Powders: Manufacturing procedure and MCQs for GPAT, NIPER, Pharmacist and Drug Inspector exam
Manufacturing procedure:
Molecular aggregation:
Precipitation and crystallization – Pharmaceutical powders can be produced by precipitation and crystallization. They are relatively similar processes, by making a solid solute precipitate out of solution.
Many approaches have been developed to accomplish precipitation or crystallization:
- Raising the concentration of solute in the solvent to a higher level, by removing a certain amount of solvent, such as by solvent evaporation.
- In most cases, the solubility of solid powder decreases, when the temperature of the solution is lowered, so, by cooling the solution, precipitation or crystallization can be achieved.
- Mixing the solution with another anti solvent in which the solid powder is insoluble or has very low solubility. For instance, for a poorly water-soluble drug, precipitation or crystallization can be obtained by adding water to the drug organic solution. In fact, there is a relatively new technology, called supercritical fluid method (SCF), based on this mechanism. Briefly speaking, a supercritical fluid is a substance maintained at a certain temperature and pressure above its critical point, which has both the properties of liquid and gas phases. It can penetrate like a gas and dissolve solids like a liquid. Supercritical fluid is a substitute for organic solvents to dissolve poorly water soluble drugs for powder generation, because the solubility of that powder in SCF can be easily altered by changing the temperature and pressure.
Spray drying – Spray drying is a technique to generate powders by transforming the feed from a liquid state into a dry form, by spraying the feed into a hot drying medium. The feed can be a solution, suspension, dispersion, or emulsion. The spray drying process mainly consists of five steps:
- Concentration—Before introduced to the spray dryer, feedstock is usually concentrated.
- Atomization—Favors evaporation to a dry powder, by having optimum properties.
- Droplet-Air Contact—In the chamber, atomized liquid contacts with hot gas, leading to evaporation of a majority of the water or solvent contained in the droplets within a few seconds.
- Droplet Drying—Water or solvent evaporation takes places.
- Separation—Cyclones, bag filters, and electrostatic precipitators may be used for the final separation stage.
Spray drying technology has many applications in the pharmaceutical industry, especially for powder technology. Spherical or non-spherical particles, hollow or solid particles, the size of the particles (frequently ranging 10–600 μm), and the uniformity of a powder can be altered by changing the parameters of the spray drier. By spray drying a poorly water-soluble drug, a coprecipitate with a polymer in a stable amorphous solid dispersion can be made. Therefore, the dissolution rate and bioavailability of many drugs can be greatly improved, such as tolbutamide, indomethacin, and ibuprofen. In addition, particles produced by spray drying can be controlled to have very a good aerodynamic performance, making them suitable for inhalation.
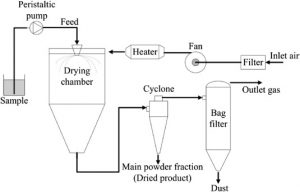
Fig 1 – Schematic diagram of spray drying (taken from science direct.com)
Spray freeze drying (SFD) – Spray freeze drying (SFD) is a technique based on the principle that the rapid solidification process induced by freezing prevents the molecules from packing in a certain order (refers to crystallization). SFD combined with freeze-drying, consists of the following steps:
- Atomization of feed using ultrasound, droplets are generated by one or two fluid nozzles or vibrating orifice (feed can be solution, suspension, or emulsion).
- Freezing of the droplets in a cryogenic liquid or cryogenic vapor, usually liquid nitrogen.
- Sublimation of solvent at low temperature and pressure by lyophilization or atmospheric freeze-drying using a cold desiccant gas stream.
- SFD has similar pharmaceutical applications as spray drying.
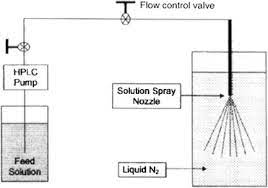
Fig 2 – Diagram of spray- freezing into liquid (taken from science direct.com)
Multiple choice questions;
1.Pharmaceutical powders can be produced by
a)precipitation
b)crystallization
c)fusion
d)a and b
2.Which of the following approaches have been developed to accomplish precipitation or crystallization?
a)Raising the concentration of solute in the solvent to a higher level, by removing a certain amount of solvent, such as by solvent evaporation.
b)In most cases, the solubility of solid powder decreases, when the temperature of the solution is lowered, so, by cooling the solution, precipitation or crystallization can be achieved.
c)Mixing the solution with another antisolvent in which the solid powder is insoluble or has very low solubility.
d)all of these
3.In most cases, the solubility of solid powder decreases, when the temperature of the solution is lowered, so, by cooling the solution, precipitation or crystallization can be achieved.
a)true
b)false
4.For a poorly water-soluble drug, precipitation or crystallization can be obtained by adding water to the drug organic solution. Which of the following new technology is based on this mechanism?
a)supercritical fluid method
b)supersaturated fluid method
c)both of these
d)none of these
5.A substance maintained at a certain temperature and pressure above its critical point, which has both the properties of liquid and gas phases is known as
a)supercritical fluid
b)supersaturated fluid
c)critical fluid
d)glassy state
6.Supercritical fluid is a substitute for organic solvents to dissolve poorly water soluble drugs for powder generation, because the solubility of that powder in SCF can be easily altered by changing the ____ and _____.
a)volume, pressure
b)temperature, pressure
c)pressure, density
d)volume, density
7.A technique to generate powders by transforming the feed from a liquid state into a dry form, by spraying the feed into a hot drying medium is called
a)Spray drying
b)Spray freeze drying
c)both of these
d)none of these
8.The feed in Spray drying can be a
a)solution
b)suspension
c)dispersion
d)all of these
9.The spray drying process mainly consists of ____ steps.
a)3
b)5
c)6
d)only one step
10.Which of the following is 1st step of spray drying?
a)Concentration
b)Atomization
c)Droplet-Air Contact
d)Droplet Drying
e)Separation
11.Which of the following steps in spray drying favors evaporation to a dry powder, by having optimum properties?
a)Concentration
b)Atomization
c)Droplet-Air Contact
d)Droplet Drying
e)Separation
12.Which of the following may be used for the final separation stage in spray drying?
a)Cyclones
b)bag filters
c)electrostatic precipitators
d)all of these
13.A technique based on the principle that the rapid solidification process induced by freezing prevents the molecules from packing in a certain order is called as
a)Spray drying
b)Spray freeze drying
c)both of these
d)none of these
14.Freezing of the droplets is done in a cryogenic liquid or cryogenic vapor, usually
a)argon
b)liquid nitrogen
c)helium
d)all of these
15.Spray freeze drying includes
a)sublimation
b)lyophilization
c)both of these
d)only a
Solutions:
- d)a and b
- d)all of these
- a)true
- a)supercritical fluid method
- a)supercritical fluid
- b)temperature, pressure
- a)Spray drying
- d)all of these
- b)5
- a)Concentration
- b)Atomization
- d)all of these
- b)Spray freeze drying
- b)liquid nitrogen
- c)both of these
References:
- Remington Essential of Pharmaceutics, 1st edition 2013, page no. 436-437.
List of Successful GPATINDIAN CANDIDATES
Participate in Online FREE GPAT TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Pharmacist TEST: CLICK HERE
Participate in Online FREE Drug Inspector TEST: CLICK HERE