by most antimalarial drugs?
A. Sporozoite
B. Liver schizont
C. Erythrocytic stage
D. Gametocyte
✅ Answer: C -
What is the mechanism of action of Chloroquine?
A. Mitochondrial inhibition
B. Free radical generation
C. Heme detoxification inhibition
D. Protein synthesis inhibition
✅ Answer: C -
Which drug class includes Artesunate and Dihydroartemisinin?
A. Quinolines
B. Sulfonamides
C. Artemisinins
D. Biguanides
✅ Answer: C -
Atovaquone primarily targets which part of the parasite’s metabolism?
A. Glycolysis
B. Nucleic acid synthesis
C. Mitochondrial electron transport chain
D. Cytoskeletal assembly
✅ Answer: C -
Why is heme toxic to Plasmodium?
A. It inhibits ATP synthase
B. It damages membranes and enzymes
C. It blocks protein synthesis
D. It interferes with DNA replication
✅ Answer: B
-