Notes on Chloramphenicol Pharmacology, Mechanism, ADR, Uses and MCQ for GPAT, NEETPG
Notes on Chloramphenicol Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action:
-
Chloramphenicol inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit.
-
It inhibits peptidyl transferase activity, preventing peptide bond formation.
-
It is bacteriostatic but can be bactericidal against H. influenzae, N. meningitidis, and Bacteroides.
💊 Pharmacokinetics:
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Absorption | Well absorbed orally |
| Distribution | Widely distributed; crosses blood-brain barrier (BBB) and placenta |
| Metabolism | Primarily in the liver via glucuronidation |
| Excretion | Renal (inactive metabolites), small amounts via bile |
| Half-life | Prolonged in neonates (due to immature liver enzymes) |
⚕️ Clinical Uses:
-
Meningitis (especially in β-lactam allergy)
-
Typhoid fever
-
Rickettsial infections (e.g., Rocky Mountain spotted fever, especially when tetracyclines are contraindicated)
-
Anaerobic infections
-
Eye infections (topically)
⚠️ Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs):
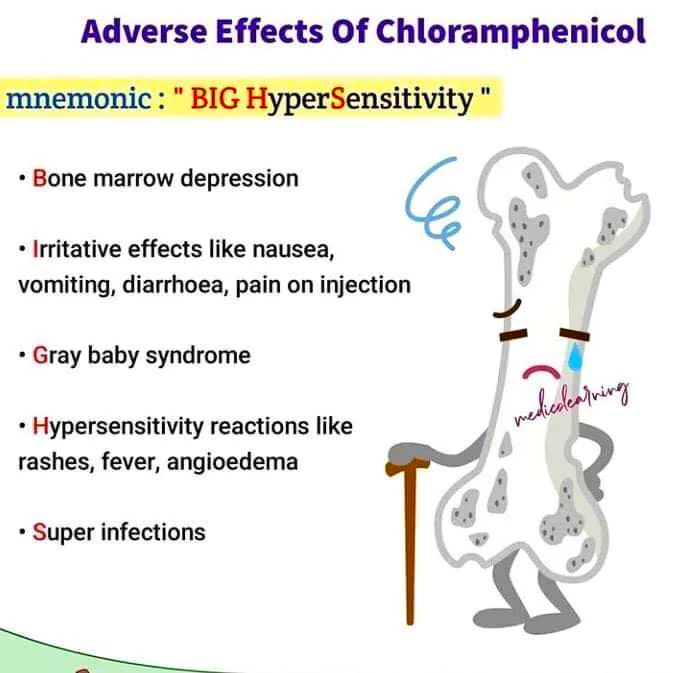
-
Bone marrow suppression:
-
Dose-dependent: reversible
-
Idiosyncratic aplastic anemia: irreversible, rare but fatal
-
-
Gray baby syndrome (due to immature hepatic metabolism in neonates)
-
Symptoms: vomiting, hypotension, cyanosis, ashen gray color
-
-
GI disturbances: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
🚫 Contraindications:
-
Neonates (due to risk of gray baby syndrome)
-
Pregnancy (crosses placenta, risk of fetal toxicity)
-
Known hypersensitivity
-
Patients with pre-existing bone marrow depression
✅ MCQs on Chloramphenicol
Get More MCQ on Cephalosporins: Click Here
-
Chloramphenicol inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to:
A. 30S ribosomal subunit
B. 50S ribosomal subunit
C. DNA gyrase
D. RNA polymerase
Answer: B. 50S ribosomal subunit -
Which of the following is a serious and irreversible adverse effect of Chloramphenicol?
A. Hepatitis
B. Nephrotoxicity
C. Aplastic anemia
D. Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Answer: C. Aplastic anemia -
Gray baby syndrome is associated with which drug?
A. Tetracycline
B. Gentamicin
C. Chloramphenicol
D. Azithromycin
Answer: C. Chloramphenicol -
Which statement about Chloramphenicol pharmacokinetics is TRUE?
A. Poor CNS penetration
B. Metabolized by CYP450
C. Excreted unchanged in urine
D. Crosses the blood-brain barrier
Answer: D. Crosses the blood-brain barrier -
Chloramphenicol is contraindicated in neonates because of:
A. Risk of renal failure
B. Risk of hepatotoxicity
C. Immature glucuronidation enzymes
D. Allergy development
Answer: C. Immature glucuronidation enzymes - Participate in GPAT MOCK TEST