PHENOXYBENZAMINE Synthesis, SAR, MCQ,Structure,Chemical Properties and Therapeutic Uses
Phenoxybenzamine
IUPAC nomenclature
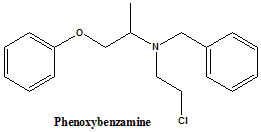
(RS)-N-Benzyl-N-(2-chloroethyl)-1-phenoxypropan-2-amine.
Classification
Phenoxybenzamine is nonselective α-adrenergic antagonist.
Physiochemical Properties
| S. NO. | PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
| 1 | Molecular weight | 303.8 g/mol |
| 2 | Physical appearance | Present in solid form; crystals from petroleum ether. |
| 3 | Melting point | 39°C |
| 4 | Solubility | Soluble in benzene |
| 5 | Octanol/water partition coefficient | 4.7 |
| 6 | Presence of ring | Benzene ring |
| 7 | Number of chiral centers | 1 |
Mechanism of Action
i. Phenoxybenzamine competitively blocks α-adrenergic receptors.
ii. It leads to relaxation of muscles and widening of blood vessels.
iii. Widening of blood vessels results in decrease in blood pressure. [1]
Structure Activity Relationship
- Substitutions with haloalkylamine provides selectivity for binding with the α-adrenoceptors.
- Lacking substituents on both phenoxy and oxyamino carbon chain produces moderate α1-adrenoceptor selectivity.
- 2-ethoxyphenoxy and a 2-i-propoxyphenoxy moiety bearing compounds will have highest potency as an α-adrenoceptor antagonist.
Method of synthesis
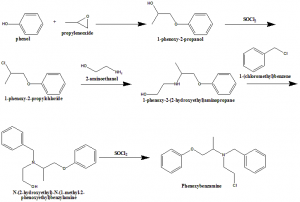
i. Phenol is reacted with propyleneoxide to form 1-phenoxy-2-propanol.
ii. Latter compound undergoes chlorination with thionyl chloride to give 1-phenoxy-2propylchloride
iii. Reacting with 2-aminomethanol will leads to the formation of 1-phenoxy -2-(2-hydroxyethyl)aminopropane.
iv. Alkylation of the secondary aminogroup gives N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N-(1-methyl-2-phenoxyethyl)benzylamine.
v. Hydroxyl group of the later compound is chlorinated to give phenoxybenzmine.
Therapeutic Uses
Phenoxybenzamine is used for:
- Treatment of high blood pressure
- Heavy sweating due to tumor in adrenal gland
- Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Treatment of Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome
Side Effects
Side effects of Phenoxybenzamine are:
- Tired feeling
- Upset stomach
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Stuffy nose
MCQs
Q.1 Match the following with correct SAR of the drug phenoxybenzamine
| i. Substitutions with haloalkylamine | A. Have high potency as an α-adrenoceptor antagonist |
| ii. Lacking substituents and both phenoxy and oxyamino carbon chain | B. Provides selectivity for binding with the α-adrenoceptors |
| iii. 2-ethoxyphenoxy bearing compounds | C. Produces moderate α1-adrenoceptor selectivity |
a) i-B, ii-C, iii-A
b) i-B, ii-A, iii-C
c) i-C, ii-B, iii-A
d) i-C, ii-A, iii-B
Q.2 Correct sequence for the True/False for correct IUPAC names of the drug can be?
- Phenoxybenzamine: 3-[(1R,2S)-2-amino-1-hydroxypropyl]phenol
- Dobutamine: (RS)-N-Benzyl-N-(2-chloroethyl)-1-phenoxypropan-2-amine
- Naphazoline: (RS)-4-(2-{[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butan-2-yl]amino}ethyl)benzene-1,2-diol
- Metaraminol: 2-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole
a) TFTF
b) FFTF
c) FFFF
d) TTFT
Q.3 Melting point of phenoxybenzamine is?
a) 129°C
b) 39°C
c) 250°C
d) 39K
Q.4 Complete the following sentence:
“Phenoxybenzamine competitively blocks………. Which results in ……… of muscles.”
a) α-adrenergic receptors, relaxation
b) ß-adrenergic receptors, contraction
c) α-adrenergic receptors, contraction
d) ß-adrenergic receptors, relaxation
Q.5 Which amongst the following is not a therapeutic use of drug Phenoxybenzamine?
a) Treatment of hypertension
b) Treatment of hypoplastic left heart syndrome
c) Treatment of complex regional pain syndrome
d) Prevention of cancers
Q.6 Which of the following drug and their classification are correct?
I. Isoproterenol: ß2-adrenergic agonist
II. Dopamine: selective α2-adrenergic antagonist
III. Amphetamine: Mixed acting sympathomimetics
IV. Doxazosin: ß1-adrenergic agonist
a) I, II
b) I, III
c) II, IV
d) III, IV
Q.7 Correct molecular weight of phenoxybenzamine?
a) 250.24 gm/mol
b) 521.3 gm/mol
c) 303.8 gm/mol
d) 124.6 gm/mol
ANSWERS
1-a
2-c
3-b
4-a
5-d
6-b
7-c
REFERENCES
[1] Mussa S, Guzik TJ, Black E, Dipp MA, Channon KM, Taggart DP. Comparative efficacies and durations of action of phenoxybenzamine, verapamil/nitroglycerin solution, and papaverine as topical antispasmodics for radial artery coronary bypass grafting. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2003 Dec 1;126(6):1798-805. [2] Giardina D, Crucianelli M, Angeli P, Buccioni M, Gulini U, Marucci G, Sagratini G, Melchiorre C. Structure–Activity relationships among novel phenoxybenzamine-Related β-Chloroethylamines. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry. 2002 May 1;10(5):1291-303.