OXAZEPAM Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Oxazepam
IUPAC nomenclature
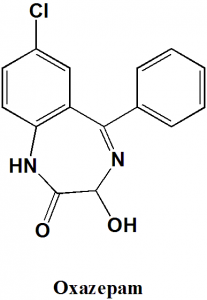
7-Chloro-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one
Classification
Oxazepam is a benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 286.71 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Creamy white to pale yellow powder |
| 3 | Melting point | 205.5°C |
| 4 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 2.24 |
| 5 | Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, chloroform, dioxane |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Diazapine and benzene |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Oxazepam binds with different receptors present in the brain and spinal cord.
ii. This increases the inhibitory effects of the GABA.
iii. Different subunits of GABA are responsible for anxiolytic, sedation, anticonvusant and anterograde amnesia effects.
Structure Activity Relationship
- Ring A should include an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring for binding with 5-phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives.
- An electronegative group at 7-position of the ring A increases the functional anxiolytic activity.
- Substitutions at 6, 8 or 9 position with electronegative group on ring A will decrease the functional anxiolytic activity.
- When Heterocycles used as ring A, drug shows poor pharmacological activity.
- A proton-accepting group is essential on Ring B for binding with GABAA
- When the proton accepting group is present on the 2-position of the ring B, and is in coplanar spatial orientation with Ring A, maximum activity is observed.
- Replacement of oxygen with sulfur in ring B results in alteration in the selectivity for binding with GABA BZR subpopulations, but anxiolytic properties are maintained.
- There is no effect on agonist activity, but the antagonist activity dereases when methylene 3-position or iminie nitrogen of the ring B is substituted.
- Derivatives having the 3-hydroxy moiety are fast excreted.
- Sterically large substituents on ring B , like tert-butyl group reduces the receptor affinity and the in vivo activity.
- 4,5-double bond and 4-position nitrogen is not essential for anxiolystic activity.
- BZR affinity is decreased if C=N bond is replaced with C-N bond.
- 5-phenyl ring C is not necessary for the binding with BZR.
- Substitution at the para position of the ring C decreases the agonist activity of the drug.
- There is no change observed in the agonist property of the drug when there is substitution at ortho position.
- When 1,2-bond f the ring C is annelated with an additional electron rich ring such as imidazole, affinity of the BZR increases. [1]
Method of synthesis
i. 6-chloro-2-xhloromethyl-4-phenylquinazolin-3-oxide is treated with sodium hydroxide to give 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1,2-dihydro-3H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-on-4-oxide.
ii. The above formed compound undergoes acetoxylation reaction of the 3rd position of the benzodiazepine ring by using acetic anhydride, and which reminiscent the Polonovski reaction to produce 7-chloro-1,3-dihydro-3-acetoxy-5-phenyl-2H-benzodiazepin-2-one.
iii. Hydrolysis of the latter formed compound gives oxazepam.[2]
Therapeutic Uses
Oxazepam is used for:
- Treatment of anxiety
- Treatment of Acute alcohol withdrawal
Side Effects
Side effects of oxazepam are:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Mood changes
- Speech problem
- Clumsiness
- Trouble in walking
- Change in libido
- Tremor
- Trouble in urination
- Sleep disturbances
- Fainting
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Pale skin and eyes
- Dark colored urine
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Allergic reactions
- Trouble breathing
MCQ
Q.1 “7-Chloro-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one” is the IUPAC nomenclature of which drug?
a) Trihexyphenidyl
b) Propantheline
c) Oxybutynin
d) Oxazepam
Q.2 Melting point of oxazepam is?
a) 152-162°C
b) 129-130°C
c) 205.5°C
d) 258.5°C
Q.3 Match the following with correct classifications of the drugs.
| i. Propantheline | A. Benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic |
| ii. Oxazepam | B. Barbiturate |
| iii. Clozapine | C. Muscarinic antagonist |
| iv. Thiamylal | D. Benzpines |
a) i-A, ii-C, iii-D, iv-B
b) i-C, ii-A, iii-D, iv-B
c) i-A, ii-B, iii-D, iv-C
d) i-C, ii-B, iii-A, iv-D
Q.4 Mechanism of action of oxazepam is based on?
a) Blocking the Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
b) Blocking the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
c) Increasing the inhibitory effects of GABA
d) Both a) and c)
Q.5 Correct sequence for True and False for the given statements related with the SAR of drug trihexyphenidyl
- Ring A should include an aromatic or heteroaromatic ring for binding with 5-phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one derivatives.
- An electronegative group at 7-position of the ring A decreases the functional anxiolytic activity.
- Substitutions at 6, 8 or 9 position with electronegative group on ring A will decrease the functional anxiolytic activity.
- When Heterocycles used as ring A, drug shows best pharmacological activity.
a) TFTF
b) FTFT
c) TTTT
d)FFTF
Q.6 Steps involved in the synthesis of Oxazepam from 6-chloro-2-xhloromethyl-4-phenylquinazolin-3-oxide in the correct sequence is?
I. Polonovski reaction
II. Treatment with sodium hydroxide
III. Hydrolysis
a) I – II – III
b) I – III
c) II
d) II – I – III
Q.7 The drug Oxazepam is mainly used for?
a) Treatment of anxiety
b) Treatment of Acute alcohol withdrawl
c) Both a) and b)
d) Constipation
Participate in Free Online Test for GPAT, Pharmacist,Drug Inspector
ANSWERS
1-d
2-c
3-b
4-c
5-a
6-d
7-c