OSELTAMIVIR Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
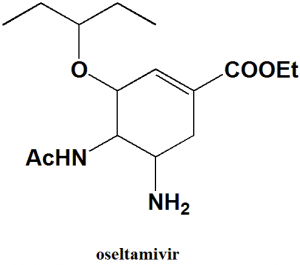
Oseltamivir
IUPAC nomenclature
Ethyl (3R,4R,5S)-5-amino-4-acetamido-3-(pentan-3-yloxy)-cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate.
Classification
Oseltamivir is a Neuraminidase inhibitor analogue.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 312.4 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Solid |
| 3 | Melting point | 190-206°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in water |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 1 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Cyclohexene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 4 |
Mechanism of Action
- Neuraminidase enzyme is necessary for the entry of the virus into new cells.
- Drug binds with neuraminidase protein and inhibits it which unable the virus to escape from the host cell and infect other cells.
Structure Activity Relationship.
- Oseltamivir sulfonate exhibit stronger binding to avian influenza neuraminidase H5N1 than their carboxylate and phosphate analogues.
- Alkoxyl ester derivatives have better bioavailability when administered orally.
- C-4 modified drug having different alkyl chains are most efficient.
- The C-4 derivatization of drug with thiocarbamates, α-amino acids or cyclic secondary amines led to decreased inhibitory activities.
- L-aspargine bearing analogues show best results. [1]
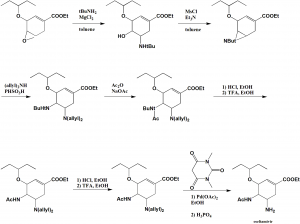
Method of synthesis
The drug can be synthesized through Roche synthesis without azide as source of nitrogen method. It is a 14 step synthesis method with 89% yield.
Therapeutic Uses
Oseltamivir is used for:
- Treatment of symptoms of influenza virus.
- Swine Flu Treatment
Side Effects
Side effects of Oseltamivir are:
- Dizziness
- Increased cough
- Breathing problems
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Allergic reactions
MCQ
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug Oseltamivir-
| i. Alkoxy ester derivatives | A. most efficient |
| ii. C-4 modified drug having different alkyl chains | B. Better bioavailability when given orally. |
| iii. Sulfonates | C. stronger binding with influenza |
| iv.C-4 derivaization with thiocarbamates | D. decreased inhibitory effects |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-B, iv-D
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-B, iv-D
c) i-B, ii-A, iii-C, iv-D
d) i-D, ii-B, iii-C, iv-A
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Chloraquine: 1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide.
- Clobazam: 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-3H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thione
- Oseltamivir: ethyl (3R,4R,5S)-5-amino-4-acetamido-3-(pentan-3-yloxy)-cyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate
- Diazepam: (RS)-2-[{4-[(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)amino]pentyl}(ethyl)amino]ethanol
a) TFTF
b) TTFF
c) FFFF
d) FFTF
Q.3 Type of ring present in the structure of Oseltamivir drug is?
a) Pyrimidine
b) Purine
c) Benzene
d) None of the above
Q.4 Oseltamivir binds with?
a) Neuraminidase protein
b) α-receptors
c) Nicotinic receptor
d) None of the above
Q.5 Which amongst the following is a therapeutic use of drug Oseltamivir?
a) Treatment of Parkinson’s disease
b) Treatment of insomnia
c) Treatment of influenza
d) Treatment of HIV
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Oseltamivir: Neuraminidase inhibitor analogue
II. Nelfinavir: Synthetic guanosin neucleoside
III. Foscarnet: Non nucleoside analogue
IV. Lopinavir: HIV protease inhibitor
a) II, III
b) III, I
c) II, IV
d) I, III, IV
Q.7 Octanol/water partition coefficient of Oseltamivir is?
a) 3
b) 2
c) 1
d) -1
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE
ANSWERS
1-c
2-d
3-d
4-a
5-c
6-d
7-c
REFERENCES
[1] Laborda P, Wang SY, Voglmeir J. Influenza neuraminidase inhibitors: synthetic approaches, derivatives and biological activity. Molecules. 2016 Nov;21(11):1513.