Oxazolidinone Antibiotics: Notes on Mechanism, Uses, Side Effects & Drug Interactions and MCQ for GPAT, NEETPG
Class Definition: Oxazolidinones are a class of synthetic antibiotics that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit.
Classification of Oxazolidinone Antibiotics
Oxazolidinones are synthetic antibiotics classified primarily based on generations and clinical development status. Here’s a structured classification:
📚 1. Based on Generation
| Generation | Drugs | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Generation | Linezolid | First approved oxazolidinone (2000); widely used. |
| 2nd Generation | Tedizolid (Tedizolid phosphate) | Newer agent; improved potency; once-daily dosing; better tolerability. |
🏥 2. Based on Development/Approval Status
| Category | Drugs | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| FDA Approved | – Linezolid – Tedizolid phosphate |
Approved for Gram-positive infections. |
| Under Investigation / Development | – Radezolid – Contezolid – TBI-223 |
Newer agents aiming to reduce side effects or resistance. |
🔬 3. Based on Chemical Structure Variants
While all share the oxazolidinone ring, some have structural modifications:
| Type | Example | Structural Feature |
|---|---|---|
| N-aryl substituted | Linezolid, Tedizolid | Enhances binding to ribosomal site. |
| Bicyclic oxazolidinones | Radezolid | More potent binding and broader spectrum (experimental). |
✅ Summary Table: Important Oxazolidinones
| Drug | Generation | Approval | Main Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linezolid | 1st | FDA Approved | MRSA, VRE, pneumonia, SSTIs |
| Tedizolid | 2nd | FDA Approved | Acute bacterial skin/skin structure inf. |
| Radezolid | Next-gen | In trials | Oral/IV; better tolerability |
| Contezolid | Next-gen | China-approved | Similar to Linezolid; fewer side effects |
| TBI-223 | Next-gen | In development | TB treatment potential |
📊 Chart: Mechanism, Uses, Side Effects & Drug Interactions
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
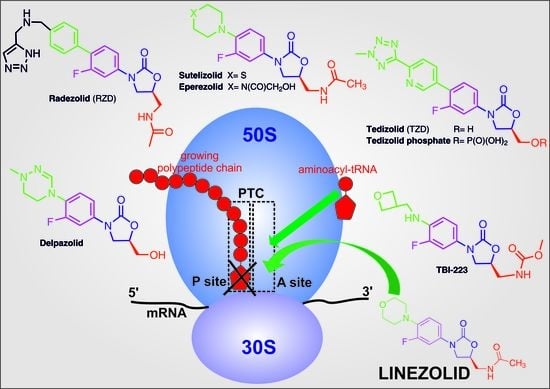
| Mechanism | Inhibits protein synthesis by binding to 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit. Prevents formation of initiation complex. |
| Spectrum | Primarily Gram-positive bacteria (MRSA, VRE, Streptococcus spp.) |
| Uses | – MRSA infections – Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) – Skin and soft tissue infections – Pneumonia |
| Common Drugs | – Linezolid – Tedizolid |
| Side Effects | – Myelosuppression (especially thrombocytopenia) – Peripheral & optic neuropathy (long-term use) – Lactic acidosis – Serotonin syndrome (with SSRIs) |
| Drug Interactions | – SSRIs/SNRIs → ↑ risk of serotonin syndrome – MAOIs → hypertensive crisis – Adrenergic/serotonergic agents |
📉 Chart: Pharmacokinetics of Individual Oxazolidinones
| Drug | Bioavailability | Half-life | Metabolism | Excretion | Dosing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linezolid | ~100% (oral = IV) | ~5-7 hours | Non-enzymatic oxidation | Urine (~30% unchanged) | 600 mg BID |
| Tedizolid | ~91% | ~12 hours | Liver (phosphatase + sulfation) | Feces & urine | 200 mg once daily |
📝 MCQs on Oxazolidinone Antibiotics
1. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of oxazolidinones?
A. Inhibit DNA gyrase
B. Inhibit folate synthesis
C. Inhibit initiation of protein synthesis
D. Bind to 30S ribosomal subunit
→ Correct Answer: C
2. Which of the following is a major side effect of Linezolid during prolonged use?
A. Hepatotoxicity
B. Optic neuropathy
C. Nephrotoxicity
D. Ototoxicity
→ Correct Answer: B
3. Linezolid has a high risk of serotonin syndrome when used with which of the following?
A. Beta-blockers
B. SSRIs
C. NSAIDs
D. ACE inhibitors
→ Correct Answer: B
4. What is the approximate oral bioavailability of Linezolid?
A. 50%
B. 70%
C. 100%
D. 20%
→ Correct Answer: C
5. Tedizolid differs from Linezolid in which pharmacokinetic aspect?
A. Lower half-life
B. Less potent
C. Once-daily dosing
D. Renal excretion unchanged
→ Correct Answer: C